Is the Vietnamese Dong expected to appreciate in value?
Will the Vietnamese Dong rise in value? The Vietnamese Dong, the official currency of Vietnam, has been a subject of speculation in recent years …
Read Article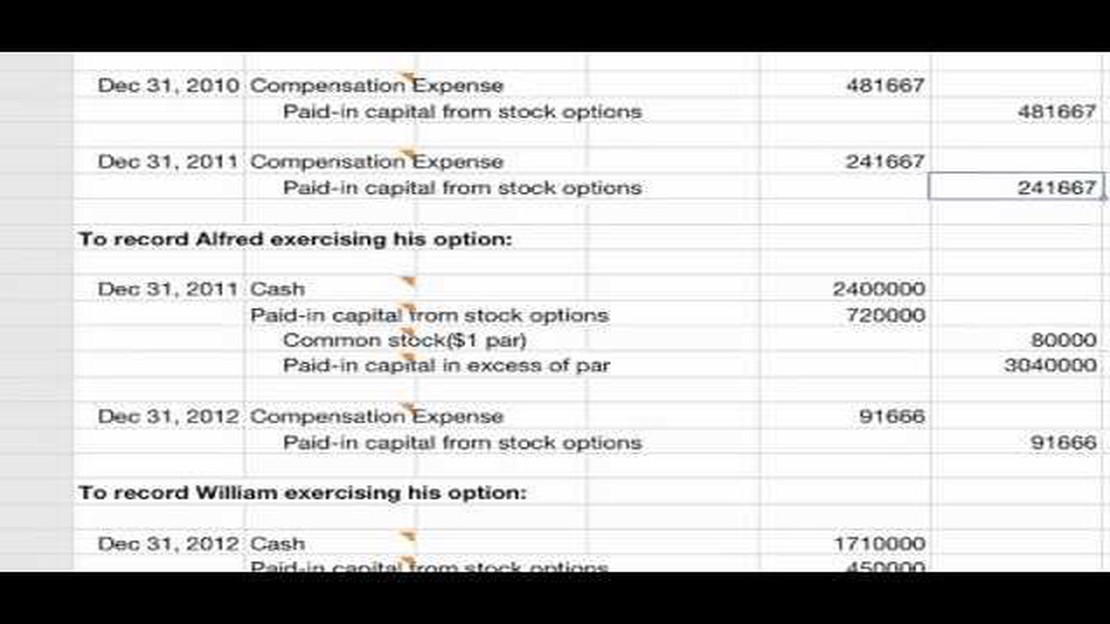
Stock options play a significant role in the world of accounting and finance. They are a form of compensation granted to employees that allow them to purchase company stock at a predetermined price within a specified period. Understanding how to properly record stock options in accounting is essential for maintaining accurate financial records and providing transparency to stakeholders.
When it comes to recording stock options, there are several key steps that need to be followed. Firstly, it is important to determine the fair value of the options at the grant date. This is typically done using an accepted valuation model, such as the Black-Scholes model, which takes into account factors such as the current stock price, exercise price, expected volatility, and time to expiration.
Once the fair value of the options has been determined, it needs to be recorded as an expense on the income statement over the vesting period. This expense is typically recognized on a straight-line basis, although alternative methods, such as accelerated recognition, may be used in some cases. The corresponding entry is a debit to the stock compensation expense account and a credit to the stock options liability account.
As time passes and the stock options vest, employees may exercise their options. When this happens, it is necessary to record the transaction by debiting the stock options liability account and crediting the common stock or additional paid-in capital accounts. The amount recorded is the fair value of the options at the grant date. Any difference between the fair value and the exercise price is treated as compensation expense.
Overall, recording stock options in accounting requires careful attention to detail and adherence to accounting principles. By following the proper procedures, companies can ensure accurate financial reporting and maintain transparency with their stakeholders.
Recording stock options is crucial in accounting because it allows companies to accurately track and value their financial instruments. Stock options are a form of compensation that can have a significant impact on a company’s financial performance and earnings per share (EPS).
By recording stock options, companies can ensure compliance with accounting standards, such as International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards require companies to provide a detailed account of stock option grants and expenses in their financial statements.
Tracking stock options also helps companies evaluate and manage their equity compensation plans effectively. Employers can measure the impact of stock options on their overall compensation expenses and understand the financial obligations associated with granting these options to employees.
Furthermore, recording stock options allows companies to accurately reflect the true value of these assets on their balance sheets. Stock options represent a contractual right to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, and their value can fluctuate based on various factors, such as the underlying stock price and market conditions. By recording stock options, companies can update the fair value of these options regularly and provide more transparent financial statements.
In conclusion, recording stock options in accounting is important for companies to comply with accounting standards, effectively manage equity compensation plans, and accurately reflect the value of these assets in their financial statements. It enables companies to make informed financial decisions and provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of the company’s financial position and performance.
