Understanding the EMA Cross Over Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn how to use the EMA crossover strategy for trading The exponential moving average (EMA) cross over strategy is a popular technical analysis tool …
Read Article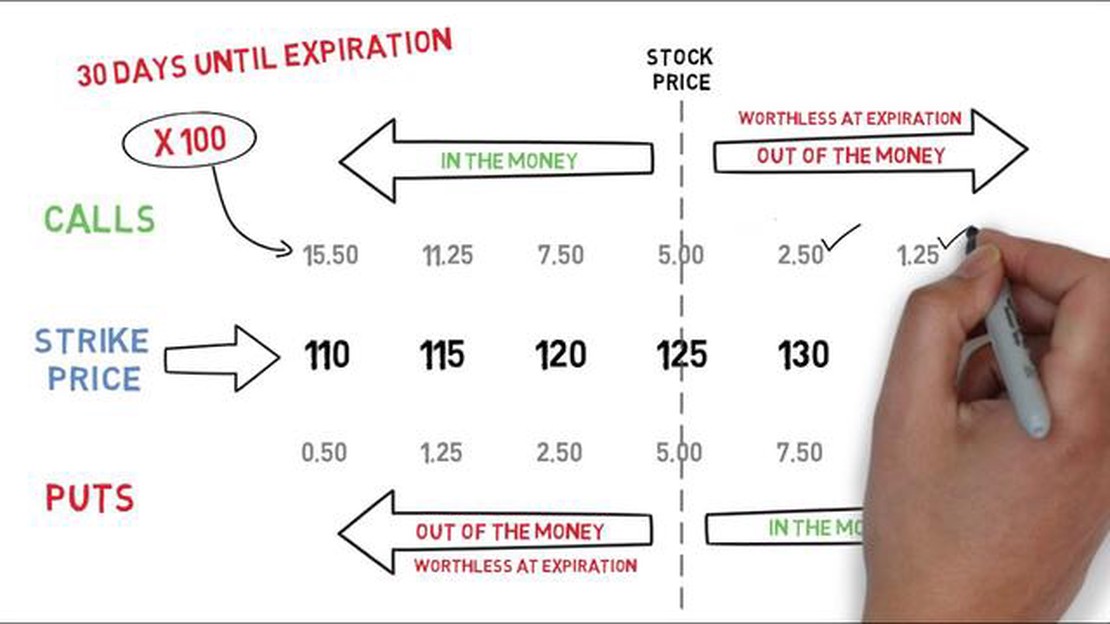
Options trading can be a complex and challenging endeavor, especially for those who are new to the world of investing. One key concept that traders must understand is the premium amount associated with options contracts. The premium refers to the price that traders pay to purchase an option, and it plays a crucial role in determining the potential profitability and risk of a trade.
What is the premium?
The premium is the upfront cost that investors pay to acquire an option. It represents the intrinsic value and time value of the option. The intrinsic value is the difference between the strike price of the option and the current market price of the underlying asset. The time value, on the other hand, is influenced by factors such as the time remaining until expiration, market volatility, and investor sentiment.
For example, let’s say an investor wants to purchase a call option on a stock with a strike price of $50. If the current market price of the stock is $55, the intrinsic value of the option would be $5. However, the premium of the option may be higher than $5 due to the additional time value.
What factors affect premium?
Several factors can impact the premium amount of an option. These include the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price of the option, the time remaining until expiration, the volatility of the underlying asset, and the overall market conditions. As these factors change, the premium amount will also fluctuate.
Highly volatile assets or those with a longer time until expiration tend to have higher premiums, as there is a greater chance for the option to move in-the-money. On the other hand, options on less volatile assets or those with a closer expiration date will generally have lower premiums.
Why is premium important?
The premium amount plays a vital role in option trading as it directly affects the potential profitability and risk of a trade. For buyers of options, the premium represents the maximum loss they can incur if the option expires out-of-the-money. Conversely, for sellers of options, the premium represents the maximum profit they can earn if the option expires out-of-the-money.
Understanding the premium amount is essential for traders to make informed decisions on whether to buy or sell options, as it helps them evaluate the potential rewards and risks involved.
In conclusion, grasping the concept of the premium amount is crucial for anyone looking to venture into option trading. As a comprehensive guide, this article has provided an overview of what the premium is, the factors that influence it, and why it is important. Armed with this knowledge, traders can approach options trading with a better understanding of how the premium impacts their potential returns and risks.
