Discovering the Optimal Trading Pair for Grid Bot Trading
Best Grid Bot Trading Pair Grid bot trading is a popular automated strategy used by cryptocurrency traders to capitalize on market volatility. The …
Read Article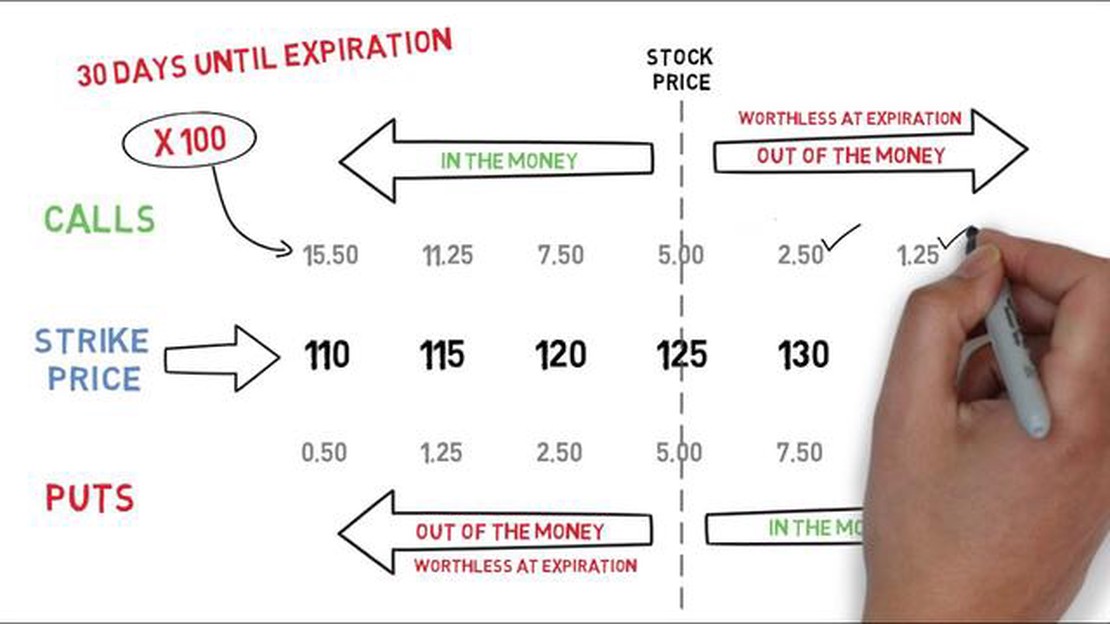
Options are financial instruments that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time. The value of an option is determined by several factors, including the price of the underlying asset, the time until expiration, and market volatility. In some cases, the price of an option can be higher than its exercise value, resulting in a discrepancy between the two.
One reason why option prices may be higher than their exercise values is the concept of time value. Options have an expiration date, which means that their value will decrease as time passes. The longer the time until expiration, the higher the time value of the option. This is because there is a greater chance that the option will move in-the-money as time goes on. Therefore, option buyers are willing to pay a premium for the additional time value.
In addition to time value, option prices can also be influenced by market volatility. Volatility refers to the rate at which the price of an underlying asset fluctuates. Higher levels of volatility increase the potential for large price swings, making options more valuable. When market volatility is high, option prices tend to be higher to account for the increased risk and potential for larger gains.
Another factor that can contribute to higher option prices is the interest rates. Interest rates affect the cost of financing and can impact the pricing of options. When interest rates are higher, option prices tend to be higher as well, as it increases the cost of carrying the underlying asset. This is known as the cost of carry, and it is factored into the option price.
In conclusion, option prices can be higher than their exercise values due to factors such as time value, market volatility, and interest rates. Time value takes into account the potential for the option to move in-the-money as time passes, while market volatility increases the potential for larger gains. Additionally, interest rates impact the cost of financing and contribute to the overall cost of carry. All of these factors combine to create option prices that may exceed their exercise values.
Option prices can be higher than their exercise values due to several factors:
Overall, option prices reflect a combination of factors, including market volatility, time remaining until expiration, interest rates, dividends, and supply and demand dynamics. These factors contribute to option prices being higher than their exercise values.
