Understanding Game Theory and its Role in Pricing Options
Understanding Game Theory Pricing Options In the world of finance, game theory plays a crucial role in understanding the complexities of pricing …
Read Article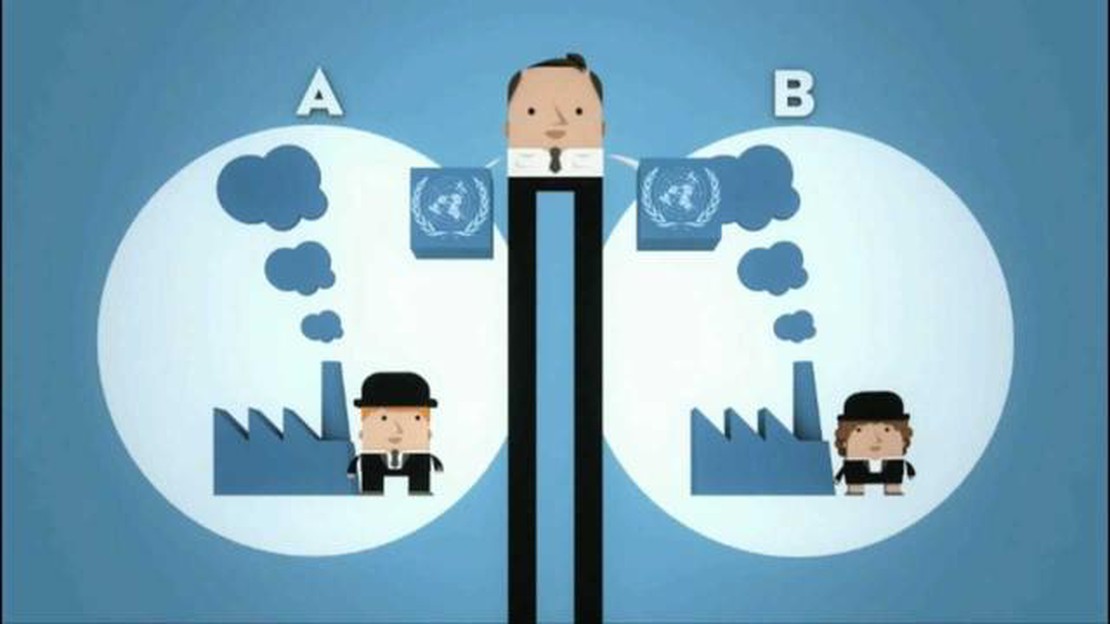
Emissions trading systems (ETS) have become an essential policy tool in the global efforts to combat climate change. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the intricate mechanism behind emissions trading systems and how they contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Emissions trading systems provide a market-based approach to addressing environmental concerns. They operate by setting a cap on the total amount of emissions allowed, and then allocating permits or allowances to companies or individuals. These permits represent a specific amount of emissions that can be released into the atmosphere.
This guide will explore the key components of emissions trading systems, including the cap and trade mechanism and the role of carbon credits. It will also delve into the benefits and challenges associated with implementing such systems at both the national and international levels.
Understanding the intricacies of emissions trading systems is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike. By understanding the mechanisms at play, stakeholders can better navigate the complexities of these systems and ensure their effective implementation.
Moreover, this guide will discuss the role of emissions trading systems in driving technological innovation and achieving emission reduction targets. It will examine the experiences of countries that have successfully implemented ETS, and highlight key lessons learned.
Overall, this comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of emissions trading systems and their role in mitigating climate change. By illuminating the mechanism of ETS, we hope to empower individuals and organizations to actively participate in the global efforts to combat climate change.
Emissions trading systems, also known as cap and trade systems, are market-based approaches to reducing pollution and controlling greenhouse gas emissions. These systems operate on the principle of setting a limit, or cap, on the total amount of emissions allowed within a specific time period. This cap is then divided into individual allowances, which represent the right to emit a certain amount of pollutants.
The main goal of emissions trading systems is to provide economic incentives for companies to reduce their emissions by giving them a financial value. Companies that can reduce their emissions below their allocated allowances can sell their extra allowances to companies that exceed their allowances. This creates a market for emissions allowances, where the price of an allowance is determined by supply and demand.
Read Also: What is the Forex Symbol for Crude Oil? | Forex Trading Guide
Emissions trading systems have several key components. First, there needs to be a legal framework that establishes the cap on emissions and defines the rules for trading allowances. This framework is typically set by government bodies or international agreements. Second, there needs to be a system for monitoring and reporting emissions to ensure compliance with the cap. Third, there needs to be a system for allocating allowances to companies. This can be done through auctioning, free allocation, or a combination of both.
