John Wick Shotgun: What Shotgun Did He Use in the Movies?
Which Shotgun Did John Wick Use? John Wick, the beloved action movie character portrayed by Keanu Reeves, is known for his impressive skills with …
Read Article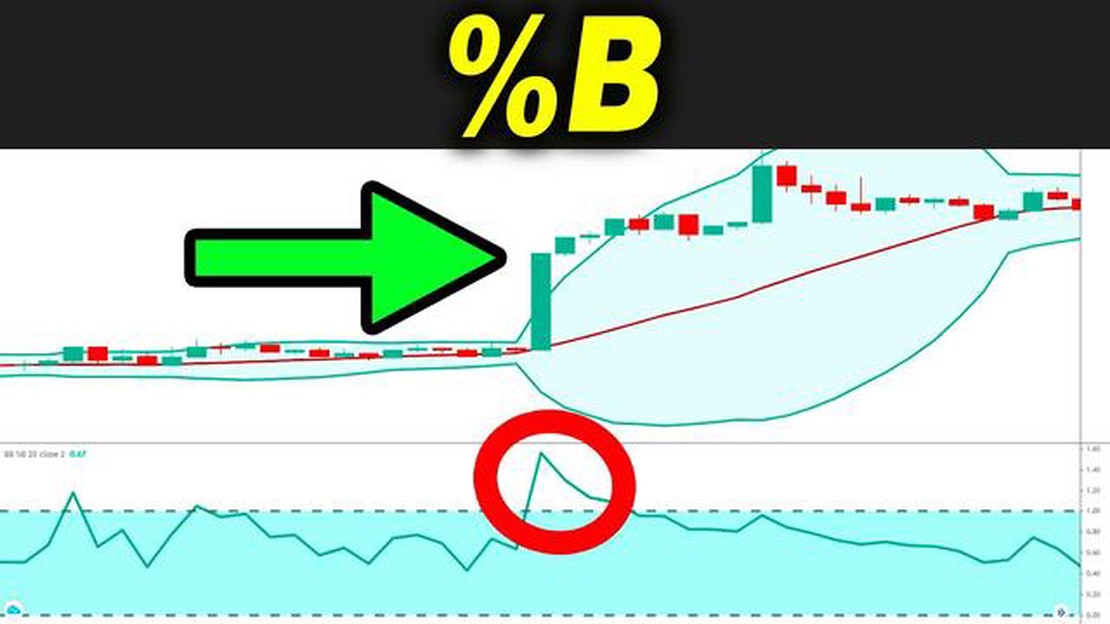
Bollinger Bands are a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to analyze price volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, Bollinger Bands consist of a simple moving average (SMA) and two standard deviation bands placed above and below the SMA. These bands provide a visual representation of price volatility and help traders determine whether prices are overbought or oversold.
Using Bollinger Bands effectively requires an understanding of how they work and how to interpret them. The middle band, the SMA, represents the average price over a specified period. The upper and lower bands are calculated by adding and subtracting a certain number of standard deviations from the SMA. Typically, the standard deviation is set to 2, which means that the upper and lower bands are two standard deviations away from the SMA.
When prices are trading within the Bollinger Bands, it suggests that the market is in a period of low volatility. Conversely, when prices start to move outside of the bands, it indicates a potential increase in volatility and the possibility of a trend reversal. Traders often look for price action to touch or cross the outer bands as a signal to enter or exit trades.
It is important to note that Bollinger Bands should not be used as a standalone indicator. They are most effective when used in conjunction with other technical analysis tools such as trendlines, moving averages, and support and resistance levels. Traders should also consider other factors such as market conditions, news events, and trading volume when making trading decisions.
In conclusion, Bollinger Bands are a valuable tool for traders looking to analyze price volatility and identify trading opportunities. By understanding how to interpret the bands and using them in conjunction with other indicators, traders can increase their chances of success in the market.
Bollinger Bands are a popular technical analysis tool developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s. They are used to measure the volatility of a financial instrument, such as a stock or a currency pair, and to identify potential price trends and reversals. The bands consist of three lines: the middle band, which is a simple moving average, and the upper and lower bands, which are typically set at two standard deviations away from the middle band.
The middle band represents the average price over a specific period, usually 20 days, and serves as a baseline for the upper and lower bands. The upper band is calculated by adding two standard deviations to the middle band, while the lower band is calculated by subtracting two standard deviations. This creates a channel or a band around the middle band, which expands or contracts depending on the volatility of the price.
Traders commonly use Bollinger Bands to analyze price action and identify potential entry and exit points. When the price touches or crosses the upper band, it is considered overbought, implying that the price may be due for a reversal or a pullback. Conversely, when the price touches or crosses the lower band, it is considered oversold, suggesting that the price may be due for a bounce or a rally.