Read Also: What is the tax rate for SPX? Understanding the tax implications of investing in SPX
When it comes to option trading, one key concept that traders need to understand is the premium amount. The premium is the price that an option buyer pays to the option seller for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specified price, known as the strike price, within a specified period of time.
The premium amount is determined by various factors, including the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time until expiration, the volatility of the underlying asset, and the interest rates in the market. All these factors combined play a role in determining the premium amount.
One can think of the premium amount as the cost of buying or selling options. It is essentially the price that traders pay to enter into an options contract. The premium is paid upfront, and it is non-refundable. Traders need to consider the premium amount when deciding whether to enter into an options contract, as it can significantly impact the potential profitability of the trade.
Higher premium amounts are typically associated with options that have a higher likelihood of being profitable or options that have a longer time until expiration. This is because these options offer more potential for price movement in the underlying asset, increasing the chances of the option being in-the-money at expiration.
Traders can calculate the premium amount by multiplying the premium per share by the number of shares per contract. For example, if the premium per share is $2 and the contract size is 100 shares, the premium amount would be $200.
It is important to note that the premium amount can change throughout the life of an options contract. This is due to changes in the underlying asset’s price, volatility, and time remaining until expiration. As these factors change, the premium amount may decrease or increase.
Understanding the premium amount in option trading is crucial for traders to make informed decisions and manage their risk. By considering the factors that influence the premium amount, traders can better evaluate the potential returns and risks associated with options trading.
When it comes to option trading, the premium plays a crucial role in determining the potential profitability and risk of a trade. The premium is the upfront cost that an options buyer pays to the options seller for the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price within a specific period of time.
Read Also: Understanding 4 for 1 Split: Meaning and Impact
One of the key reasons why the premium is important in option trades is that it represents the market’s expectation of the future movement of the underlying asset. The premium is determined by various factors, such as the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time to expiration, and the implied volatility. By analyzing the premium, traders can gain insights into market sentiment and make informed decisions.
Moreover, the premium also affects the potential profitability of option trades. The premium paid by the options buyer is the maximum potential loss for the buyer, while it represents the maximum potential profit for the options seller. For example, if an options buyer pays a premium of $100 for a call option and the underlying asset’s price increases, the buyer can potentially profit by exercising the option at a higher price.
Furthermore, the premium acts as a buffer against adverse price movements. Options give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset. The premium already paid helps protect traders from losses in case the market moves against their desired direction. This risk management aspect is especially important in volatile markets.
| Benefits of Understanding Premium in Option Trades: |
|---|
| 1. Ability to assess market sentiment. |
| 2. Potential for profitable trades. |
| 3. Protection against adverse price movements. |
In conclusion, the premium in option trades is of utmost importance as it reflects market expectations, affects potential profitability, and provides risk management. By understanding and analyzing the premium, traders can make more informed decisions and enhance their chances of success in option trading.
The premium amount in option trading is the price that an option buyer pays to an option seller for the rights conveyed by the option contract. It is determined by various factors such as the current market price of the underlying asset, the strike price of the option, the time remaining until expiration, and the volatility of the underlying asset.
The premium amount is calculated using a pricing model such as the Black-Scholes model, which takes into account various factors such as the current market price of the underlying asset, the strike price of the option, the time remaining until expiration, the risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset.
There are several factors that affect the premium amount in option trading. These include the current market price of the underlying asset, the strike price of the option, the time remaining until expiration, the risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset. As these factors change, the premium amount may also change.
The premium amount varies for different options because each option has different characteristics such as the current market price of the underlying asset, the strike price of the option, the time remaining until expiration, the risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset. These characteristics determine the level of risk and potential return associated with the option, which in turn affects its premium amount.
Learn how to use the EMA crossover strategy for trading The exponential moving average (EMA) cross over strategy is a popular technical analysis tool …
Read ArticleTypes of Booths: A Complete Guide When it comes to showcasing products or services at trade shows or exhibitions, booths are an essential element. …
Read ArticleTrading Fixed Income: A Comprehensive Guide Fixed income trading is a complex and highly specialized field within the financial industry. It involves …
Read ArticleIs IQ Option a Good Trading Platform? IQ Option has gained significant recognition as a popular online trading platform. It offers a wide range of …
Read ArticleUnderstanding EA Trades: What They Are and How They Work If you’re new to the world of trading, you may have come across the term “EA trade”. But what …
Read ArticleTrading in gold options in India: A comprehensive guide Interested in trading gold options in India? Wondering how to get started? Look no further! …
Read Article