How to Determine the Fair Value of an ESOP: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Fair Value of an ESOP for Effective Management and Decision Making An Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) is a beneficial …
Read Article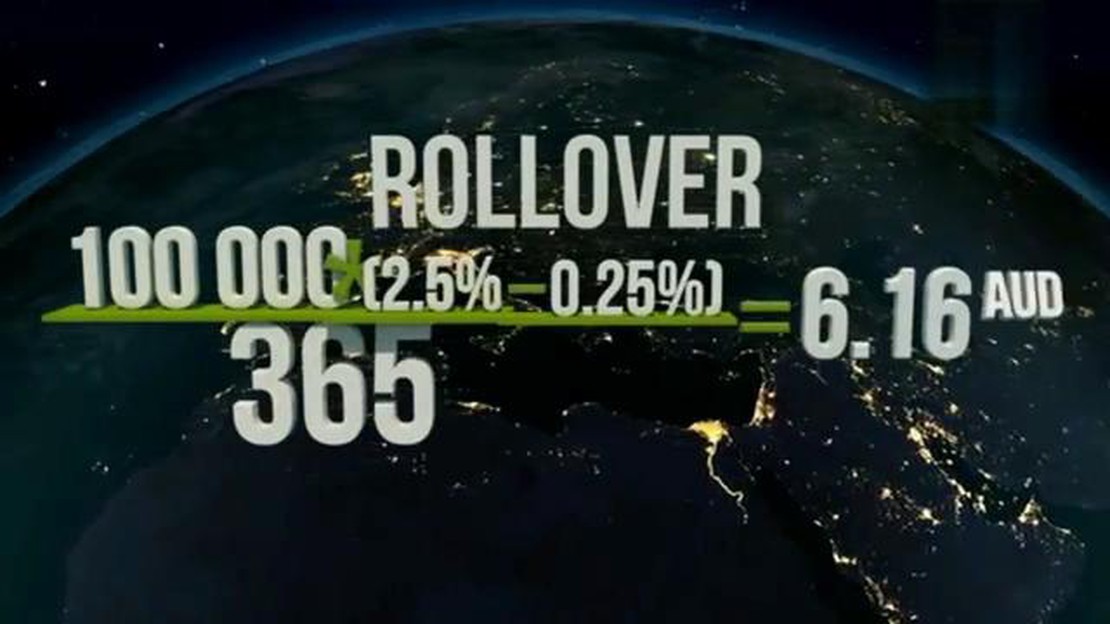
When it comes to forex trading, there are a lot of terms and concepts that can be overwhelming for beginners. One of those terms is the rollover rate. Understanding what the rollover rate is and how it works is crucial for any forex trader. In this article, we will break down everything you need to know about the rollover rate.
The rollover rate, also known as the swap rate, is the interest earned or paid for holding a position overnight in the forex market. In simple terms, it is the cost of holding a position open beyond the end of the trading day. Forex trading involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another currency, and the rollover rate is the difference between the interest rates of the two currencies being traded.
For example, if you are trading the EUR/USD currency pair and the interest rate of the euro is higher than the interest rate of the US dollar, you will earn rollover interest. On the other hand, if the interest rate of the US dollar is higher than the interest rate of the euro, you will have to pay rollover interest. The rollover rate can have a significant impact on your overall profitability in forex trading.
It is important to note that the rollover rate is usually calculated on a daily basis and is automatically applied by your forex broker. The specific amount of rollover interest earned or paid depends on the size of your position and the difference in interest rates between the two currencies. It is also worth mentioning that the rollover rate can be positive or negative. A positive rollover rate means you earn interest, while a negative rollover rate means you have to pay interest.
In conclusion, the rollover rate is an essential aspect of forex trading that determines the cost of holding a position overnight. It is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies being traded. Understanding and carefully considering the rollover rate is crucial for developing a successful forex trading strategy.
In forex trading, the rollover rate refers to the interest gained or paid on positions that are held overnight. When traders hold positions overnight, they are essentially borrowing or lending currencies to other traders in the forex market, and the rollover rate represents the interest rate differential between the currencies being traded.
The rollover rate is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies involved in the trade and is usually expressed as an annual percentage rate. It is important to note that the rollover rate can be positive or negative, depending on the direction of the trade.
