Is Forex Trading Legal in India? Know the Facts
Is forex trading legal in India? Forex trading is a popular investment option that allows individuals and businesses to trade currencies and make …
Read Article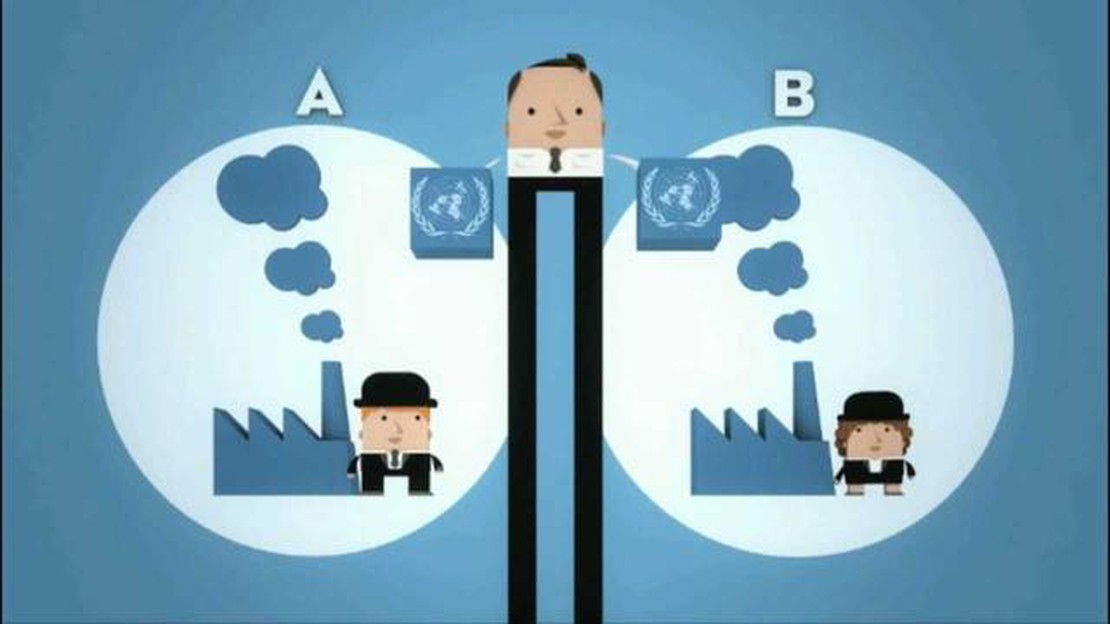
The issue of climate change has become increasingly urgent in recent years. Governments, organizations, and individuals are seeking effective solutions to mitigate the impacts of greenhouse gas emissions. One of the most commonly discussed mechanisms to achieve this is the implementation of emission trading systems.
An emission trading system, also known as a cap-and-trade system, is a market-based approach to reduce pollution. It involves setting a cap on the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions that can be released into the atmosphere. This cap is then divided into allowances, which are allocated to different entities, such as companies or countries.
The entities covered by the trading system can then buy and sell these allowances on a secondary market. This allows entities that can easily reduce their emissions to do so and sell their excess allowances to those entities that find it more challenging to reduce emissions. The goal of the system is to provide economic incentives for entities to reduce their emissions in the most cost-effective way.
Understanding the mechanics of emission trading systems is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of how these systems work, their benefits and limitations, and the different types of designs and approaches that have been implemented worldwide. With this knowledge, stakeholders can make informed decisions and contribute to the overall effort to combat climate change.
The concept of emission trading systems (ETS) has gained significant attention in recent years as a key policy tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. ETS is a market-based approach that allows countries or industries to buy or sell emission allowances based on their pollution levels. This system is designed to provide economic incentives for reducing emissions and promote the adoption of cleaner technologies.
In an ETS, a cap on the total amount of allowable emissions is set, and this cap is then divided into individual allowances. These allowances can be bought and sold in a market, allowing for flexibility in reducing emissions. Industries or countries that can reduce emissions more easily can sell their excess allowances to those who find it more challenging.
The carbon market, where these allowances are traded, plays a crucial role in the functioning of an ETS. It creates a monetary value for emissions, incentivizing businesses to reduce their pollution levels. The price of these allowances is determined by supply and demand dynamics in the market, and it reflects the cost of reducing emissions.
Emission trading systems have been implemented in various forms in different countries and regions around the world, including the European Union Emission Trading System (EU ETS), the California Cap-and-Trade Program, and the pilot programs in China. These systems have shown both successes and challenges, highlighting the complexity of designing and implementing effective ETS.
Overall, ETS is a market-based approach that aims to reduce emissions by creating economic incentives for industries and countries to adopt cleaner technologies. It provides flexibility in reducing emissions and allows for cost-effective pollution control. However, the effectiveness of ETS depends on various factors, including the design of the system, monitoring and verification mechanisms, and international cooperation.
Emission Trading Systems (ETS) offer several benefits that make them an attractive policy tool for tackling greenhouse gas emissions and promoting environmental sustainability. Some of the key benefits of ETS include:
Overall, ETS is a powerful policy tool that offers a range of benefits to support the transition to a low-carbon economy and combat climate change. It provides a market-based approach that encourages emissions reductions, promotes innovation, and helps achieve environmental sustainability goals.
