What to Expect from Bossbot HQ: Rewards, Strategies, and More
What Rewards and Cog Suits can you get from Bossbot HQ? As a Toon fighting against the invading Cogs in Toontown, heading to Bossbot Headquarters is …
Read Article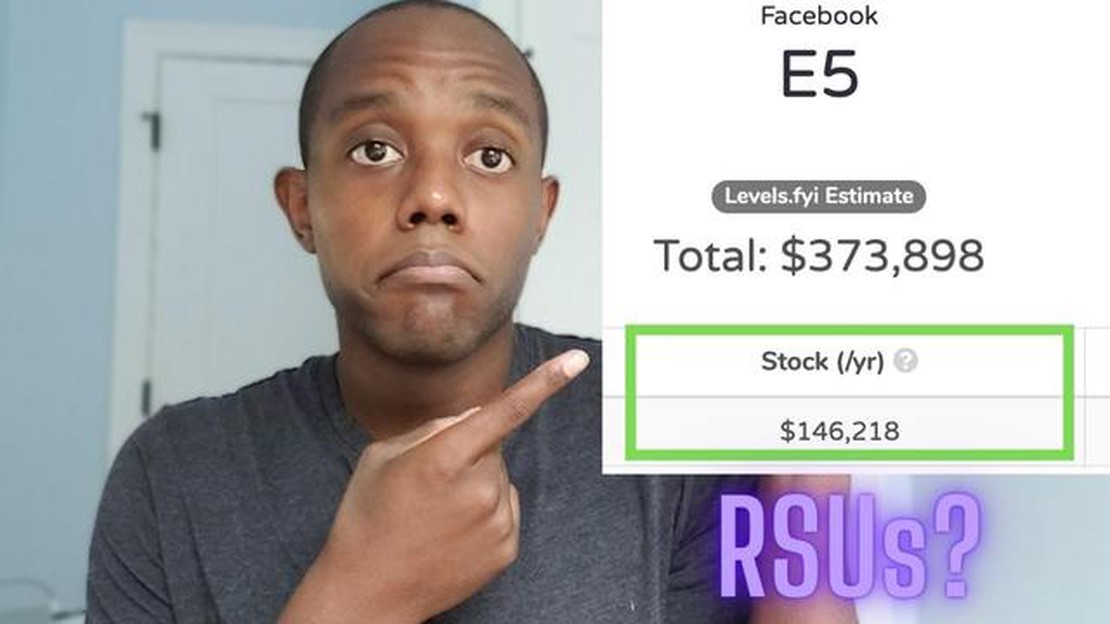
RSU grants, or Restricted Stock Unit grants, are a form of compensation that many companies offer to their employees. These grants provide employees with a certain number of shares in the company, which are typically granted over a specific period of time.
One of the key features of RSU grants is that they are “restricted”, meaning that the shares cannot be sold or transferred until certain conditions are met. These conditions can include a specific time period, the achievement of performance goals, or the occurrence of a liquidity event, such as an IPO or merger.
RSU grants are often used as a way to incentivize and retain employees, as the value of the shares can increase over time. When the conditions are met, employees can choose to sell their shares and receive the resulting cash payout.
It is important to note that RSU grants differ from stock options in key ways. With stock options, employees have the option to purchase company stock at a set price, while with RSUs, the shares are granted outright. Additionally, RSU grants are generally considered more favorable for employees, as they are not subject to the potential financial risks associated with options.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of RSU grants, exploring how they work, the tax implications, and the potential benefits and drawbacks. Whether you are considering a job offer with RSU grants or already have them as part of your compensation package, this article aims to provide you with the knowledge you need to navigate this aspect of employee compensation.
RSU grants, or Restricted Stock Unit grants, are a common form of equity compensation offered by companies to their employees. This type of grant gives employees the right to receive a certain number of company shares at a future date, often as part of their overall compensation package.
Unlike stock options, which give employees the right to buy company stock at a specified price, RSUs are units of stock that are actually granted to the employee. The number of RSUs granted is typically based on factors such as the employee’s job level, performance, and the overall value of the company.
RSUs are often subject to a vesting period, which means that employees must wait a certain amount of time before they can receive the shares. Once the vesting period has passed, the employee becomes the owner of the shares and can choose to keep them or sell them.
