Understanding the Intrinsic Value of an Option: A Comprehensive Guide
The Intrinsic Value of an Option Options are a popular financial instrument that allow investors to speculate on the future price movement of an …
Read Article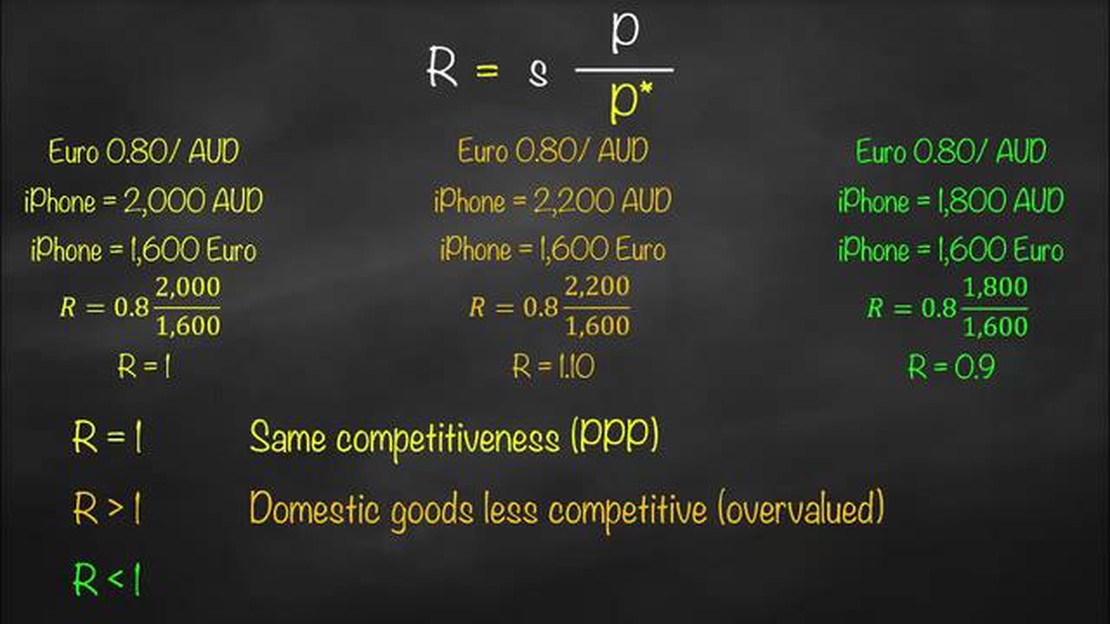
The exchange rate is a critical economic indicator that reflects the value of one currency relative to another. However, when discussing exchange rates, it’s important to distinguish between nominal and real exchange rates. While both are used to measure currency values, they serve different purposes and provide distinct insights into the economic landscape.
The nominal exchange rate represents the current market value of one currency in terms of another. It is the rate at which currencies are exchanged on the foreign exchange market, also known as Forex. For example, if the nominal exchange rate between the US dollar and the euro is 1.10, it means that one US dollar can be exchanged for 1.10 euros.
On the other hand, the real exchange rate takes into account the effects of inflation on currency values. It is adjusted for price level differences between countries and provides a more accurate measure of purchasing power. The real exchange rate is calculated by dividing the nominal exchange rate by the ratio of price indices between two economies. It shows how much a unit of a country’s currency can buy in terms of goods and services in another country.
In summary, the nominal exchange rate reflects the market value of currencies, while the real exchange rate provides a measure of purchasing power and accounts for inflation. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is crucial for economists, policymakers, and investors in analyzing international trade, competitiveness, and economic health.
The concept of exchange rates refers to the value of one currency expressed in terms of another currency. It determines how much of one currency is needed to buy a unit of another currency. Exchange rates play a crucial role in international trade, investment, and travel.
Exchange rates can be either nominal or real. Nominal exchange rates are the current rates at which one currency can be exchanged for another in the foreign exchange market. These rates are influenced by factors such as inflation, interest rates, and market conditions. Nominal exchange rates are typically used for day-to-day transactions and are widely reported in financial news.
However, nominal exchange rates do not provide a true reflection of the relative value of currencies over time. This is where real exchange rates come into play. Real exchange rates are adjusted for inflation and reflect the purchasing power of currencies. They are calculated by taking into account the relative price levels of different countries and adjusting the nominal exchange rate accordingly.
Understanding the difference between nominal and real exchange rates is essential for assessing the competitiveness of a country’s exports, the impact of exchange rate movements on trade balances, and the purchasing power of individuals in different countries. It is also important to note that exchange rates can be floating (determined by market forces) or fixed (set by a government or central bank).