Read Also: How to Verify the Authenticity of FX Royale: A Step-by-Step Guide
One of the main goals of emission trading systems is to reduce the environmental impact of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), which is one of the major contributors to climate change. By implementing an emissions trading system, countries and organizations can effectively manage and reduce their CO2 emissions, leading to a significant reduction in their overall environmental impact.
The basic principle behind emissions trading is that a certain limit, or cap, is set on the total amount of CO2 that can be emitted by a particular entity or sector. This cap is typically gradually reduced over time, creating a decreasing emissions trajectory. The entities or sectors covered by the emissions trading system are then allocated a certain number of allowances, which represent the right to emit a specific quantity of CO2.
Read Also: Is AvaTrade a Legit Broker? Expert Analysis and Review
Allowances can be bought and sold between different entities or sectors, creating a market for trading these allowances. This market-based approach incentivizes entities to reduce their CO2 emissions, as they can profit from selling excess allowances if they are able to reduce their emissions below their allocated allowances. Conversely, entities that exceed their allocated allowances must purchase additional allowances on the market, which can be expensive and financially burdensome.
By creating a financial incentive to reduce CO2 emissions, emissions trading systems encourage the adoption of cleaner technologies and practices. Entities are motivated to invest in energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy sources, and carbon capture and storage systems in order to reduce their emissions and thereby lower their costs. This ultimately leads to a reduction in overall CO2 emissions and a decrease in the environmental impact of these emissions.
| Benefits of Emission Trading Systems | Challenges of Emission Trading Systems |
|---|---|
| 1. Reduced CO2 emissions and environmental impact | 1. Complexity and administrative costs |
| 2. Market-based approach incentivizes emissions reductions | 2. Ensuring compliance and monitoring emissions |
| 3. Encourages investment in cleaner technologies | 3. Establishing accurate emissions baselines |
| 4. Creates a global market for emissions trading | 4. Addressing equity and distributional concerns |
In conclusion, emissions trading systems play a crucial role in reducing CO2 emissions and mitigating the environmental impact of greenhouse gases. By implementing these systems, countries and organizations can incentivize emissions reductions, encourage investment in cleaner technologies, and create a global market for emissions trading, all of which contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
An Emission Trading System, or ETS, is a market-based approach that allows companies and countries to buy and sell allowances for greenhouse gas emissions. It sets a limit on the total amount of emissions, and companies can trade their allowances to meet their emissions targets.
An Emission Trading System works by creating a market where companies and countries can buy and sell emissions allowances. The system sets a cap on the total amount of emissions allowed, and companies are given a certain number of allowances that represent their emissions rights. If a company exceeds its allowances, it can buy additional allowances from other companies. Conversely, if a company emits less than its allowances, it can sell the excess allowances to other companies.
An Emission Trading System has several benefits. Firstly, it provides an economic incentive for companies to reduce their emissions, as they can sell any allowances they don’t use. This encourages the adoption of cleaner technologies and practices. Secondly, it allows for flexibility in meeting emissions targets, as companies can trade allowances instead of being restricted to specific reduction measures. Lastly, it provides a transparent and measurable way to track and reduce emissions, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
While Emission Trading Systems have their benefits, there are also drawbacks to consider. One potential drawback is the risk of market manipulation and price volatility. If the market is not properly regulated, companies could exploit loopholes or drive up prices for allowances. Another drawback is the potential for emissions to be shifted from one region to another, known as carbon leakage. This can occur if companies relocate to regions with less stringent emissions regulations, resulting in a net increase in global emissions. It is important to address these challenges to ensure the effectiveness of Emission Trading Systems.
To ensure the effectiveness of Emission Trading Systems, governments can take several steps. Firstly, they can set ambitious emissions reduction targets that align with global climate goals. This will provide a clear signal to companies and create a strong demand for emissions allowances. Secondly, governments can implement robust regulations and oversight to prevent market manipulation and ensure transparency. Thirdly, governments can provide support and incentives for the development and adoption of low-carbon technologies. Lastly, international cooperation is crucial to address issues such as carbon leakage and ensure the global effectiveness of Emission Trading Systems.
An Emission Trading System (ETS) is a market-based approach that allows companies to trade emissions allowances to meet their emission reduction targets.
Is forex trading legal in India? Forex trading is a popular investment option that allows individuals and businesses to trade currencies and make …
Read ArticleUnderstanding FX Spot Risk Foreign exchange (FX) spot transactions are a common form of currency trading in the global financial markets. These …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Fundamentals of Forex Trading Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the decentralized marketplace where the …
Read ArticleWhat is the easiest forex trading platform? Forex trading can seem overwhelming to beginners, with its complex charts, endless analysis, and frequent …
Read ArticleHow to Spot a Trend Reversal: Key Indicators and Strategies Spotting a trend reversal is an essential skill for traders and investors in the financial …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Leverage in Forex Trading Forex trading is a popular form of investment that allows individuals to buy, sell, and exchange currencies …
Read Article