In addition to identifying overbought and oversold conditions, Bollinger Bands can also provide signals for potential trend reversals. When the price moves outside the bands and then returns back inside, it may indicate a reversal in the current trend. This is known as a “Bollinger Band squeeze,” which often precedes a significant price move.
It is important to note that Bollinger Bands are not a standalone trading strategy but rather a tool that can be used in conjunction with other technical indicators and chart patterns. Traders often combine Bollinger Bands with other oscillators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Stochastic Oscillator, to confirm their trading signals.
In conclusion, Bollinger Bands are a versatile technical analysis tool that can help traders identify potential price trends, reversals, and entry and exit points. By understanding how Bollinger Bands are constructed and how they can be interpreted, traders can enhance their trading strategies and make more informed trading decisions.
Bollinger Bands are a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to analyze a security’s volatility and identify potential entry and exit points. They were created by John Bollinger in the 1980s and consist of three lines plotted on a price chart.
Read Also: Is Day Trading Options Halal? Exploring the Perspective in Islamic Finance
The middle line is a simple moving average (SMA), typically set to a 20-day period. The upper and lower bands are positioned a certain number of standard deviations away from the middle line. The standard deviation is a measure of price volatility.
When the price is in a relatively calm period, the Bollinger Bands will contract, and the distance between the upper and lower bands will narrow. In contrast, during periods of high volatility, the bands will expand, indicating wider price ranges.
Read Also: How to Install Currency Strength Indicator in MT4: Step-by-Step Guide
Traders primarily use Bollinger Bands to identify overbought and oversold conditions. When the price touches or exceeds the upper band, it may be a signal that the security is overbought and due for a reversal. Similarly, when the price touches or goes below the lower band, it may indicate an oversold condition and a potential buying opportunity.
Furthermore, Bollinger Bands can be used to spot potential trend reversals. If the price pierces through the upper or lower band and then retreats, it could suggest a trend reversal is imminent.
In addition to these signals, traders often look for patterns such as Bollinger Squeezes, where the bands contract to their tightest point in a long time. This setup indicates a big move could be on the horizon, but it is up to the trader to determine the direction of the potential breakout.
Bollinger Bands can be applied to different chart types and timeframes and are often used in conjunction with other technical indicators and chart patterns to confirm signals and provide a more comprehensive analysis.
Overall, Bollinger Bands are a valuable tool for traders to assess a security’s volatility, identify potential entry and exit points, and spot potential trend reversals. However, like any technical analysis indicator, Bollinger Bands should not be used in isolation and should be used alongside other forms of analysis and risk management techniques.
Bollinger Bands are a technical analysis tool that consists of three lines: a middle band, an upper band, and a lower band. The middle band is usually a simple moving average, while the upper and lower bands are typically two standard deviations away from the middle band. Bollinger Bands are used to measure volatility and identify potential overbought or oversold conditions in a market.
When the price is trading near the upper band, it suggests that the market is overbought, and when the price is trading near the lower band, it suggests that the market is oversold. Traders can also look for price breakouts above or below the bands, as this could indicate a potential trend reversal or continuation.
Some common strategies for using Bollinger Bands include the Bollinger Squeeze, which involves identifying periods of low volatility and anticipating a breakout, and the Bollinger Band Width, which measures the width between the upper and lower bands to gauge the volatility of a market. Traders can also use Bollinger Bands in conjunction with other technical indicators to confirm signals and make more informed trading decisions.
Yes, Bollinger Bands can be used with any financial instrument, including stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices. The concept of Bollinger Bands is based on price volatility, so it can be applied to any market that exhibits price fluctuations.
Some limitations of using Bollinger Bands include false signals during periods of low volatility, as the bands may narrow and give misleading indications. In addition, Bollinger Bands should not be used as a standalone indicator, but rather in conjunction with other technical analysis tools to confirm signals. It is also important to note that Bollinger Bands are a lagging indicator, meaning that they may not provide timely signals for quick entries or exits.
Bollinger Bands are a technical analysis tool that consists of a set of lines plotted two standard deviations away from a simple moving average. They are used to determine volatility, overbought or oversold conditions, and potential price reversals.
Which Shotgun Did John Wick Use? John Wick, the beloved action movie character portrayed by Keanu Reeves, is known for his impressive skills with …
Read ArticleOpening a Foreign Currency Account in Sri Lanka: Everything You Need to Know If you are planning to travel to Sri Lanka or invest in the country, …
Read ArticleHistory of 0DTE Options: Origins and Evolution Options trading has been a popular strategy for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Authorized Shares of Stock Authorized shares of stock are an important concept to understand for anyone looking to invest in a company …
Read ArticleBest Places to Exchange Dollar to Peso in Makati City If you’re visiting Makati, the financial capital of the Philippines, and need to exchange your …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Functioning of Bollinger Bands The Bollinger Band is a technical analysis tool that is widely used by traders to help them make …
Read Article