Stock Market in India: All You Need to Know
Stock Market in India: Key Information and Insights The stock market in India is a dynamic and complex entity that plays a crucial role in the …
Read Article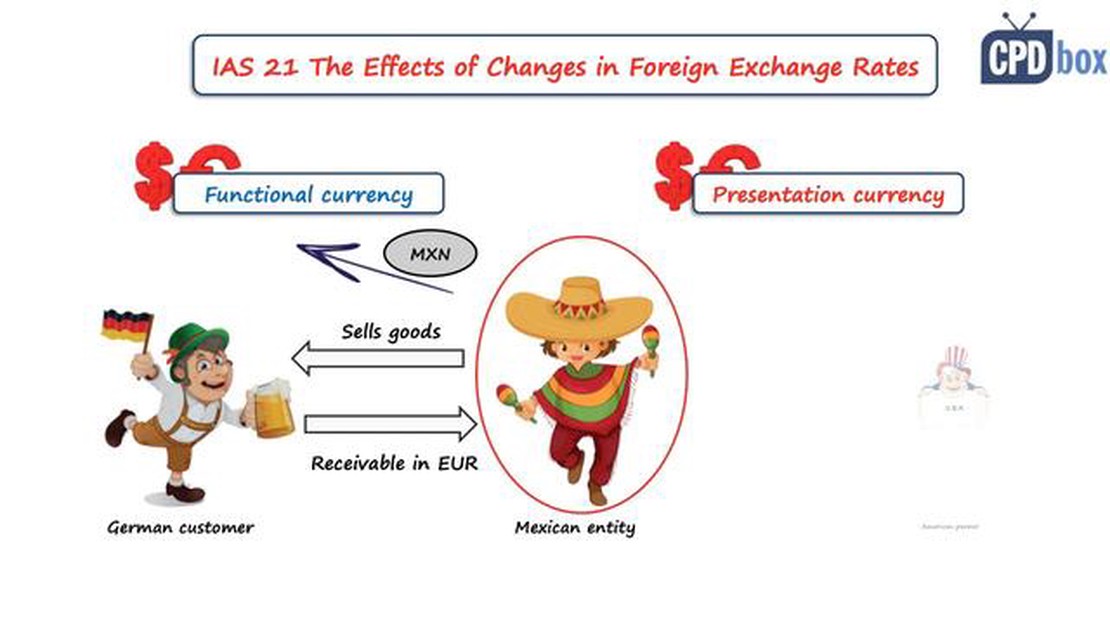
The International Accounting Standard (IAS) 21, also known as IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates, is a standard developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) that provides guidelines for accounting and reporting of foreign currency transactions and operations.
Foreign currency transactions are common for multinational companies conducting business in multiple countries. The standard aims to ensure that financial statements accurately reflect the effects of such transactions and to provide consistency in the treatment of foreign currency exchanges.
IAS 21 requires companies to record foreign currency transactions at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies at the balance sheet date are translated into the reporting currency at the closing rate. The resulting gain or loss is recognized in the income statement.
The standard also addresses the translation of foreign operations, which are the activities of a subsidiary, associate, joint venture, or branch that are conducted in a currency different from the reporting entity’s functional currency. The translation process involves bringing these activities into the reporting currency using the appropriate exchange rates.
In conclusion, IAS 21 is a crucial standard that ensures accurate and consistent accounting for foreign currency transactions and operations. By following this standard, companies can provide reliable financial information to stakeholders and maintain transparency in their international business activities.
IAS 21, or International Accounting Standard 21, is a financial reporting standard that sets out the guidelines for accounting and reporting foreign currency transactions and translating the financial statements of foreign operations into a presentation currency.
IAS 21 provides guidance on how to determine the functional currency of an entity, which is the currency of the primary economic environment in which it operates. The standard also outlines the rules for translating foreign currency transactions and balances into the functional currency for recognition in the financial statements.
