Is TransferWise available in Singapore?
Is Transferwise available in Singapore? TransferWise is a popular online money transfer service that allows users to send and receive money across …
Read Article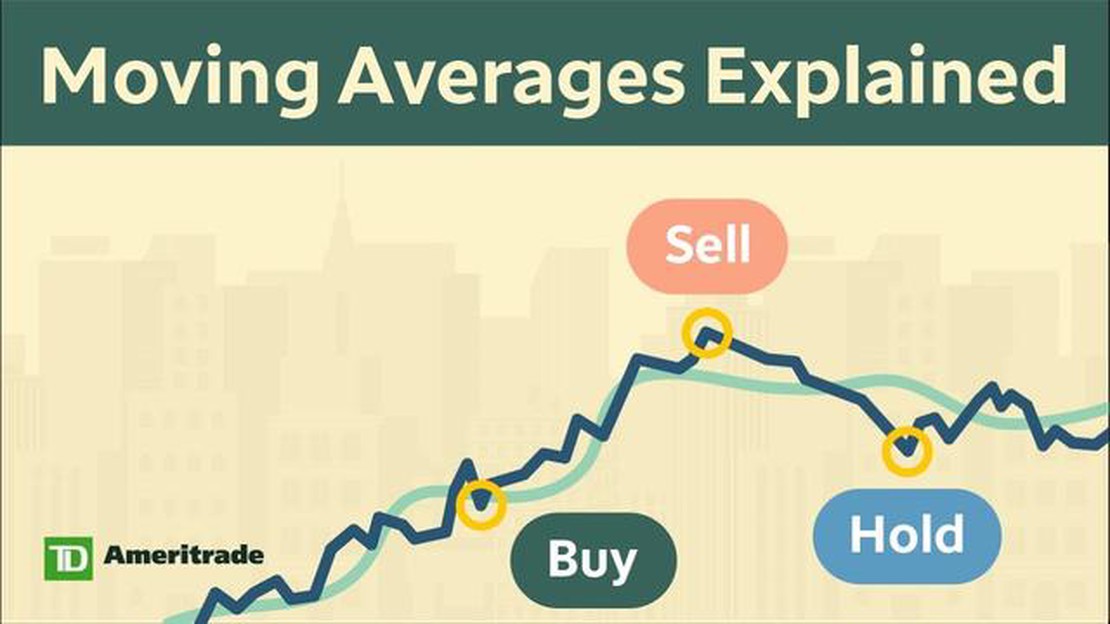
When it comes to analyzing financial data, one of the most commonly used tools is the moving average. The moving average is a mathematical calculation that helps traders and investors identify trends and patterns in price movements over a specific period of time. By smoothing out the price data, the moving average can provide valuable insights into the overall direction of the market.
There are various types of moving averages, such as the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). The SMA is calculated by adding up the closing prices over a certain number of periods and then dividing the sum by the number of periods. On the other hand, the EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to changes in the market.
Traders and investors use moving averages for a variety of purposes. One common approach is to look for crossovers between different moving averages. For example, when the shorter-term moving average crosses above the longer-term moving average, it is often seen as a bullish signal, indicating that the market is trending upwards. Conversely, when the shorter-term moving average crosses below the longer-term moving average, it is considered a bearish signal, suggesting that the market is trending downwards.
Key Takeaway: The moving average is a powerful tool that can help traders and investors make more informed decisions in the financial markets. By smoothing out price data and identifying trends, moving averages provide valuable insights that can guide buying and selling strategies. Whether it’s a simple moving average or an exponential one, understanding how to decode the information provided by moving averages is essential for successful trading.
When it comes to data analysis, moving averages are an essential tool for understanding trends and patterns. A moving average is a statistical calculation used to analyze a set of data points by creating a series of averages over a specific time period. This technique is particularly useful for smoothing out short-term fluctuations and identifying long-term trends.
The concept of a moving average is relatively straightforward. It involves taking the average of a set of data points over a specific window or time period and moving that window along the data set. For example, a 10-day moving average would calculate the average of the most recent 10 data points, then move one day forward and recalculate the average based on the new set of 10 data points. This process continues until the entire data set has been analyzed.
Moving averages can be calculated using different methods, including simple moving average (SMA) and exponential moving average (EMA). A simple moving average assigns equal weights to each data point within the time period, while an exponential moving average gives more weight to recent data points, making it more responsive to changes in the data set. The choice of which method to use depends on the specific analysis goals and the characteristics of the data set.
Moving averages are commonly used in various fields, including finance, economics, and stock market analysis. They can help identify trends, support/resistance levels, and potential entry or exit points for trading. Moving averages can also be used in time series forecasting, where they act as a baseline for predicting future values.
Overall, moving averages are a powerful tool in data analysis that can provide valuable insights into data trends and patterns. Whether used in finance, economics, or any other field, understanding how to effectively interpret and utilize moving averages can greatly enhance the analysis process.
