Is Option Trading Halal or Haram in Islam? Exploring the Rulings and Perspectives
Is Option Trading Halal or Haram in Islam? Option trading is a popular form of investment that involves buying and selling financial contracts, known …
Read Article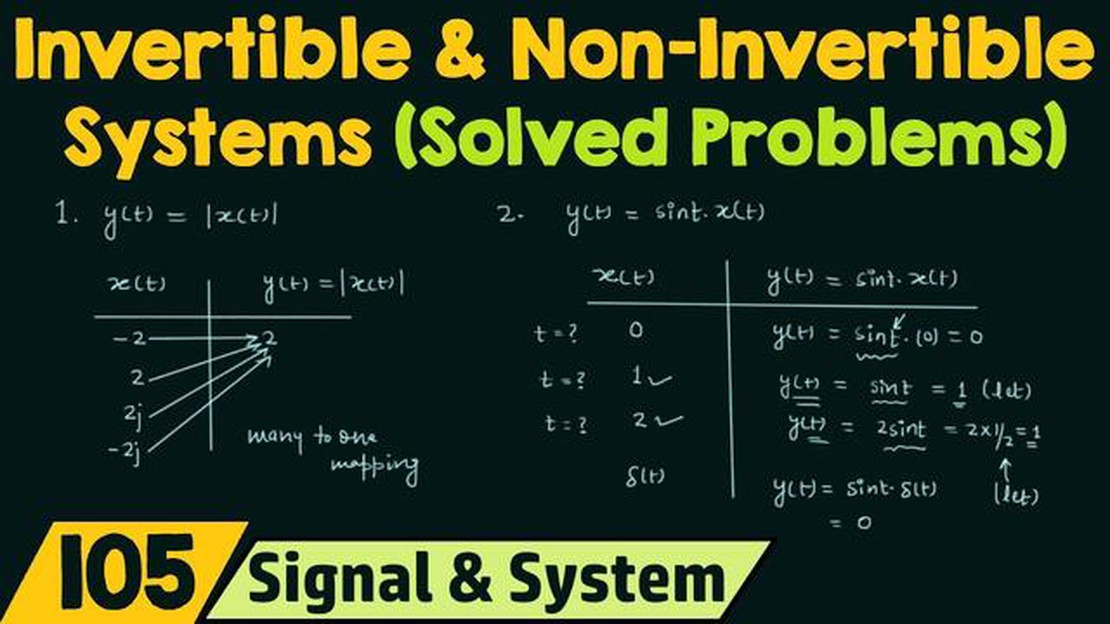
When studying systems, one important concept to understand is invertibility. In mathematical terms, a system is considered invertible if it is possible to recover the inputs from the outputs. In other words, given the output of a system, we can determine the input that produced it. This property plays a crucial role in many fields, including signal processing, control systems, and communication.
An invertible system is often represented by a mathematical model or equation. In such a model, the inputs are denoted by x(t) or x[n], depending on whether the system is continuous or discrete, while the outputs are represented by y(t) or y[n]. The model describes the relationship between the inputs and outputs of the system.
However, not all systems are invertible. Some systems do not have a one-to-one mapping between inputs and outputs, making it impossible to recover the inputs from the outputs. These systems are called non-invertible systems. In practical terms, this means that if we have the output of a non-invertible system, we cannot determine the exact input that caused it.
Non-invertible systems can arise due to various reasons. One common reason is the presence of noise or uncertainty in the system. When a system is affected by noise, it becomes difficult to accurately determine the input based on the noisy output. Another reason for non-invertibility is the loss of information during the transformation process. If a system discards or compresses certain aspects of the input, it becomes impossible to recover the original input from the output.
Understanding invertibility in systems is essential for many applications. By knowing whether a system is invertible or not, we can determine the limitations and possibilities of the system. It allows us to design more efficient and robust systems, and to analyze the effects of noise and uncertainty on the output. Invertibility is a fundamental concept that helps us make sense of the relationship between inputs and outputs in various fields of study.
A non-invertible system is a system that cannot be reversed or undone. In other words, it is not possible to determine the input given the output of the system. This can happen for various reasons, such as information loss or multiple inputs that lead to the same output.