In conclusion, exchange rates are a fundamental concept in international economics. They determine the value of currencies and play a vital role in global economic interactions. By understanding the distinction between nominal and real exchange rates, one can better analyze and interpret the impact of exchange rate movements on various aspects of the economy.
The nominal exchange rate is the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another currency. It is an important economic indicator that impacts various aspects of international trade and investment. Understanding the significance of nominal exchange rates is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers.
Read Also: Convert 30,000,000 RUB to EUR: Latest Currency Exchange Rates2. Inflation and Price Stability: Nominal exchange rates are closely linked to a country’s inflation rate. If a country has high inflation, its currency tends to depreciate to maintain price competitiveness with other countries. On the other hand, low inflation may lead to an appreciation of the currency. Central banks often monitor and adjust the nominal exchange rate to control inflation and maintain price stability.
3. Foreign Investment: Nominal exchange rates impact foreign investment decisions. Investors consider the potential returns in different currencies, taking into account the exchange rate fluctuations. A favorable exchange rate can attract foreign investment, as it enhances the potential gains for investors when they convert their profits back to their home currency.
Read Also: Can You Be Profitable with Binary Options? Find Out Here!4. Monetary Policy: Nominal exchange rates directly affect a country’s monetary policy. Central banks can influence the exchange rate through interventions in the foreign exchange market, such as buying or selling currencies. Changes in the nominal exchange rate can impact a country’s money supply, interest rates, and overall economic growth. 5. Economic Stability: Stable nominal exchange rates are crucial for maintaining economic stability. Excessive fluctuations in exchange rates can lead to volatile financial markets and disrupt economic activities. Governments and central banks often intervene to stabilize exchange rates by implementing various policy measures.
In conclusion, the significance of nominal exchange rates cannot be overlooked. It affects international trade, inflation, foreign investment, monetary policy, and overall economic stability. Monitoring and understanding nominal exchange rates is essential for individuals and businesses engaged in international transactions and for policymakers formulating economic policies.
The nominal exchange rate is the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another currency, without taking into account factors such as inflation. The real exchange rate, on the other hand, is adjusted for inflation and reflects the actual purchasing power of a currency.
The nominal exchange rate is determined by the foreign exchange market, where the forces of supply and demand for different currencies interact. Factors such as interest rates, inflation rates, economic performance, and political stability can affect the demand and supply for currencies, ultimately influencing the nominal exchange rate.
Understanding the difference between nominal and real exchange rates is important because it helps in assessing the competitiveness of a country’s exports, determining the impact of exchange rate changes on trade balance, and analyzing the purchasing power of a currency in international markets. It allows policymakers, businesses, and investors to make informed decisions regarding international trade, investment, and monetary policy.
The real exchange rate plays a crucial role in a country’s exports and imports. If a country’s real exchange rate appreciates, meaning its currency strengthens, its exports become more expensive for foreign buyers and imports become cheaper for domestic consumers. This could lead to a decrease in exports and an increase in imports, possibly resulting in a trade deficit.
Sure! Let’s say the nominal exchange rate between the US dollar and the Japanese yen is 100 yen per dollar. However, if the US has a higher inflation rate than Japan, the real exchange rate may be lower than the nominal exchange rate. This means that the purchasing power of the US dollar is actually lower compared to the yen, even though the nominal exchange rate suggests otherwise.
The nominal exchange rate is the rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another, without any adjustments for inflation. The real exchange rate, on the other hand, takes into account the inflation rates of the two countries and provides a more accurate measure of the relative value of the two currencies.
Understanding the difference between nominal and real exchange rates is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to determine the purchasing power of a currency in different countries. Secondly, it allows for comparisons of the competitiveness of different countries’ economies. Lastly, it can have significant implications for international trade and investment flows.
The Intrinsic Value of an Option Options are a popular financial instrument that allow investors to speculate on the future price movement of an …
Read ArticleEuro Rate in ANZ Are you planning to travel to Europe or make purchases in euros? Knowing the current exchange rate is crucial for making informed …
Read ArticleHow Does Xe com Make Money? Xe com is a popular online platform that provides currency exchange and international money transfer services. It offers …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Bullish and Bearish Gartley Patterns The Gartley pattern is a powerful and popular technical analysis tool that traders use to …
Read ArticleWho is the CEO of IPC Systems? IPC Systems is a global provider of communication and networking solutions for the financial markets. With a strong …
Read ArticleWhat is the 123 method of trading? If you’re looking to take your trading to the next level and maximize your potential profits, then it’s time to …
Read Article