Exploring Options on eToro: All You Need to Know
Can I trade options on eToro? When it comes to investing in the stock market, it’s important to have access to a platform that offers a wide range of …
Read Article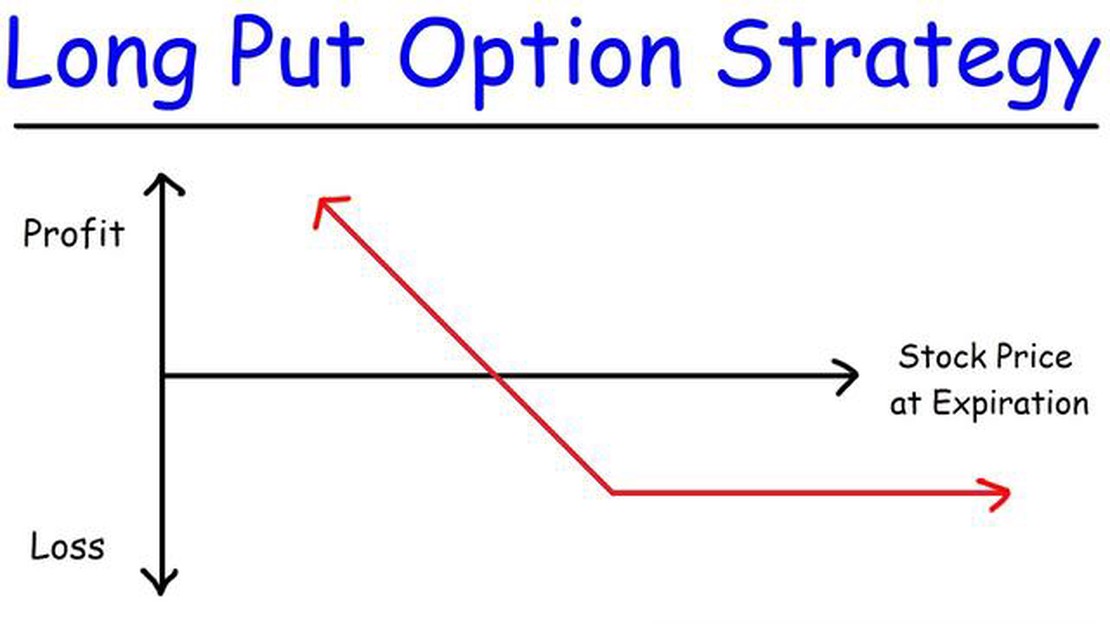
In the world of investing, understanding different types of options can be crucial for success. One commonly used option strategy is the long put option. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what a long put option is, how it works, and discuss some of the key factors to consider when using this strategy.
A long put option is a type of financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific asset, such as a stock, at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) within a specified period of time (known as the expiration date). This strategy is often employed by investors who anticipate a decline in the price of the underlying asset.
When purchasing a long put option, the investor pays a premium to the seller (also known as the writer) of the option. This premium gives the buyer the right to sell the asset at the strike price, regardless of its market value at expiration. If the price of the underlying asset falls below the strike price, the buyer can exercise their option and sell the asset at a profit.
It is important to note that the potential loss for a long put option is limited to the premium paid, while the potential gain can be substantial if the price of the underlying asset decreases significantly.
There are several factors to consider when using a long put option strategy. These include selecting an appropriate strike price and expiration date, as well as understanding the potential risks and rewards. Additionally, it is important to consider market conditions and other factors that may impact the price of the underlying asset. By carefully evaluating these factors, investors can make informed decisions when using long put options to hedge against potential declines in the market.
A long put option is a type of options contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific asset at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) on or before a specific date (known as the expiration date).
By purchasing a long put option, the investor profits if the price of the underlying asset decreases below the strike price. This allows the investor to profit from a decline in the price of the asset, as they can sell it at a higher strike price even if the market price has fallen.
Long put options are typically used as a form of insurance or protection against potential downside risk in an investment portfolio. They allow investors to limit their losses in the event of a market downturn or price decline.
It’s important to note that long put options have a limited lifespan, as they have an expiration date. If the price of the underlying asset does not decrease below the strike price before the expiration date, the long put option may expire worthless, and the investor would lose the premium paid for the option.
Investors who believe that the price of an asset is likely to decline in the future may consider buying long put options to profit from this expected decline. However, it’s essential to carefully consider factors such as the cost of the option, the potential profit, and the likelihood of the asset’s price reaching the strike price before the expiration date.
A long put option is a financial instrument that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specified quantity of an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time.
When an investor purchases a long put option, they are expecting the price of the underlying asset to decrease. If the price does decrease below the predetermined price, the investor can exercise the option and sell the asset at a profit.
The holder of a long put option pays a premium for the option, which is the cost of purchasing the right to sell the asset. This premium is determined by various factors, including the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time until expiration, and the volatility of the asset.
Read Also: Understanding the Factors that Influence CDS Spreads
Long put options can be used for a variety of purposes, including hedging against potential losses in the underlying asset, speculating on a decline in price, or as part of a more complex options trading strategy.
It’s important for investors to understand that while long put options can offer potential profits, they also carry risks. If the price of the underlying asset remains above the strike price, the option may expire worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid.
Read Also: Unlocking the Complexity of Option Pricing: Why is it so Difficult?
Investors should carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before trading long put options. It may be beneficial to consult with a financial advisor or options trading professional to fully understand the risks and potential rewards associated with this strategy.
Long put options can offer various benefits and risks to investors. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions when trading options.
Benefits of long put options:
Risks of long put options:
Overall, long put options can be a useful tool for investors seeking downside protection and profit potential from a decline in the price of an underlying asset. However, it’s important to carefully consider the risks involved and have a solid understanding of options trading before engaging in this strategy.
A long put option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific asset, such as stocks, at a predetermined price within a specified time frame.
A long put option allows the holder to profit from a decline in the price of the underlying asset. If the price of the asset falls below the strike price of the put option, the holder can exercise the option and sell the asset at the higher strike price.
The main advantage of buying long put options is the potential for significant profit in the event of a decline in the price of the underlying asset. It also provides a way to protect against potential losses in a long position.
One of the main risks of buying long put options is the possibility of the underlying asset’s price not falling below the strike price, resulting in the option expiring worthless. Additionally, options have a limited lifespan, so the holder must be correct about the timing of the price decline.
The choice of strike price and expiration date for a long put option depends on various factors, including the expected price movement of the underlying asset, the desired level of protection or profit, and the holder’s risk tolerance. It’s important to consider these factors and possibly consult with a financial advisor before making a decision.
A long put option is a type of financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific asset at a predetermined price within a specified time period.
A long put option gives the investor the ability to profit from a decline in the price of the underlying asset. If the price of the asset drops below the strike price of the put option, the investor can exercise the option and sell the asset at the higher strike price, thus making a profit.
Can I trade options on eToro? When it comes to investing in the stock market, it’s important to have access to a platform that offers a wide range of …
Read ArticleDoes MT4 work on Apple? If you are an Apple user and interested in trading on the foreign exchange market, you might be wondering if the popular …
Read ArticleChoosing the Best Time Frame for Forex Trading Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the buying and selling of currencies on the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Position Ratio in Forex Trading In the world of forex trading, understanding the importance of position ratio is crucial for …
Read ArticleWhat is a portfolio in trading? When it comes to trading, having a well-diversified portfolio is key to success. But what exactly is a portfolio in …
Read ArticleHow to Use 20, 50, and 200 EMA in Trading When it comes to trading, understanding and effectively using technical indicators can make all the …
Read Article