Moving averages are one of the most popular technical analysis tools used by traders and investors. They are widely used to identify trends, gauge the strength of the current trend, and generate buy or sell signals.
A moving average is simply an average of a set of data points over a specified period of time. It helps to smooth out the fluctuations in the data and provide a clearer picture of the overall trend. The most common types of moving averages are simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA).
A simple moving average is calculated by adding up the closing prices of the asset over a specific number of periods and then dividing that sum by the number of periods. For example, a 10-day simple moving average is calculated by adding up the closing prices of the asset over the past 10 days and then dividing that sum by 10.
Read Also: Is Zara listed in the stock market? Find out everything you need to know
An exponential moving average, on the other hand, puts more weight on recent data points and gives less weight to older data points. This makes it more responsive to changes in the price movement and can help to identify trends more quickly. The calculation for an exponential moving average is more complex than a simple moving average.
Moving averages can be used in different ways depending on the trader’s strategy and objectives. Some common uses include:
It’s important to note that moving averages are lagging indicators, meaning they are based on past data and may not always accurately predict future price movements. They work best in trending markets and may produce false signals in choppy or sideways markets. Therefore, it’s important to use moving averages in conjunction with other technical analysis tools and indicators to confirm signals and minimize false signals.
Moving averages are a powerful tool in technical analysis that can help traders and investors unlock valuable insights in the financial markets. By smoothing out price data over a certain period of time, moving averages allow analysts to identify trends, determine market direction, and generate trading signals.
Read Also: History of Forex Trading in South Africa: When Did It Start?
The concept behind a moving average is simple: it calculates the average price of an asset over a specific time period by constantly updating the calculation as new data becomes available. This helps remove some of the noise and volatility in the price data, providing a clearer picture of the underlying trend.
There are different types of moving averages, such as the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). The SMA gives equal weight to each data point in the calculation, while the EMA assigns more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to the latest market movements.
Traders and investors use moving averages in various ways to unlock insights in the market. One common approach is to identify support and resistance levels. When the price of an asset is above its moving average, it is considered to be in an uptrend and the moving average can act as a support level. Conversely, when the price is below the moving average, it is considered to be in a downtrend and the moving average can act as a resistance level.
Moving averages can also be used to generate trading signals. For example, a popular strategy is to look for a crossover between two moving averages. When a shorter-term moving average crosses above a longer-term moving average, it is seen as a bullish signal, indicating a potential buying opportunity. On the other hand, when a shorter-term moving average crosses below a longer-term moving average, it is seen as a bearish signal, indicating a potential selling opportunity.
In addition to identifying trends and generating trading signals, moving averages can also help traders and investors determine the strength of a trend. The steepness of the moving average can provide insights into the intensity and momentum of the trend. A steep upward slope indicates a strong bullish trend, while a steep downward slope indicates a strong bearish trend.
In conclusion, moving averages are a powerful tool that can help traders and investors unlock valuable insights in the financial markets. By smoothing out price data and identifying trends, support and resistance levels, and generating trading signals, moving averages provide a valuable tool for technical analysis.
A moving average is a commonly used statistical indicator that is used to analyze market trends. It helps to smooth out price fluctuations and identify the overall direction of a market. It is calculated by taking the average price of a security over a specific period of time and updating it as new data points become available.
There are several different types of moving averages, including the simple moving average (SMA), exponential moving average (EMA), and weighted moving average (WMA). Each type of moving average has its own characteristics and is used in different ways by traders and analysts.
The moving average is used in technical analysis to identify trends and support/resistance levels. It is often used as a signal to enter or exit a trade. When the price of a security is above its moving average, it is considered to be in an uptrend, and when the price is below its moving average, it is considered to be in a downtrend. Traders also use moving averages to identify potential support or resistance levels, where the price may encounter buying or selling pressure.
The main difference between a simple moving average (SMA) and an exponential moving average (EMA) is the way the average is calculated. The SMA gives equal weight to all data points in the moving average period, while the EMA gives more weight to recent data points. This means that the EMA reacts faster to price changes and is more sensitive to short-term trends, while the SMA is smoother and less responsive to short-term price movements.
Is Transferwise available in Singapore? TransferWise is a popular online money transfer service that allows users to send and receive money across …
Read ArticleCurrent Rwanda currency exchange rate to USD Rwanda is a small East African country known for its stunning landscapes and rich cultural heritage. If …
Read ArticleWho Owns Travel Group? When it comes to the travel industry, there is one company that stands out among the rest. This leading travel group has become …
Read ArticleThe Key Difference Between an FX Forward and an FX Futures Contract Foreign exchange (FX) markets offer a range of derivative products for hedging or …
Read ArticleCalculating the Time Constant: A Step-by-Step Guide The time constant is a fundamental parameter used in various fields of science and engineering to …
Read ArticleWhen is Forex Most Important? Forex, short for foreign exchange, is one of the largest and most liquid financial markets in the world. Trillions of …
Read Article