How much does Bloomberg trading platform cost? - All you need to know
Cost of Bloomberg Trading Platform: Explained When it comes to trading platforms, Bloomberg is a name that is well-known and widely used in the …
Read Article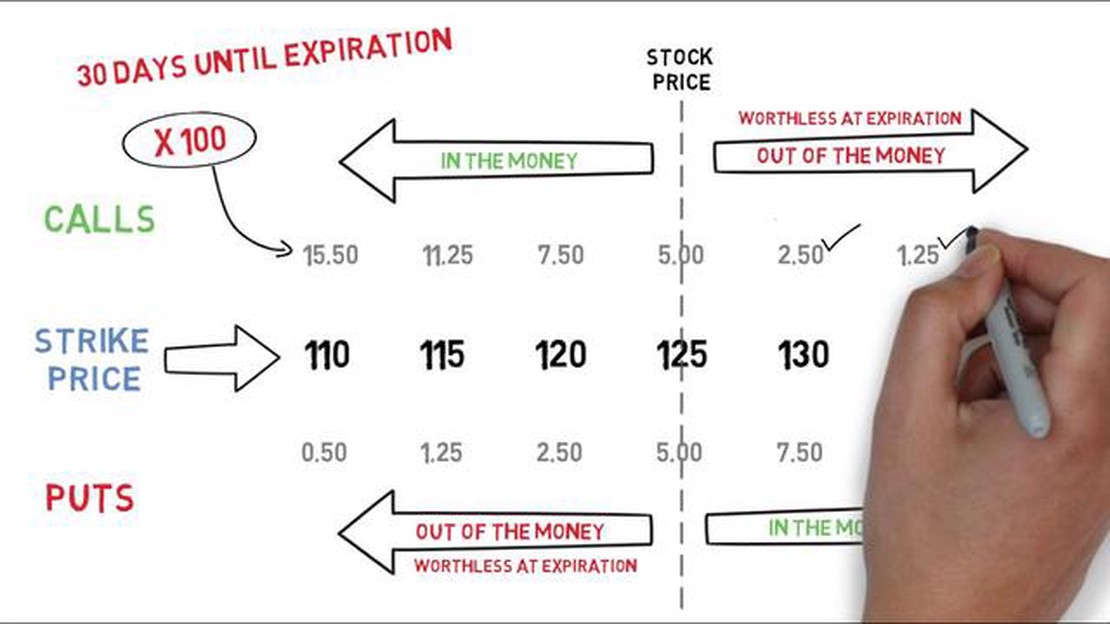
Investing in options can be a complex and intimidating process, especially for beginners. One of the key components of options trading is understanding the formula for call options. Call options give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe.
But how do you calculate the value of a call option? This guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of understanding the formula for call options, so you can make informed investment decisions.
The formula for call options takes into account several key variables, including the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time to expiration, the risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset. By plugging in these variables, you can calculate the theoretical value of a call option.
Let’s break down the formula into its key components:
1. Current Price of the Underlying Asset: This is the current market price of the underlying asset, such as a stock or commodity.
2. Strike Price: The strike price is the predetermined price at which the underlying asset can be bought if the call option is exercised.
3. Time to Expiration: This refers to the remaining time until the call option contract expires. The longer the time to expiration, the higher the value of the call option.
4. Risk-Free Interest Rate: The risk-free interest rate is the rate of return on a risk-free investment, such as a government bond. It is used as a discount factor in the formula to calculate the present value of the call option.
5. Volatility of the Underlying Asset: Volatility measures the degree of price fluctuation of the underlying asset. Higher volatility increases the value of the call option, as there is a greater chance for the price of the underlying asset to move significantly.
By plugging these variables into the formula for call options, investors can determine the theoretical value of the call option. This value can then be compared to the market price of the call option to identify potential investment opportunities.