When the interest rate on the currency being bought is higher than the interest rate on the currency being sold, the trader will earn a positive rollover rate. This means that the trader will receive an interest payment on their position. On the other hand, when the interest rate on the currency being bought is lower than the interest rate on the currency being sold, the trader will be charged a negative rollover rate and will have to pay interest on their position.
The rollover rate is applied to positions that are held overnight or over the weekend. Traders who wish to avoid incurring rollover fees can close their positions before the end of the trading day, which is typically at 5:00 PM Eastern Standard Time (EST).
It is important for forex traders to consider the rollover rate when planning their trades, as it can have a significant impact on profitability. Traders who take advantage of positive rollover rates can earn additional income on their positions, while traders who incur negative rollover rates may see a decrease in their overall profits.
| Key Points |
|---|
| - The rollover rate in forex trading refers to the interest gained or paid on positions held overnight. |
| - The rollover rate is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the currencies being traded. |
| - The rollover rate can be positive or negative, depending on the direction of the trade. |
| - Traders can avoid incurring rollover fees by closing their positions before the end of the trading day. |
| - The rollover rate can significantly impact profitability in forex trading. |
In forex trading, the rollover rate refers to the interest earned or paid on overnight positions. When a trader holds a position overnight, they are essentially borrowing one currency to buy another, and the interest rate differential between the two currencies determines whether they will earn or pay interest.
Read Also: Choosing the Most Effective Parabolic SAR Settings for Day Trading
The rollover rate is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies being traded, as well as the position size and the length of time the position is held. It is important to note that the rollover rate is only applicable to positions that are held overnight, as positions that are closed within the same trading day do not incur rollover fees.
When the interest rate of the currency being bought is higher than the interest rate of the currency being sold, the trader will earn interest on the position. This is known as a positive rollover. Conversely, when the interest rate of the currency being bought is lower than the interest rate of the currency being sold, the trader will have to pay interest on the position. This is known as a negative rollover.
Read Also: Understanding EOD Charts: A Comprehensive Guide | Website Title
The rollover rate is typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR) and is adjusted for the length of time the position is held. It is important for forex traders to be aware of the rollover rate, as it can significantly impact the profitability of their trades.
Additionally, it is worth noting that the rollover rate can vary between brokers, as different brokers have different access to liquidity providers and may charge different fees. Therefore, it is important for traders to carefully consider the rollover rate offered by their chosen broker when making trading decisions.
In conclusion, the rollover rate plays a crucial role in forex trading as it determines whether a trader will earn or pay interest on overnight positions. Understanding how the rollover rate is calculated and how it can impact trading profitability is essential for successful forex trading.
A rollover rate, also known as the overnight rate or swap rate, is the interest paid or earned for holding a forex position overnight.
The rollover rate is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in a currency pair, as well as any applicable fees or charges set by the broker.
Forex positions need to be rolled over because the forex market operates on a 24-hour basis, and trades that are left open overnight are subject to interest rate differentials.
The factors that affect the rollover rate include the interest rates set by central banks, market demand for a particular currency, and any additional fees or charges set by the broker.
Yes, the rollover rate can have a significant impact on trading profits, especially for trades that are held open for a longer period of time. It is important for traders to consider the potential impact of rollover rates when making trading decisions.
The rollover rate in forex trading refers to the interest paid or earned for holding a position overnight. It is the difference between the interest rates of the two currencies involved in the trade.
The rollover rate is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies involved in the trade, as well as other factors such as market liquidity. It is determined by the broker and can be positive or negative.
Understanding the Fair Value of an ESOP for Effective Management and Decision Making An Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) is a beneficial …
Read ArticleStock price prediction for Cheesecake Factory The Cheesecake Factory is a well-known restaurant chain that has gained popularity for its delicious …
Read ArticleWhich economic indicator is the most important? Economic indicators play a crucial role in providing insights into the overall health of an economy. …
Read ArticleGuide to Paying Tax on Forex Trading in New Zealand Forex trading has become increasingly popular in New Zealand, with many individuals eager to try …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Concept of a Displaced Formula Displaced formulas are a fundamental concept in mathematics and physics, playing a crucial role in …
Read ArticleAn Example of a Pairs Trade Strategy A pairs trade strategy is a type of investment strategy that involves taking positions in two related securities …
Read Article