Does TradingView Offer Options Trading? Find Out Here!
TradingView Options: Everything You Need to Know If you’re an options trader or are interested in exploring options trading, you may be wondering if …
Read Article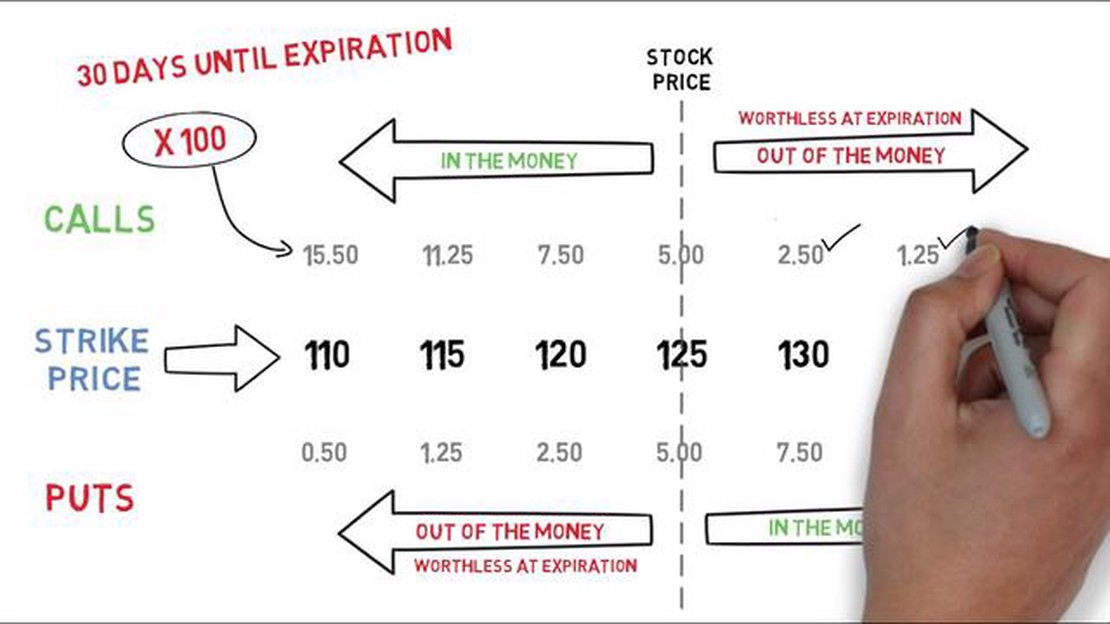
Stock options are a popular form of compensation offered by many companies as a way to attract and retain top talent. However, understanding the cost of stock options is crucial for both employees and employers. In this article, we will explore the various factors that determine the cost of stock options and provide you with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions.
When it comes to stock options, there are several key terms that you need to be familiar with. The most important one is the strike price, which is the price at which you can buy the stock when exercising your options. The strike price is typically set at the fair market value of the stock on the date of grant. Other important terms include the vesting period, which is the time period over which you gradually gain ownership of the stock options, and the expiration date, which is the date by which you must exercise your options or they will expire.
The cost of stock options can vary depending on a number of factors. One of the main determinants is the volatility of the underlying stock. Higher volatility increases the likelihood of a large price swing, which in turn increases the value of the options. Another important factor is the time remaining until the options expire. The longer the time period, the greater the chance for the stock price to move in a favorable direction, increasing the value of the options. Additionally, the strike price and the current market price of the stock will also affect the cost of the options.
It is important to carefully consider the cost of stock options before accepting them as part of your compensation package. While they can provide significant financial upside, they also come with risks. The value of the options can fluctuate greatly depending on market conditions and the performance of the underlying stock. It is also important to understand any tax implications associated with stock options, as they can impact the overall cost. By understanding the cost and risks associated with stock options, you can make well-informed decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
When investing in stocks, it is important to understand the cost associated with stock options. Stock options give individuals the right to buy or sell a specific stock at a predetermined price within a certain timeframe.