Understanding the formula for call options is a crucial step in becoming a successful options trader. By grasping the key variables and their impact on the value of call options, investors can make more informed decisions and navigate the options market with confidence.
Understanding the formula for call options is essential for investors looking to trade these financial derivatives. This formula allows traders to calculate the theoretical price of a call option and understand the factors that affect its value.
The formula for call options is based on several key components. These include the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time to expiration, the risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset.
The formula for call options is as follows:
Understanding each step of the formula can help traders make informed decisions when trading call options. By analyzing the underlying asset’s price, strike price, time to expiration, risk-free interest rate, and volatility, investors can determine whether a call option is overvalued or undervalued and decide on the appropriate course of action.
Keep in mind that the formula for call options provides a theoretical price, and the actual market price may differ due to various factors such as market supply and demand dynamics, market sentiment, and other external events. Therefore, it is crucial to combine the formula with market analysis and intuition when making trading decisions.
Calculating the value of a call option involves several steps. Here, we will break down the process step by step to help you understand the formula for call options.
Read Also: How much does VantagePoint AI pay? - VantagePoint AI Compensation and Salary Guide
Step 1: Determine the current stock price
Before calculating the call option value, you must first determine the current price of the underlying stock. This is typically done by looking up the current market price or using a stock quote service.
Read Also: Understanding FX Swap Example: A Comprehensive Guide
Step 2: Calculate the intrinsic value
The intrinsic value of a call option is the difference between the current stock price and the strike price. If the current stock price is higher than the strike price, the intrinsic value is positive. Otherwise, it is zero.
Step 3: Calculate the time value
The time value of a call option is the portion of its value that is not accounted for by the intrinsic value. It represents the amount that investors are willing to pay for the potential upside in the future. The time value decreases as the expiration date approaches.
Step 4: Determine the volatility factor
Volatility is a measure of how much the price of the underlying stock is expected to fluctuate in the future. Higher volatility generally leads to higher option prices.
Step 5: Consider interest rates and dividends
Interest rates and dividends can also affect the price of call options. Higher interest rates or the absence of dividends can increase the attractiveness of holding the underlying stock, which may lower the call option price.
Step 6: Use the Black-Scholes formula or an alternative
Finally, you can use the Black-Scholes formula or an alternative options pricing model to calculate the exact value of the call option. The formula incorporates the stock price, strike price, time to expiration, volatility, interest rates, and dividends to arrive at an estimated option value.
By following these steps, you can gain a better understanding of how call option formulas are calculated and make more informed investment decisions in the options market.
A call option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specified quantity of an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific time period.
The formula for call options, also known as the Black-Scholes formula, takes into account several variables such as the stock price, strike price, time to expiration, risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset. This formula calculates the theoretical price of a call option.
Sure! To calculate the price of a call option, you need to follow these steps: 1) Determine the current stock price; 2) Calculate the time to expiration in years; 3) Determine the risk-free interest rate; 4) Calculate the annualized volatility of the underlying asset; 5) Use the Black-Scholes formula to calculate the theoretical price of the call option.
Understanding the formula for call options is crucial for investors as it allows them to evaluate the fair value of call options and make informed investment decisions. By calculating the theoretical price of a call option, investors can determine if the option is overpriced, underpriced, or fairly priced, and take appropriate actions based on their analysis.
Cost of Bloomberg Trading Platform: Explained When it comes to trading platforms, Bloomberg is a name that is well-known and widely used in the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Key Characteristics of a CSR Platform In today’s business landscape, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has become a crucial …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the mechanics of the emission trading system The issue of climate change has become increasingly urgent in recent years. Governments, …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Permanent Differences in IFRS International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a set of accounting principles and rules that guide …
Read ArticleWhat are the best times to trade Forex GMT? In the world of forex trading, timing is everything. The value of currencies fluctuates constantly, and …
Read ArticleWhat percentage of people make on Forex? Forex, also known as foreign exchange, is a decentralized global market for trading currencies. With …
Read Article