Is FBS Safe in Pakistan? Find out the Truth Here!
Is FBS safe in Pakistan? Forex trading has gained popularity in Pakistan in recent years, with more and more people looking to make money from the …
Read Article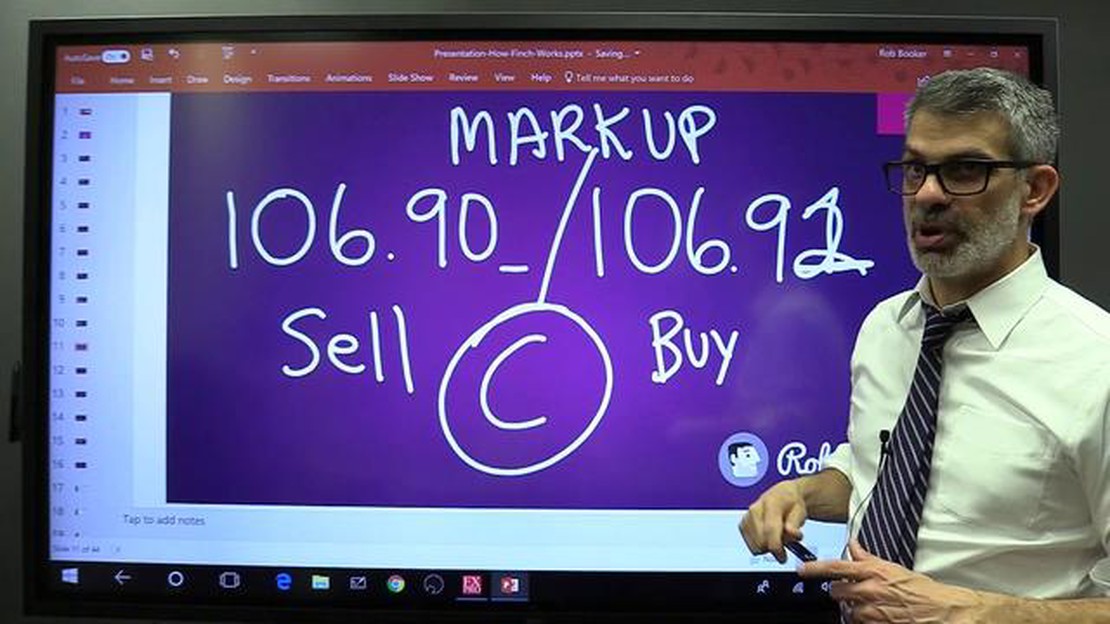
Foreign exchange (FX) spreads play a crucial role in the world of currency trading. For those new to the world of forex trading, understanding how spreads work is essential. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear explanation of the mechanics behind FX spreads and how they can impact your trades.
A spread is essentially the difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair. The bid price represents the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for a currency, while the ask price represents the lowest price that a seller is willing to accept. The spread is typically measured in pips, which is the smallest unit of measurement in the forex market.
Brokers make money by charging a spread on each transaction. When you place a trade, you are effectively buying the currency at the ask price and selling it at the bid price. The difference between these two prices is the spread, and it represents the broker’s profit. The narrower the spread, the lower the cost of trading for the trader.
There are several factors that can influence the size of the spread. One of the main factors is market liquidity. Highly liquid currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, tend to have tighter spreads compared to less liquid pairs. Additionally, market volatility and economic events can also impact the spread. During times of high volatility, spreads may widen as liquidity providers adjust their prices to reflect the increased risk.
Understanding the mechanics of FX spreads is crucial for successful trading. By choosing a broker with competitive spreads and being aware of the factors that can impact spreads, traders can make more informed decisions and minimize trading costs. With this comprehensive guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge necessary to navigate the world of forex spreads and improve your trading strategy.
FX spread, also known as the bid-ask spread, is the difference between the price at which a trader can buy a currency pair and the price at which they can sell it. The spread is essentially the cost of trading in the forex market.
When it comes to trading currency pairs, there are two prices quoted: the bid price and the ask price. The bid price is the price at which a trader can sell a currency pair, while the ask price is the price at which they can buy it.
The spread exists because forex brokers and market makers need to make money. They do this by charging a slightly higher ask price than the bid price. The difference between these two prices is the spread.