One example of a non-invertible system is a hash function. A hash function is used to map data of arbitrary size to a fixed-size output. However, it is not possible to determine the original input given only the hash value. This property is desirable for secure password storage, but it makes it impossible to retrieve the original data from the hash.
Another example is a compression algorithm. Compression algorithms aim to reduce the size of data by removing redundant information. This process is generally irreversible, meaning that it is not possible to reconstruct the original data from the compressed version.
Non-invertible systems are common in many fields, including cryptography, signal processing, and data compression. They provide useful functionalities but come with the trade-off that the original input cannot be recovered from the output.
Read Also: What is IB rebate? An ultimate guide to understanding and maximizing IB rebates
In the field of systems theory, invertibility refers to the ability of a system to be reversed or undone. It is an important concept that is used to analyze and evaluate the behavior of various systems in different domains, such as control theory, signal processing, and communication networks.
In a system, invertibility means that the output of the system can be used to reconstruct the input. This implies that the system has a one-to-one mapping between its input and output, with no loss or distortion of information.
Mathematically, an invertible system can be represented using a function or an operator. If the system is linear and time-invariant, it can be described by a transfer function or an impulse response. For a discrete-time system, invertibility can be assessed using z-transforms.
There are several benefits of having an invertible system. One of the main advantages is the ability to recover the original signal or information from the system’s output. This is particularly useful in applications where the integrity of the data is crucial, such as in error correction or encryption algorithms.
On the other hand, a non-invertible system is one in which the input cannot be accurately reconstructed from the output. This occurs when there is a loss or distortion of information during the system’s operation. Non-invertibility can be caused by various factors, such as noise, nonlinearities, or limited bandwidth.
Identifying whether a system is invertible or non-invertible is important for designing and analyzing systems. Invertibility can affect the stability, controllability, and observability of a system. It also plays a role in determining the performance and quality of the system’s output.
Read Also: Can I Make a Fortune with Options Trading? Unveiling the Potential for Wealth
In conclusion, understanding the concept of invertibility in systems is essential for engineers and scientists working in various fields. It allows for the analysis and evaluation of system behavior and enables the design of robust and efficient systems.
A non-invertible system is a system that does not have an inverse. In other words, it is impossible to uniquely determine the input signal from the output signal.
Understanding the concept of invertibility in systems is important because it allows us to know whether we can accurately determine the input signal based on the output signal. It helps us analyze the behavior of systems and make predictions about their behavior.
One example of a non-invertible system is a low-pass filter. When a low-pass filter is applied to a signal, it removes the high-frequency components of the signal. However, it is impossible to uniquely determine the original high-frequency components from just the filtered signal.
Dealing with a non-invertible system can have several consequences. Firstly, it limits our ability to accurately determine the input signal from the output signal. Secondly, it can lead to loss of information and loss of fidelity in the signal. Additionally, it can make it difficult to perform certain operations and transformations on the signal.
To determine if a system is invertible, we can examine its mathematical representation or its physical properties. In the case of a mathematical representation, we can check if it is possible to uniquely solve for the input signal given the output signal. In the case of physical properties, we can analyze the system’s behavior and see if it is possible to accurately determine the input signal from the output signal.
Invertibility in systems refers to the ability to reverse the effect of a system by applying an inverse operation or function. In other words, an invertible system can recover the original input signal from the output signal.
Is Option Trading Halal or Haram in Islam? Option trading is a popular form of investment that involves buying and selling financial contracts, known …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Athex Fix Server: A Comprehensive Guide The Athex Fix Server is an essential tool for investors and traders participating in the …
Read ArticleDo options expire on Friday or Saturday? Options trading can be a complex and confusing area for many investors. One common question that arises is …
Read ArticleIs black gold real or fake? Black gold is a term that has captured the curiosity and imagination of many. It is often associated with great wealth and …
Read ArticleCardstock Paper Prices at FedEx: What to Expect If you are in need of high-quality cardstock paper for your printing needs, look no further than …
Read ArticleOptions as Products in OpenCart: Explained OpenCart is a popular open-source e-commerce platform that provides a wide range of features and options …
Read Article