What is the average conveyancing fee in the UK? Find out here
Exploring the Average Conveyancing Fee in the UK Conveyancing is an essential process when buying or selling a property in the UK. It involves …
Read Article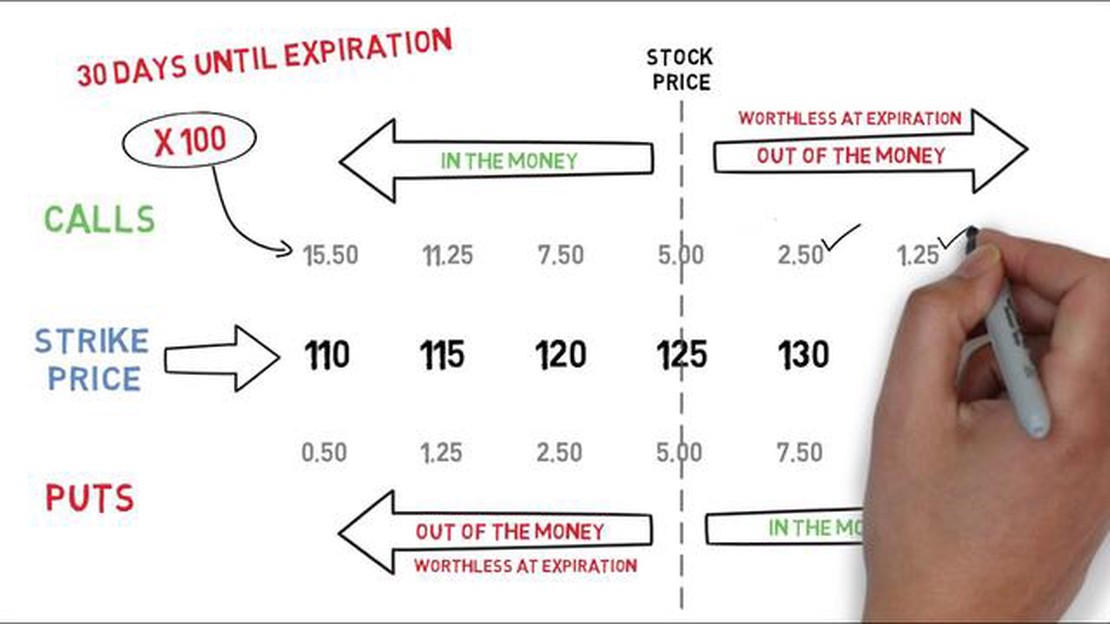
Option trading is a financial strategy that involves buying and selling options contracts based on the price movements of underlying assets. It is a popular and complex form of trading that can provide investors with flexible investment opportunities and potential returns. However, to successfully navigate the world of option trading, it is crucial to understand the logic behind it.
Option trading allows traders to speculate on the price movements of assets without owning the assets themselves. Instead, traders purchase the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price within a certain time period. This right, known as an option, provides the trader with the potential to profit from both upward and downward price movements, depending on whether they buy a call option or a put option.
Call options give traders the right to buy the underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, before the option expires. This is advantageous when the trader expects the price of the asset to increase. On the other hand, put options provide traders with the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price, which is beneficial when the trader anticipates a decrease in the asset’s price.
Understanding the logic of option trading involves grasping key concepts such as intrinsic value and time value. Intrinsic value refers to the difference between the strike price and the actual market price of the asset. This determines whether an option is in-the-money, at-the-money, or out-of-the-money. Time value, on the other hand, reflects the potential future movement of the asset and the length of time remaining until the option expires.
By comprehending the logic behind option trading, investors can better evaluate market conditions, assess risks, and make informed trading decisions. This complete guide will delve into the intricacies of option trading, providing valuable insights and strategies to help individuals navigate the often complex and ever-changing world of options.
Option trading is a financial instrument that gives traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time frame. These options are contracts that derive their value from the underlying asset, which can be stocks, commodities, or indices.
Option trading can be divided into two categories: call options and put options. Call options give traders the right to buy the underlying asset, while put options give traders the right to sell the underlying asset.
Traders who buy options are called option holders, while those who sell options are called option writers. Option trading allows investors to speculate on the direction of the market, hedge against potential losses, or generate income through options premiums.
Read Also: Understanding the Kelly's Formula and its Role in Financial Decision Making
Option trading involves several key terms that traders should familiarize themselves with, such as strike price, expiration date, and premium. The strike price is the price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold, the expiration date is the date by which the option must be exercised, and the premium is the price paid for the option contract.
It is important for traders to understand the risks associated with option trading, as the price of options can be volatile and unpredictable. Options also have a limited lifespan, meaning they expire at a certain point in time. Traders should carefully consider their risk tolerance and investment goals before engaging in option trading.
Overall, option trading offers traders a flexible and diverse set of strategies to capitalize on market movements and manage risk. It is essential for traders to educate themselves on the intricacies of option trading and develop a well-thought-out plan before entering the market.
Option trading is a derivative contract that gives traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price before a specific date. It is a popular investment strategy that allows traders to profit from changes in the price of the underlying asset without actually owning it.
Call Options: A call option is a contract that gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at a specific price, known as the strike price, before the expiration date. If the price of the underlying asset goes above the strike price, the option is in-the-money and the holder can exercise the option to buy the asset at the lower strike price.
Put Options: A put option is a contract that gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price, known as the strike price, before the expiration date. If the price of the underlying asset goes below the strike price, the option is in-the-money and the holder can exercise the option to sell the asset at the higher strike price.
Read Also: Mastering Supply and Demand: Key Strategies for Success
Expiration Date: Option contracts have an expiration date, after which the options become worthless. Traders must decide whether to exercise their options before the expiration date or let them expire.
Strike Price: The strike price is the price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold. It is determined at the time the option contract is created and does not change during the life of the contract.
Premium: When buying options, traders pay a premium, which is the price of the option contract. The premium is determined by factors such as the price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the expiration date, market volatility, and interest rates.
Note: Option trading involves risks and may not be suitable for all investors. It is important to understand the fundamentals of option trading and carefully consider your investment goals and risk tolerance before trading options.
Option trading is a type of investment strategy that involves buying and selling options on the stock market. Options are financial instruments that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time.
Option trading works by individuals or institutions buying and selling options contracts. These contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price, known as the strike price, within a certain timeframe. Traders can profit from option trading by accurately predicting the movement of the underlying asset’s price.
Some advantages of option trading include the potential for high returns, the ability to profit from both rising and falling markets, and the flexibility to tailor strategies to individual risk tolerance. However, option trading also carries risks, including the potential for loss of the entire investment, the complex nature of options contracts, and the need for accurate predictions of price movements.
Exploring the Average Conveyancing Fee in the UK Conveyancing is an essential process when buying or selling a property in the UK. It involves …
Read ArticleIs Trading 212 profitable? Trading 212 is a popular online trading platform that provides individuals with access to a wide range of financial …
Read ArticleMinimum capital requirements for LLC in UAE When it comes to setting up a limited liability company (LLC) in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), one of …
Read ArticleWhat is the best adaptive moving average setting? Developing an effective trading strategy is crucial for success in the financial markets. One …
Read ArticleIs an option expiration considered a day trade? Day trading options can be a complex and exciting strategy for traders looking for short-term profits. …
Read ArticleUnderstanding CCI in Forex Trading When it comes to Forex trading, there are numerous technical indicators that traders use to help analyze the market …
Read Article