For example, if the bid price of EUR/USD is 1.1000 and the ask price is 1.1002, the spread is 0.0002, or 2 pips. This means that a trader would have to pay an additional 2 pips when buying the currency pair.
The size of the spread can vary depending on various factors, such as market volatility, liquidity, and the currency pair being traded. Major currency pairs such as EUR/USD typically have lower spreads due to their high liquidity, while exotic currency pairs may have wider spreads.
Read Also: Can You Trade Electricity on the Market? Exploring the Possibilities of Electricity Trading
Traders need to take the spread into account when determining their profit or loss on a trade. They must make enough profit to cover the cost of the spread before they can be in a profitable position.
Understanding how FX spread works is essential for anyone looking to trade currencies. By being aware of the spread, traders can make informed decisions and manage their risk effectively.
FX spread, also known as the bid-ask spread, is the difference between the buying price (bid) and the selling price (ask) of a currency pair in the foreign exchange market. It represents the cost or fee that traders pay to execute a trade.
The spread is quoted in pips, which is the smallest unit of price movement in forex trading. The spread varies depending on various factors such as market conditions, liquidity, and volatility. Generally, major currency pairs tend to have tighter spreads compared to exotic or less liquid currency pairs.
The bid price is the price at which the market is willing to buy a currency pair, while the ask price is the price at which the market is willing to sell. The difference between these two prices is the spread, and it is calculated by subtracting the bid price from the ask price.
For example, if the bid price for EUR/USD is 1.2000 and the ask price is 1.2005, the spread would be 5 pips. This means that in order to break even and cover the spread, the value of the trade needs to move at least 5 pips in the trader’s favor.
Read Also: Understanding Employee Stock Options in Nigeria: a Guide for Businesses and Employees
Brokers make money through the spread, as they buy at the bid price and sell at the ask price, profiting from the difference. The tighter the spread, the more competitive the broker is considered to be.
Understanding and monitoring the spread is important for forex traders, as it directly impacts their trading costs and potential profits. Traders should compare spreads offered by different brokers before choosing one to trade with, as tighter spreads can result in lower trading costs and potentially higher profitability.
FX spread, also known as foreign exchange spread or bid-ask spread, is the difference between the buying and selling prices of a currency pair. The spread represents the cost of trading in the forex market and is influenced by various factors:
Understanding the factors that affect FX spread can help traders make informed decisions while executing trades in the forex market. By considering these factors, traders can better manage their trading costs and improve their profitability.
The FX spread is the difference between the buying and selling prices of a currency pair. It represents the cost of trading in the foreign exchange market.
The FX spread is calculated by subtracting the bid price (the selling price) from the ask price (the buying price) of a currency pair.
The FX spread exists because financial institutions and brokers need to make a profit from the transactions they facilitate in the foreign exchange market. The spread represents their compensation for providing liquidity and execution services.
The size of the FX spread can be affected by various factors, including market liquidity, volatility, trading volume, and the relationship between the bid and ask prices. Higher liquidity and trading volume usually result in a tighter spread, while higher volatility and wider bid/ask spreads can lead to a larger spread.
Traders can minimize the impact of the FX spread on their profits by choosing brokers that offer competitive spreads, trading during times of high liquidity, and using limit orders to enter and exit positions at specific price levels. Additionally, traders can consider strategies that aim to generate larger profits relative to the spread cost.
Is FBS safe in Pakistan? Forex trading has gained popularity in Pakistan in recent years, with more and more people looking to make money from the …
Read ArticleWhat is the 4 week rule trend trading? Are you looking to gain a better understanding of trend trading? If so, the 4 Week Rule is a crucial concept to …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Value of Forex and Its Significance The foreign exchange market, commonly known as Forex, plays a vital role in the global economy. …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the 1 to 5 Risk Reward Strategy When it comes to trading in the financial markets, having a well-defined risk management strategy is …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Intrinsic Value in Stock Options When it comes to investing in stock options, understanding the concept of intrinsic value is crucial. …
Read ArticleIs Put Call Ratio a good indicator? The put call ratio is a widely used tool in the financial markets to measure investor sentiment and market …
Read Article