Is Kraken Legit or Not? Unbiased Review and Analysis
Is Kraken legit or not? With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrency, more and more people are turning to crypto exchanges to buy and sell digital …
Read Article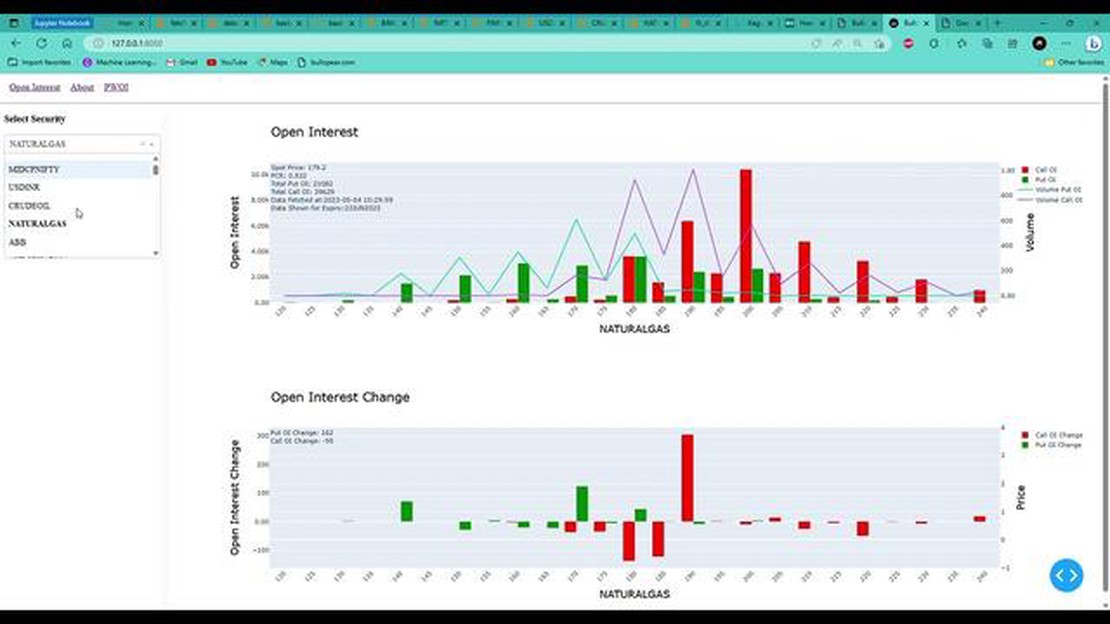
Natural gas is a highly sought-after commodity, used in various industries such as energy production, heating, and transportation. As with any commodity, the market for natural gas is subject to fluctuations and uncertainty. To mitigate these risks, traders and investors turn to futures contracts, which allow them to buy or sell natural gas at a predetermined price on a specified date in the future.
One important metric that traders consider when analyzing natural gas futures is the open interest rate. Open interest refers to the total number of outstanding contracts for a specific commodity, in this case, natural gas. It provides insight into the level of participation and liquidity in the market. A high open interest rate suggests increased activity and a greater number of market participants.
The open interest rate for natural gas futures is influenced by various factors, including supply and demand dynamics, weather patterns, geopolitical events, and government policies. Traders use this information to gauge market sentiment and make informed trading decisions. For example, a significant increase in open interest may indicate growing bullish sentiment, as more traders are entering long positions betting on rising natural gas prices.
Understanding the open interest rate for natural gas futures is essential for traders and investors looking to navigate the complex and volatile energy markets. It provides valuable information about market sentiment, liquidity, and potential price movements. By keeping a close eye on open interest, market participants can gain an edge in their trading strategies and take advantage of profitable opportunities in the natural gas futures market.
Open interest rate is an important concept in the world of natural gas futures trading. It refers to the total number of outstanding contracts that have not been closed or delivered by the end of a trading day.
Open interest is an indicator of market activity and liquidity. It shows the level of interest and participation in a particular futures contract. A higher open interest suggests that there is more buying and selling activity, while a lower open interest indicates less trading activity.
Open interest is calculated by adding up all the long positions and all the short positions in a futures contract. Long positions represent buyers who expect the price of natural gas to rise, while short positions represent sellers who anticipate a decrease in price.
Traders and analysts often use open interest as a tool to gauge the trend and strength of the market. For example, if the price of natural gas is rising and open interest is also increasing, it suggests a bullish trend with increasing market participation. Conversely, if the price is falling and open interest is decreasing, it indicates a bearish trend with decreasing market interest.
