What is the Current 22k Gold Price in Pakistan? Find Out Here!
22k Gold Price in Pakistan Gold has always been a precious metal that holds immense value and significance in Pakistani culture. Whether it’s for …
Read Article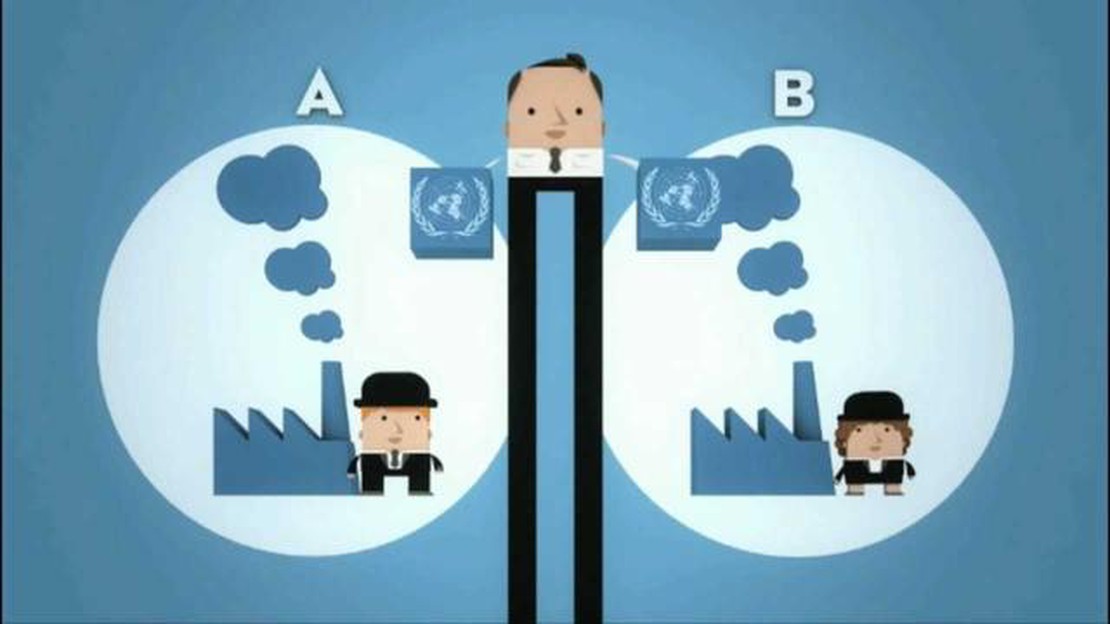
Emissions trading, also known as cap and trade, is a market-based approach to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It is a key instrument in the fight against climate change, as it allows countries and industries to meet their emissions targets in a cost-effective manner.
The basic principle of emissions trading is to set an overall limit or cap on the amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted. This limit is then divided into individual allowances, which are allocated to companies or countries. These allowances can be bought, sold, or traded on the emissions market.
By creating a market for emissions, companies and countries are encouraged to find the most cost-effective ways to reduce their emissions. Those that can reduce their emissions below their allocated allowances can sell their extra allowances to those that are unable to meet their targets.
Emissions trading has been implemented in various countries and regions around the world, including the European Union, the United States, and China. It has been praised for its ability to drive innovation and encourage the adoption of cleaner technologies. However, it has also faced criticism for potentially allowing companies to simply buy their way out of reducing emissions and for not guaranteeing a sufficient reduction in overall emissions.
Emissions trading, also known as cap and trade, is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by creating a financial incentive to reduce emissions. It is a system that allows companies and countries to buy and sell permits that represent the right to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide.
The concept of emissions trading emerged as a way to address the problem of climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Instead of implementing strict regulations and penalties, emissions trading provides a flexible and market-oriented solution to reduce emissions.
In an emissions trading system, a government sets a cap on the total amount of emissions that can be released by all participants. This cap is usually determined by the government’s environmental policy goals and targets. The government then issues a limited number of permits, each representing the right to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases.
Companies and countries that emit below their allotted limit can sell their surplus permits to those that exceed their emissions allowance. This creates a market where those who can reduce emissions more cost-effectively are incentivized to do so and can sell their excess permits for a profit. At the same time, companies that find it more challenging to reduce emissions can purchase permits to meet their emissions obligations.
Emissions trading not only encourages emission reductions but also promotes innovation and investment in cleaner technologies. By putting a price on emissions, it gives companies an economic incentive to develop and adopt cleaner and more sustainable practices. It helps to level the playing field and rewards those who take early action to reduce emissions.