Read Also: Reasons behind the low performance of MDT stock
The main objective of IAS 21 is to ensure that foreign currency transactions are properly accounted for and that the financial statements of an entity provide relevant and reliable information for users, despite the use of different currencies.
IAS 21 applies to all entities that prepare financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
It is important for entities involved in international transactions or with foreign operations to understand and comply with the requirements of IAS 21 to ensure accurate and consistent reporting of their financial information.
IAS 21, or International Accounting Standard 21, provides guidelines for the accounting treatment and reporting of foreign currency transactions and foreign operations in the financial statements of an entity.
The scope of IAS 21 includes:
It is important for entities to apply IAS 21 when dealing with foreign currency transactions and foreign operations to ensure transparent and accurate financial reporting in a global business environment.
IAS 21, also known as International Accounting Standard 21, sets out the guidelines for accounting and reporting of foreign currency transactions and foreign operations. This standard provides a framework for how entities should handle the translation of foreign currency transactions into their functional currency.
The key principles of IAS 21 include:
Read Also: Is Forex Trading in the Future Halal? Exploring the Permissibility of Forex Trading in Islamic Finance
| 1. Functional Currency | The functional currency is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates. It is crucial to determine the functional currency as it dictates the appropriate exchange rates and translation methods to be used. |
| 2. Foreign Currency Transactions | Foreign currency transactions should be recorded in the entity’s functional currency using the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Any difference in exchange rates between the transaction date and the settlement date should be recognized as a gain or loss in the income statement. |
| 3. Translation of Foreign Currency Financial Statements | When an entity has foreign operations with a functional currency different from its reporting currency, the financial statements of the foreign operations need to be translated into the reporting currency. This translation should be done using either the current rate method or the temporal method, depending on the circumstances. |
| 4. Presentation of Exchange Differences | The exchange differences resulted from translating foreign currency transactions and foreign operations should be included in the financial statements. These differences are recognized in the income statement, except when they relate to qualifying cash flow hedges or qualifying net investment hedges, in which case they are recognized in other comprehensive income. |
| 5. Disclosures | Entities are required to disclose information about the methods used for translating foreign currency transactions and foreign operations, as well as the resulting exchange differences. They must also disclose the amounts of significant exchange differences that have been recognized in the financial statements. |
By following the key principles of IAS 21, entities can ensure accurate and reliable accounting and reporting of foreign currency transactions and foreign operations. Compliance with this standard allows for consistency and comparability in financial statements across different entities operating in diverse economic environments with varying currencies. It provides users of financial statements with valuable information for making informed decisions.
IAS 21, or International Accounting Standard 21, is a standard issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) that provides guidance on how to account for foreign currency transactions and the translation of financial statements into a functional currency.
IAS 21 is important because it helps companies handle the accounting implications of foreign currency transactions and the translation of financial statements. It ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the economic reality of the company, even when transactions are conducted in different currencies.
IAS 21 defines functional currency as the currency of the primary economic environment in which the company operates. It is the currency that most effectively reflects the underlying transactions, events, and conditions of the company.
Some of the key requirements of IAS 21 include determining the functional currency, translating foreign currency transactions into the functional currency at the exchange rate on the date of the transaction, and translating financial statements into the presentation currency at the closing rate for assets and liabilities, and average rate for income and expenses.
Stock Market in India: Key Information and Insights The stock market in India is a dynamic and complex entity that plays a crucial role in the …
Read ArticleValue of a 1000 Chilean peso bill The Chilean peso is the official currency of Chile, a country located in South America. The currency is issued and …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Triangular Trade System: A Comprehensive Guide The system of Triangular Trade, also known as the Transatlantic Slave Trade, was a …
Read ArticleIs it possible to earn money through spot trading? Spot trading, also known as cash trading, is a common form of trading in financial markets. It …
Read ArticleIdentifying Reversal Patterns in Candlestick Charts When it comes to trading in the financial markets, being able to identify trend reversals is …
Read ArticleExploring the various types of moving averages in time series analysis When analyzing time series data, moving averages are an important tool. They …
Read Article