Open interest can also be used to identify potential support and resistance levels. When the price of natural gas approaches a level where there is a significant amount of open interest, it can act as a psychological barrier that may cause the price to reverse or stall.
It’s important to note that open interest does not provide information about the direction of future price movements. It is merely a measure of market activity and sentiment. Traders must use other tools and analysis techniques to make informed trading decisions.
Read Also: Discover the Latest Trends in Forex Trading at [Your Website Name]
In conclusion, understanding open interest rate is crucial for those involved in natural gas futures trading. It provides insights into market activity, trends, and potential support and resistance levels. By monitoring open interest, traders can better navigate the dynamic and ever-changing natural gas futures market.
The open interest rate for natural gas futures is influenced by various factors. These factors can provide valuable insights into market trends and help traders make informed decisions. Here are some of the key factors affecting the open interest rate:
1. Market Sentiment: The overall sentiment of traders towards natural gas futures can greatly impact the open interest rate. If traders are optimistic about future price movements, they may increase their open interest, leading to a higher rate.
2. Price Volatility: Higher price volatility can attract more traders to the market, resulting in an increase in open interest. Conversely, if price volatility decreases, traders may reduce their open positions, leading to a decline in open interest.
3. Seasonal Demand: Natural gas is heavily influenced by seasonal demand patterns. During the winter months, when heating demand is high, open interest may increase as traders anticipate potential price spikes. Conversely, during periods of low demand, open interest may decrease.
4. Economic Factors: Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation can influence the open interest rate for natural gas futures. Positive economic forecasts may attract more traders and increase open interest.
Read Also: Open Market Krona to PKR Exchange Rate: All You Need to Know
5. Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations or government policies related to the natural gas industry can have a significant impact on the open interest rate. Traders closely monitor such developments and adjust their positions accordingly.
6. Weather Conditions: Weather forecasts play a crucial role in natural gas trading. Unusually cold or hot weather patterns can lead to increased demand for heating or cooling, respectively. Traders may adjust their open interest based on these weather forecasts.
7. Speculative Activity: Speculators can greatly influence the open interest rate for natural gas futures. Their activity can result in significant changes in open interest, as they take positions based on their expectations of future price movements.
8. Storage Levels: Natural gas storage levels can also impact the open interest rate. Traders closely monitor storage data to assess supply and demand dynamics. High storage levels can lower the open interest rate, while low levels can lead to an increase.
By considering these factors, traders can gain a better understanding of the open interest rate for natural gas futures and make more informed trading decisions.
Open interest rate is the total number of outstanding contracts of a futures or options contract. It represents the total number of contracts that are held by market participants, either long or short, that have not been offset or fulfilled by delivery.
Open interest rate is calculated by taking the total number of contracts that are long and subtracting the total number of contracts that are short. This gives the net open interest rate. It is important to note that each contract can have multiple positions, so if one trader is long 2 contracts and another trader is short 1 contract, the open interest rate would be 3.
Open interest rate is important in natural gas futures trading because it provides insights into the market sentiment and the level of participation in the market. A rising open interest rate suggests that new money is flowing into the market, indicating increased interest or bullishness. On the other hand, a declining open interest rate suggests that money is leaving the market, indicating decreased interest or bearishness. Traders often use open interest rate along with other technical indicators to make trading decisions.
Several factors can affect the open interest rate for natural gas futures. These include changes in market sentiment, new information or news that impacts the supply and demand dynamics for natural gas, changes in weather patterns that affect natural gas consumption, regulatory changes or policy announcements that impact the natural gas industry, and macroeconomic factors that influence the overall investment climate. These factors can all affect the level of participation in the market and therefore impact the open interest rate.
Is Kraken legit or not? With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrency, more and more people are turning to crypto exchanges to buy and sell digital …
Read ArticleAre Binary Options Profitable? Binary options have gained popularity in recent years as a way to make money online. But are they really profitable? …
Read ArticleExponentially Weighted Moving Average in Deep Learning Deep Learning is a constantly evolving field, with new techniques and algorithms being …
Read ArticleWho is FX Leader? FX Leader is a renowned expert in the field of forex trading, providing valuable insights and analysis for traders worldwide. With …
Read ArticleHow to interpret a PSY indicator Understanding and interpreting the PSY (Psychological Price Index) indicator can be a valuable tool for traders and …
Read ArticleWhen to Set Trailing Stop Losses: Expert Tips Setting a trailing stop loss is a popular strategy used by traders and investors in the financial …
Read Article