Stock options are a form of compensation that companies offer to employees and other stakeholders. They give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a certain number of company shares at a predetermined price within a specified time frame.
Read Also: What is the FD currency? A comprehensive guide on the FD currency system
Accounting for stock options involves recording the expense and the value of the options granted. This is important because stock options can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements.
When a company grants stock options to employees, it must determine the fair value of the options. This value is typically estimated using a mathematical model, such as the Black-Scholes model, which takes into account various factors such as the current stock price, the exercise price, the expected term of the options, and the volatility of the company’s stock.
Once the fair value of the options is determined, the company records the expense associated with the options over the vesting period. This expense is included in the company’s income statement and reduces its net income. It is also recorded as a liability on the company’s balance sheet until the options are exercised or expire.
When the options are exercised, the company must record the corresponding increase in its share capital and share premium accounts. This reflects the fact that the company is issuing new shares to the option holder.
If an employee forfeits their stock options or if the options expire unexercised, the company may need to reverse the previously recorded expense. This is done by debiting the expense account and crediting the liability account.
It is important for companies to carefully track and account for stock options granted to ensure accurate financial reporting. Failure to do so can result in misstated financial statements and potential legal and regulatory issues.
In conclusion, stock options in accounting involve determining the fair value of the options, recording the expense over the vesting period, and accounting for the exercise or expiration of the options. Proper accounting for stock options is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards.
When it comes to stock options, accurate and transparent financial reporting is essential. As an accounting professional, it is important to understand how to properly record stock options in your financial statements.
Read Also: Exploring the Three Technical Analysis Approaches: A Comprehensive Guide
Stock options are a form of compensation that companies offer to employees or executives, providing them with the opportunity to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. These options can be a valuable incentive for employees and serve as a way to align the interests of employees and shareholders.
When recording stock options in your financial statements, it is important to distinguish between stock options that have already vested and stock options that have not yet vested. Vested stock options are ones that can be exercised immediately, while non-vested stock options have certain conditions or time-based restrictions that must be met before they can be exercised.
To reflect vested stock options in your financial statements, you will need to record an expense in the income statement and create a corresponding liability on the balance sheet. This expense is typically calculated using an option pricing model, such as the Black-Scholes model, which takes into account factors such as the current stock price, strike price, expected volatility, time to expiration, and risk-free interest rate. The liability on the balance sheet represents the future obligation to deliver shares of stock to employees upon exercise of their options.
For non-vested stock options, you do not record an expense in the income statement until the options vest. Instead, you will need to track these options separately and disclose the unvested options in the footnotes of your financial statements. Once the options vest and become exercisable, you will follow the same process as for vested options, recording an expense and creating a related liability.
It is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest accounting standards and regulations related to stock options. Different jurisdictions may have specific rules regarding the accounting treatment of stock options, so it is important to consult with experts or refer to the appropriate accounting guidance to ensure compliance.
Recording stock options accurately and transparently in your financial statements is crucial to providing users of the financial statements with a comprehensive and reliable picture of the company’s financial position and performance. By following the proper accounting procedures and adhering to relevant accounting standards, you can ensure the integrity of your company’s financial reporting.
Stock options are financial instruments that give an individual the right to buy or sell shares of a company’s stock at a specific price within a certain period of time.
Stock options are recorded in accounting using the fair value method or the intrinsic value method. The fair value method requires the company to estimate the fair value of the stock options and record an expense over the vesting period. The intrinsic value method records the difference between the market price of the stock and the exercise price as an expense.
The fair value method and the intrinsic value method are two different approaches to recording stock options in accounting. The fair value method requires the company to estimate the fair value of the stock options and record an expense over the vesting period. The intrinsic value method records the difference between the market price of the stock and the exercise price as an expense.
Properly recording stock options in accounting is important because it allows companies to accurately reflect the value of their stock options on their financial statements. This information is important for investors, regulators, and other stakeholders who rely on accurate and transparent financial information to make informed decisions.
Will the Vietnamese Dong rise in value? The Vietnamese Dong, the official currency of Vietnam, has been a subject of speculation in recent years …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Concept of Exercising in Options Trading Options trading is a popular financial market activity that allows investors to profit from …
Read ArticleExercising Options After IPO: Everything You Need to Know Introduction: Initial Public Offering (IPO) is an exciting time for a company and its …
Read ArticleAn Example of Electricity Trading Electricity trading is a vital part of the modern energy market, allowing businesses and consumers to buy and sell …
Read ArticleMT4 Market Watch: How to Find It and Use It MetaTrader 4, also known as MT4, is one of the most popular trading platforms among forex traders. It …
Read ArticleWhat is Kiwi in forex trading? The New Zealand dollar, also known as the Kiwi, is the official currency of New Zealand and is widely used in …
Read Article