One of the key benefits of RSUs is that they offer employees the opportunity to share in the success of the company. If the company’s stock price increases, the value of the RSUs also increases, potentially allowing employees to make a profit when they sell the shares.
It’s important to note that RSUs are subject to taxation. When the RSUs vest, the value of the shares is considered taxable income. The employee is responsible for paying taxes on this income, even if they choose to keep the shares instead of selling them.
Read Also: Understanding the Concept of Options in M&A
Overall, RSU grants can be a valuable form of compensation for employees, providing them with an opportunity to benefit from the success of the company. It’s important for employees to fully understand the terms and conditions of their RSU grants and consult with a financial advisor to make informed decisions about when to sell or hold onto the shares.
RSU stands for Restricted Stock Unit. RSU grants are a form of compensation commonly used by companies to reward and incentivize their employees. When an employee is granted RSUs, they are given the right to receive company stock at a future date, typically once certain vesting requirements are met.
Unlike stock options, RSUs represent actual shares of company stock from the beginning. However, employees do not own the stock immediately upon receiving RSUs. Instead, they receive a promise that these shares will be given to them at a later date, once the vesting period is completed.
The vesting period is the length of time an employee must wait before they can exercise their right to receive the stock. It is used to encourage employee loyalty and retention. Typically, RSUs vest over a period of several years, with a portion of the RSUs becoming available for the employee each year.
Once the RSUs have vested, employees have the right to receive the shares, which will be transferred to their brokerage account. At that point, they can decide to hold onto the shares or sell them on the open market. The value of the RSUs at the time of vesting determines the taxable income for the employee.
It is important to note that RSU grants often come with certain conditions or performance goals that need to be met for the RSUs to fully vest. If these conditions are not met, the RSUs may be forfeited, and the employee will not receive the shares.
Read Also: Understanding the Principle of Moving Average: A Comprehensive Guide
Overall, RSU grants are a way for companies to reward and incentivize their employees by offering them ownership in the company. It aligns the interests of the employees with those of the company, as the value of the RSUs increase with the company’s success.
RSU grants can be a valuable benefit for employees, providing an opportunity to share in the success of the company. However, there are several key considerations that employees should keep in mind when it comes to RSU grants:
By considering these key factors, employees can make informed decisions about their RSU grants and maximize the potential benefits they offer.
An RSU grant, or Restricted Stock Unit grant, is a form of compensation given to an employee by a company in the form of company stock.
When an employee receives an RSU grant, they are given a specific number of stock units, which will vest over time according to a predetermined schedule. Once the RSUs vest, the employee has the right to receive the underlying shares of stock.
The main difference between RSUs and stock options is that RSUs are actual shares of stock, while stock options give an employee the right to buy shares at a predetermined price. RSUs are usually less risky than stock options because they are not dependent on the stock price reaching a certain level.
RSUs are typically taxed as ordinary income when they vest. The value of the vested RSUs is added to the employee’s W-2 form and is subject to regular income tax withholding. If the employee sells the shares after they vest, they may also be subject to capital gains tax.
If you leave the company before your RSUs vest, you will generally forfeit any unvested RSUs. However, some companies have different policies, so it’s important to read the terms of your RSU grant carefully.
An RSU grant stands for Restricted Stock Unit grant. It is a form of equity compensation given by a company to its employees. Unlike traditional stock options, RSUs do not have an exercise price, and the shares are delivered to the employee upon vesting.
What Rewards and Cog Suits can you get from Bossbot HQ? As a Toon fighting against the invading Cogs in Toontown, heading to Bossbot Headquarters is …
Read ArticleUnderstanding FTSE 100: Beginner’s Guide Welcome to our beginner’s guide to understanding the FTSE 100. If you’re new to the world of finance, it’s …
Read ArticleIs now a good time to buy AUD with GBP? In today’s global economy, currency exchange rates fluctuate constantly, and it can be difficult to determine …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Binary Option Payments Binary options are a popular form of trading in the financial markets. They offer traders the opportunity to make …
Read ArticleExploring the Fees on OANDA: What You Need to Know In the world of online trading, it is important to carefully consider any fees and charges …
Read ArticleWays to Enhance Your Forex Market Performance Forex trading is a highly competitive and volatile market, where traders aim to make profits by buying …
Read Article