Understanding the Forward Premium for USD INR: Everything You Need to Know
Understanding the Forward Premium for USD INR The forward premium for USD INR, or United States Dollar - Indian Rupee, is an important concept in the …
Read Article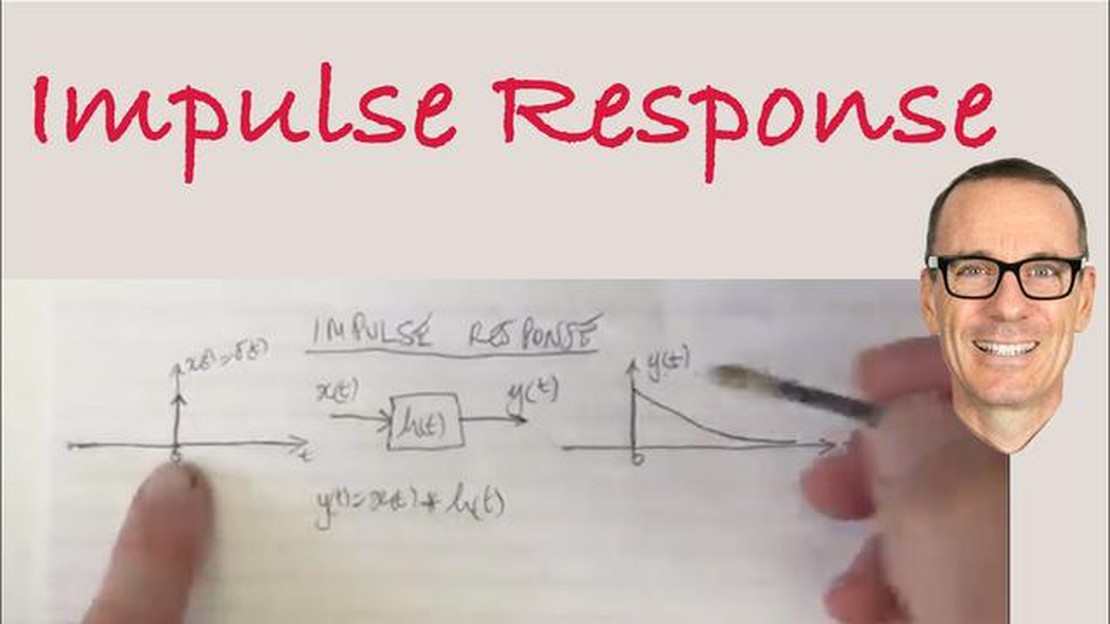
Impulse response functions (IRFs) are a fundamental tool in time series analysis. They provide insights into the dynamic relationship between variables, allowing us to understand how shocks in one variable affect the others over time.
When we talk about impulse response functions, we are referring to the response of a variable to a one-time shock, or impulse, in another variable. The response is measured in terms of the change from the initial level of the variable and how it evolves over time.
IRFs are especially valuable in studying the impact of economic policy changes, such as changes in interest rates or government spending, on economic variables like GDP, inflation, or unemployment. By examining the impulse response functions, we can assess the short and long-term effects of these policy changes.
Using time series analysis techniques, we can estimate the parameters of a model based on historical data and then derive the impulse response functions. These functions allow us to simulate how the system would respond to different shocks and analyze the interdependencies between variables.
Overall, understanding impulse response functions is crucial for analyzing the dynamics and interconnections of variables in time series data. It provides a valuable framework for assessing the effects of shocks and policymaking, facilitating better decision-making and forecasting in various fields like economics, finance, and engineering.
In time series analysis, impulse response functions (IRFs) play a crucial role in understanding the dynamic relationship between variables. An impulse response function measures the reaction of a variable to a unit shock or impulse in another variable, while holding all other variables constant.
When analyzing time series data, researchers are often interested in examining the effects of a specific shock or impulse on the variables of interest. The impulse response function allows us to do just that, by quantifying the magnitude and duration of the response over a given time period.
Impulse response functions are commonly used in various fields, such as economics, finance, and engineering. They are particularly useful in studying the effects of policy changes, economic shocks, or natural disasters on the economy or financial markets.
To estimate impulse response functions, various statistical methods can be employed, such as vector autoregression (VAR) models or structural time series models. These models provide a framework for estimating the dynamic relationship between variables and capturing the complex interactions that may exist.
