Is Forex B1? Everything You Need to Know About Forex Trading
Is Forex B1? Forex, also known as foreign exchange or FX, is the largest financial market in the world. With a daily trading volume of over $6 …
Read Article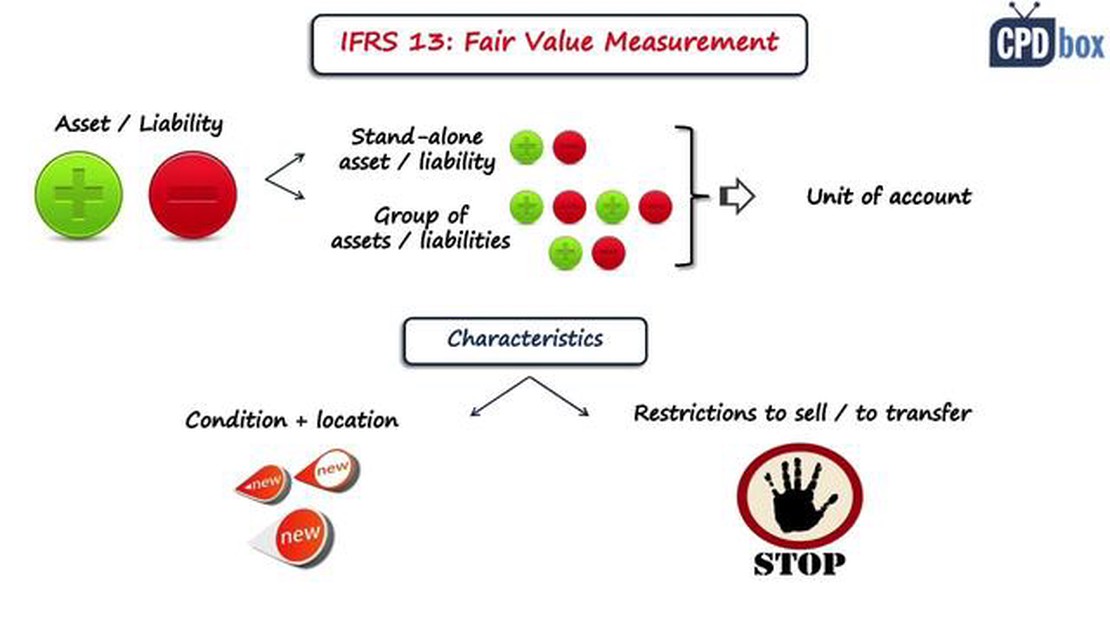
In today’s global economy, financial reporting is a critical aspect of business operations. It is essential for companies to provide accurate and transparent financial information that is consistent across borders. To achieve this goal, the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have been developed and implemented. One of the key standards within the IFRS framework is IFRS 13 - Fair Value Measurement.
IFRS 13 provides principles and guidance on how to define and measure fair value, which is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. It applies to financial and non-financial assets and liabilities, and also addresses various valuation techniques and disclosures.
“The objective of this standard is to increase consistency and comparability in fair value measurements and disclosures across different markets and industries,” explains John Smith, a renowned expert in financial reporting.
The implementation of IFRS 13 ensures that companies report their financials using a common language and transparent valuation methods. This allows investors, shareholders, and other users of financial information to make more informed decisions and understand the true value of a company’s assets and liabilities. It also promotes international consistency, making it easier for multinational companies to operate and attract investors globally.
IFRS 13, or International Financial Reporting Standard 13, is a global accounting standard that provides guidance on how to measure and disclose fair value for financial instruments. It was issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) to improve consistency and comparability in financial reporting.
The standard defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. It sets out a framework for determining fair value and provides enhanced disclosures to help users of financial statements understand the impact of fair value measurements on an entity’s financial position and performance.
IFRS 13 applies to all entities that prepare financial statements in accordance with IFRS, including listed companies, financial institutions, and other organizations that provide financial instruments.
The key principles of IFRS 13 include:
Read Also: Understanding Income for Child Support in California
By following the guidelines outlined in IFRS 13, entities can provide transparent and consistent fair value measurements, enhancing the quality and comparability of financial information. This allows investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate and reliable financial statements.
IFRS 13, also known as the International Financial Reporting Standard, provides guidance on fair value measurement. It sets out the principles and requirements, as well as the disclosures needed for fair value measurement.
There are several key concepts that are important to understand when it comes to IFRS 13. These concepts include:
These key concepts provide the foundation for understanding and applying the principles of IFRS 13. By following these concepts, entities can ensure that their fair value measurements are consistent, reliable, and relevant.
Read Also: How do you calculate MAD? A step-by-step guide
IFRS 13 is a financial reporting standard that provides guidance on how to measure and disclose fair value. It is important because fair value is a key concept in the financial industry and affects the valuation of assets and liabilities.
The main guidelines of IFRS 13 include defining fair value, providing a framework for measuring fair value, and establishing disclosure requirements for fair value measurements.
IFRS 13 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
Some of the challenges of implementing IFRS 13 include determining the appropriate valuation techniques to use, gathering the necessary data to calculate fair values, and ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the fair value measurements.
IFRS 13 requires entities to disclose information about fair value measurements, including the techniques and inputs used, the level of the fair value hierarchy, and any significant unobservable inputs.
IFRS 13 is an International Financial Reporting Standard that provides guidance on how to measure the fair value of assets and liabilities. It sets out a framework for determining fair value, defines fair value, and applies to all assets and liabilities that are required to be measured at fair value in the financial statements.
Is Forex B1? Forex, also known as foreign exchange or FX, is the largest financial market in the world. With a daily trading volume of over $6 …
Read ArticleHow to Get Approved for Stock Options Stock options are an attractive form of compensation for employees, with the potential for significant financial …
Read ArticleWhich system is non-invertible? When studying systems, one important concept to understand is invertibility. In mathematical terms, a system is …
Read ArticleThe Role and Responsibilities of a Forex Trader Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, involves buying and selling currencies on the …
Read ArticleWithdrawal of 1000% Bonus from Instaforex If you have been trading on the Instaforex platform, you might have come across the lucrative 1000% bonus …
Read ArticleTop NHL Trade Targets The NHL trade deadline is fast approaching, and teams are scrambling to make deals and improve their rosters before the …
Read Article