An option is a financial derivative that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific time period.
Read Also: Understanding the Various Types of Hammers in Forex Trading
The value of an option is determined by various factors, including the price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time until expiration, and the volatility of the underlying asset. The relationship between the option price and its exercise value is a key concept to understand when trading options.
The exercise value of an option is the difference between the price of the underlying asset and the strike price, multiplied by the number of shares or contracts. For a call option, the exercise value is positive if the price of the underlying asset is higher than the strike price. For a put option, the exercise value is positive if the strike price is higher than the price of the underlying asset.
However, the price of an option in the market is often higher than its exercise value. This is because the price of an option also incorporates the value of the time remaining until expiration, as well as the uncertainty or volatility of the underlying asset’s price. These factors contribute to what is known as the time value or extrinsic value of an option.
The time value is the additional amount that traders are willing to pay for an option above its exercise value, in anticipation of future price movements in the underlying asset. The longer the time remaining until expiration, the higher the time value, as there is more opportunity for the underlying asset’s price to move in a favorable direction.
Additionally, the volatility of the underlying asset’s price also affects the price of an option. Higher volatility increases the likelihood of substantial price movements, which increases the potential for the option to be profitable. Therefore, options on assets with higher volatility will have higher prices due to the additional value placed on the possibility of larger price swings.
In summary, the price of an option is higher than its exercise value due to the inclusion of the time value, which accounts for the remaining time until expiration and the potential for the underlying asset’s price to change. The volatility of the underlying asset also plays a role in determining the price of an option, with higher volatility leading to higher option prices.
Read Also: Discover the Historical Highs of MetaStock and its Record-Breaking Performance
The exercise value of an option is the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the strike price of the option.
Option prices are higher than their exercise values because the price of an option is influenced by various factors such as the time remaining until expiration, the volatility of the underlying asset, and the interest rates.
The time remaining until expiration affects option prices because the longer the time remaining, the greater the chance that the option will move in the buyer’s favor. As a result, options with more time remaining until expiration have higher prices.
Volatility plays a crucial role in determining option prices. Higher volatility increases the likelihood of large price swings, which can lead to greater potential profits for option holders. Therefore, options on highly volatile assets tend to have higher prices.
Interest rates affect option prices because higher interest rates lead to higher opportunity costs for investors. When interest rates are high, investors may prefer to allocate their funds to other investments rather than holding options, resulting in lower demand and lower option prices.
Option prices can be higher than their exercise values due to a number of factors. One factor is the time value of money, which considers the potential for the underlying asset to increase in value over time. Another factor is the volatility of the underlying asset, as higher volatility can increase the potential for the option to be profitable. Additionally, market demand and supply dynamics can also influence option prices, as buyers may be willing to pay a premium for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price in the future.
There are several factors that contribute to option prices being higher than their exercise values. Firstly, the time value of money plays a role, as the option price takes into account the potential for the underlying asset to increase in value over time. Secondly, the volatility of the underlying asset also factors in, as higher volatility can increase the likelihood of the option being profitable. Additionally, market demand and supply dynamics can impact option prices, with buyers potentially willing to pay a premium for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price in the future.
Best Grid Bot Trading Pair Grid bot trading is a popular automated strategy used by cryptocurrency traders to capitalize on market volatility. The …
Read ArticleWhat is the currency in the British Virgin Islands? The British Virgin Islands (BVI) is a stunning Caribbean destination known for its pristine …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Price of 1 Lot in Forex Trading When it comes to trading in the forex market, understanding the cost of 1 lot is crucial. A lot is a …
Read ArticleCurrent Dollar Purchase Rate in Pakistan In today’s global economy, currencies play a crucial role in determining the value of goods and services. For …
Read ArticleWhat is the significance of the DXY index? The DXY index, also known as the U.S. Dollar Index, is a widely recognized measure of the value of the …
Read ArticleIs Forex Trading Allowed in Singapore? Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has gained popularity in recent years as a way to …
Read Article