Read Also: Mastering Currency Trading Online: Tips and Tricks for Success
Interpreting impulse response functions requires careful consideration. The response of a variable may be immediate or delayed, positive or negative, and may peak at a certain time before returning to its initial level. By examining the shape and duration of the impulse response, researchers can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms at work.
Overall, impulse response functions are powerful tools in time series analysis. They provide a way to quantify and analyze the dynamic relationships between variables, shedding light on the short-term and long-term effects of shocks or impulses in a time series data set.
As with any statistical analysis, it is important to use caution and interpret the results in the appropriate context. Impulse response functions should be considered alongside other relevant information and variables to generate meaningful insights and inform decision-making processes.
An impulse response function (IRF) is a fundamental concept in time series analysis. It measures the dynamic response of a system to a unit impulse, or shock, in one of its inputs. In other words, it quantifies how the system’s output changes over time in response to a sudden change in its input.
The impulse response function is commonly used in fields such as economics, finance, engineering, and physics to analyze and model various systems. It provides insights into the system’s characteristics, such as its stability, magnitude, and duration of response.
To calculate the impulse response function, time series data is typically used. The data is divided into two parts: the pre-shock period and the post-shock period. The shock is typically represented by a delta function, which has a value of 1 at time zero and zero elsewhere. The system’s response is then measured and analyzed over a certain time frame.
When analyzing the impulse response function, it is common to plot it graphically. The x-axis represents time, while the y-axis represents the magnitude of the system’s response. The impulse response function can be informative on its own, but it is often more useful when combined with other techniques and models, such as autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models or vector autoregression (VAR) models.
By studying the impulse response function, researchers and analysts can gain a better understanding of a system’s behavior and response to shocks. It allows them to examine the impact of a specific event or input on the system and predict how it may affect the system’s future behavior. This knowledge can be valuable in various fields, such as forecasting economic variables, designing engineering systems, and understanding complex phenomena in physics.
Read Also: Can a US Citizen Open a Brokerage Account Abroad? | Exploring International Investment Opportunities
In conclusion, an impulse response function is a powerful tool in time series analysis that helps to study the dynamic response of a system to a shock in its inputs. It provides insights into the system’s behavior and allows researchers to make predictions and analyze the impact of specific events or inputs on the system’s future behavior.
Impulse response functions in time series analysis allow us to measure the dynamic effects of a shock to a variable on other variables in the system over time. They provide a way to understand how the system responds and adjusts in the aftermath of a shock.
Impulse response functions are typically computed using econometric techniques such as vector autoregression (VAR) models. These models estimate the relationship between variables in a system and allow us to simulate the response of the system to a shock.
Impulse response functions provide valuable insights into the dynamics of a system. They can help us understand the magnitude, duration, and timing of the response to a shock. Additionally, they can reveal any long-term effects or feedback loops that may occur in the system.
While impulse response functions are primarily used for understanding system dynamics, they can also be used for forecasting. By simulating the response of the system to different shocks, we can generate forecasts of future variables based on the estimated relationships in the model.
Yes, there are some limitations to using impulse response functions. Firstly, they rely on the assumption that shocks to variables are temporary and have no permanent effects. Additionally, the accuracy of the impulse response functions depends on the quality of the underlying model and the assumptions made during estimation.
Impulse response functions in time series analysis are a tool that helps to understand the dynamic relationship between variables in a system. They show the response of a variable to a shock or impulse in another variable over time.
Understanding the Forward Premium for USD INR The forward premium for USD INR, or United States Dollar - Indian Rupee, is an important concept in the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Williams %R Indicator: A Powerful Technical Analysis Tool When it comes to trading and investing, having the right tools and …
Read ArticleWhat Does a Sales Trader Do? A sales trader is a financial professional who specializes in executing trades on behalf of clients. They play a crucial …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Long Call Option Strategy in Stock Options Investing in the stock market can seem daunting at first, with its complex jargon and …
Read ArticleMinimum Balance in Affin Bank When choosing a bank, one important factor to consider is the minimum balance requirement. This is the minimum amount of …
Read ArticleJoining a Trading Group: Step-by-Step Guide and Tips Are you interested in joining a trading group? Whether you are a novice trader or have some …
Read Article