The cost of stock options varies depending on several factors, such as the strike price, expiration date, and the current market price of the stock. The strike price is the price at which the option can be exercised, while the expiration date is the last day that the option can be exercised.
One of the key costs associated with stock options is the premium. The premium is the price that an investor pays to purchase the options contract. It is determined based on the current market price of the stock, the strike price, the expiration date, and other factors such as market volatility.
Another cost to consider is the opportunity cost. When buying stock options, investors give up the opportunity to invest that money elsewhere. This is an important consideration, as it is not guaranteed that the stock options will be profitable.
Additionally, there may be transaction costs associated with stock options, such as brokerage fees. These fees can vary depending on the broker and the volume of options being traded.
Understanding the cost of stock options is crucial for investors to make informed decisions. It is important to carefully evaluate the potential costs and benefits before entering into any options contract. Consulting with a financial advisor can also be helpful in understanding the associated costs and making the best investment decisions.
Read Also: What symbol is this? Decode symbols and their meanings
When it comes to understanding the cost of stock options, it’s important to start with the basics. Stock options are a form of compensation that companies offer to their employees, typically as a way to incentivize performance and retain talent.
Stock options give employees the right to buy a specified number of shares of company stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. This strike price is usually set at or above the current market price of the stock at the time the options are granted.
One key factor to consider is the vesting period. Stock options usually have a vesting period, which means that employees need to work at the company for a certain amount of time before they can exercise their options. This incentivizes employees to stay with the company and work towards its long-term success.
It’s also important to understand the concept of dilution. When a company grants stock options, it is essentially giving away a portion of its ownership to employees. This can result in dilution of ownership for existing shareholders, as the number of outstanding shares increases.
Read Also: How to Calculate a 7-Day Moving Average in Excel - Step-by-Step Guide
Another factor to consider is the tax implications of stock options. When employees exercise their options, they may be subject to taxes on the difference between the strike price and the market price of the stock at the time of exercise. It’s important for employees to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific tax implications in their jurisdiction.
In summary, understanding the basics of stock options cost involves considering factors such as the strike price, vesting period, dilution, and tax implications. By grasping these fundamental concepts, individuals can gain a better understanding of the financial impact of stock options.
The cost of stock options can be influenced by a variety of factors. Understanding these factors can help investors make informed decisions about whether to buy or sell options.
By considering these factors, investors can better understand and evaluate the cost of stock options and make informed decisions based on their individual investment goals and risk tolerance.
Stock options are a form of compensation that a company can offer to its employees, giving them the opportunity to purchase a certain number of company shares at a predetermined price within a specified time frame.
Stock options are different from regular stocks in that they give the holder the right to purchase shares at a fixed price, while regular stocks are shares already owned by the holder.
The cost of stock options for employees can vary. Typically, the cost is the difference between the exercise price (the price at which the employee can purchase the stock) and the fair market value of the stock on the date of exercise.
Stock options can be a good form of compensation for employees, as they provide the opportunity to benefit from increases in the company’s stock price. However, they also carry risks, as the stock price may decrease, resulting in little or no value for the options.
Companies offer stock options as compensation to attract and retain talented employees. Stock options can align the interests of employees with those of the company’s shareholders, as employees have a financial incentive to help the company succeed.
TradingView Options: Everything You Need to Know If you’re an options trader or are interested in exploring options trading, you may be wondering if …
Read ArticleDoes Bloomberg offer brokerage services? When it comes to financial services, Bloomberg is a name that often comes up. Known for its extensive news …
Read ArticleWhat is the day bar info indicator? The Day Bar Info Indicator is a powerful tool that traders use to monitor the market and make informed trading …
Read ArticleCrude Oil ETF Options: Exploring Your Investment Opportunities Crude oil is one of the most traded commodities in the world, with prices and demand …
Read ArticleWhat is a mini 30 good for? If you’re looking for a versatile and compact rifle, the Mini 30 might be just what you need. The Ruger Mini 30 is a …
Read ArticleIs Binary Options Trading Legit? Binary options trading has gained popularity in recent years as a way to make money online. But the question remains: …
Read Article