One of the key advantages of emissions trading systems is their flexibility. By allowing companies to trade allowances, the system encourages cost-effective emission reductions. Companies that can reduce emissions at a lower cost can sell their allowances to companies that face higher costs. This creates a financial incentive for companies to innovate and find the most cost-effective ways to reduce emissions.
Another advantage of emissions trading systems is that they provide a clear and transparent method for tracking and reducing emissions. The cap ensures that emissions are limited to a specific level, and the trading system allows for continuous monitoring and adjustment of emissions levels. This provides a clear pathway for achieving emissions reduction goals and allows for accountability and transparency in the process.
Overall, emissions trading systems are an effective tool for reducing pollution and controlling greenhouse gas emissions. By providing economic incentives and a market-based approach, these systems encourage companies to reduce their emissions in a cost-effective manner. They also provide a transparent and accountable framework for tracking and reducing emissions, making them an important tool in the fight against climate change.
The market mechanism is a core concept in emissions trading systems, which aims to create a market for the trading of emissions allowances. This mechanism allows companies to buy and sell emissions allowances in order to meet their compliance obligations and manage their carbon emissions.
At the heart of the market mechanism is the concept of the allowance. An allowance represents the right to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases, typically one metric ton of carbon dioxide equivalent. These allowances are allocated or auctioned by the government or other regulatory bodies to companies that are covered by the emissions trading system.
The market mechanism allows companies with excess allowances to sell them to companies that need additional allowances to meet their emissions targets. This creates a market where the price of allowances is determined by supply and demand. If there is a surplus of allowances, the price will typically be low, while a scarcity of allowances will drive up the price.
The market mechanism also helps to incentivize emission reductions by allowing companies that have reduced their emissions below their allocated allowances to sell the excess allowances and profit from their efforts. This provides an economic incentive for companies to reduce their carbon emissions and promotes the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Read Also: Do dark pools display limit orders? | Everything you need to know
In addition to the trading of allowances, emissions trading systems may also include other market-based instruments, such as offset credits. These credits represent emission reductions achieved outside of the capped sectors and can be used by companies to offset their own emissions or sold to companies that need additional allowances.
Overall, the market mechanism plays a central role in emissions trading systems by creating a market for the trading of emissions allowances and other market-based instruments. This market allows companies to manage their emissions, meet their compliance obligations, and incentivize emission reductions, ultimately contributing to the overall goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The purpose of an Emissions Trading System is to incentivize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by creating a market for emissions allowances. This market allows companies to buy and sell allowances, giving them flexibility in how they meet their emissions reduction targets.
An Emissions Trading System works by setting a cap on the total amount of emissions allowed in a particular jurisdiction. This cap is divided into allowances that can be bought, sold, and traded. Companies are given or can purchase these allowances, which represent the right to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases. If a company emits more than its allocated allowances, it must buy additional allowances or face penalties.
An Emissions Trading System offers several benefits. First, it provides a market-based approach to reducing emissions, allowing for flexibility and cost-effectiveness in achieving reduction targets. Second, it encourages innovation and the adoption of cleaner technologies by providing financial incentives for companies to reduce their emissions. Lastly, an Emissions Trading System can also generate revenue for governments through the sale of allowances.
The allocation of allowances in an Emissions Trading System can vary depending on the design of the program. Some systems allocate allowances for free to companies based on historical emissions or other criteria, while others auction allowances to the highest bidder. Some systems may also have hybrid approaches, combining free allocation with auctions or other methods.
Some examples of existing Emissions Trading Systems include the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), the California Cap-and-Trade Program, and the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) in the northeastern United States. These systems have been implemented to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in their respective regions.
Understanding Game Theory Pricing Options In the world of finance, game theory plays a crucial role in understanding the complexities of pricing …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Morning Star and Evening Star Forex Patterns Forex candlestick patterns are a popular tool used by traders to forecast market movements. …
Read ArticleIs an M pattern bullish? If you are a trader or investor, you might have come across various chart patterns that are used to predict future price …
Read ArticleHow to Calculate a Weighted Average: Examples and Formulas Calculating a weighted average is a fundamental mathematical concept that is used in …
Read ArticleHow to Determine the Value of the Smoothing Constant in Exponential Smoothing Method Exponential smoothing is a widely used technique in forecasting …
Read ArticleWhy is the expectation of Brownian motion 0? Brownian motion is a continuous random walk that is widely used in many areas of science, including …
Read Article