This market-based approach to controlling pollution has gained popularity worldwide. It has been successfully used in various countries and regions to tackle different types of air and water pollutants. The emissions trading system has the potential to be an effective tool in combating climate change by encouraging widespread emissions reductions and facilitating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Emissions trading, also known as cap-and-trade, is a market-based approach used to reduce air pollution and control greenhouse gas emissions. The concept revolves around the idea of creating a financial incentive for companies to reduce their emissions.
Under an emissions trading system, a regulatory authority sets a cap on the total amount of emissions that can be produced by a specified group of companies. This cap is gradually reduced over time to meet environmental targets and encourage emission reduction.
Read Also: Understanding India's 1991 Balance of Payments Crisis: Causes, Impacts, and Lessons Learned
Trading allowances are then distributed among the companies within the system. Each allowance represents the right to emit a certain amount of pollutants, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4). Companies that can reduce their emissions below their allocated allowances can sell or ’trade’ their excess allowances to companies that have exceeded their limits.
The trade of allowances allows companies that find it more costly to reduce their emissions to purchase allowances from those that have achieved emission reductions more cost-effectively. This creates a financial incentive for companies to invest in cleaner technologies and practices to reduce their emissions, as it becomes more economically beneficial to do so.
Read Also: Understanding the Formula for Forward Forward Rate: Explained by Experts
Furthermore, emissions trading promotes a dynamic market for emissions reductions. As companies innovate and find more cost-effective ways to reduce emissions, the supply of allowances increases and prices decrease. This process encourages continuous emission reduction efforts and provides flexibility for companies to adapt to changing environmental regulations and market conditions.
Emissions trading has both economic and environmental benefits. From an economic standpoint, it helps to achieve emission reduction goals at a lower cost compared to traditional command-and-control regulations. Moreover, it promotes innovation and the development of cleaner technologies.
From an environmental perspective, emissions trading contributes to the overall reduction of greenhouse gases, aiding in the fight against climate change. It also enhances air quality by reducing other harmful pollutants that lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
However, emissions trading is not without its challenges. It requires careful design and monitoring to prevent market manipulation and ensure that emission reductions are genuinely achieved. Additionally, the effectiveness of emissions trading relies on accurate measurement and reporting of emissions, which can be challenging for certain sectors.
Overall, emissions trading provides a tool to achieve emission reduction goals while balancing economic growth. By creating incentives and promoting innovation, it offers a market-based solution to address environmental challenges and ensure sustainable development.
Emissions trading is a market-based approach that allows companies to buy and sell permits to emit greenhouse gases. It is a mechanism designed to reduce overall emissions by creating a financial incentive for companies to reduce their emissions.
Emissions trading works by setting a limit, or cap, on the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions allowed. Companies are then allocated a certain number of permits to emit those gases. If a company exceeds its allocated permits, it must buy permits from other companies that have emissions below their allocated allowances.
Emissions trading has several benefits. It provides a financial incentive for companies to reduce their emissions, as they can sell any excess permits they have. It also encourages innovation and the development of cleaner technologies. Additionally, it can lead to cost savings for companies by allowing them to choose the most cost-effective way to reduce emissions.
Emissions trading has a positive environmental impact by effectively reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions. By putting a price on emissions and creating a market for permits, it encourages companies to find ways to reduce their emissions. This, in turn, helps to mitigate climate change and reduce air pollution.
Yes, there are some criticisms of emissions trading. Some argue that it allows companies to simply buy their way out of reducing emissions, rather than making meaningful changes to their operations. Others believe that it can lead to environmental injustices, as companies in low-income communities may bear the brunt of pollution if they are unable to afford permits. Additionally, there are concerns about the integrity and effectiveness of emissions trading systems in accurately measuring and reducing emissions.
22k Gold Price in Pakistan Gold has always been a precious metal that holds immense value and significance in Pakistani culture. Whether it’s for …
Read ArticleCalculating average in VB: a comprehensive guide Calculating the average of a set of numbers is a fundamental task in many programming languages, …
Read ArticleTrading Opportunities in a Rising Interest Rate Environment Interest rate changes can have a significant impact on the financial markets, and being …
Read ArticleCan NRI do futures trading in India? Are you a Non-Resident Indian (NRI) interested in futures trading in India? If so, there are a few things you …
Read ArticleIs a 401K a type of stock? When it comes to planning for retirement, one of the most common investment options people consider is a 401K. However, …
Read ArticleWhat is the average salary of forex traders in London? When it comes to the world of forex trading, it’s no secret that London is one of the major …
Read Article