How Much Do Forex Traders Make in London? Revealing the Earnings Potential
What is the average salary of forex traders in London? When it comes to the world of forex trading, it’s no secret that London is one of the major …
Read Article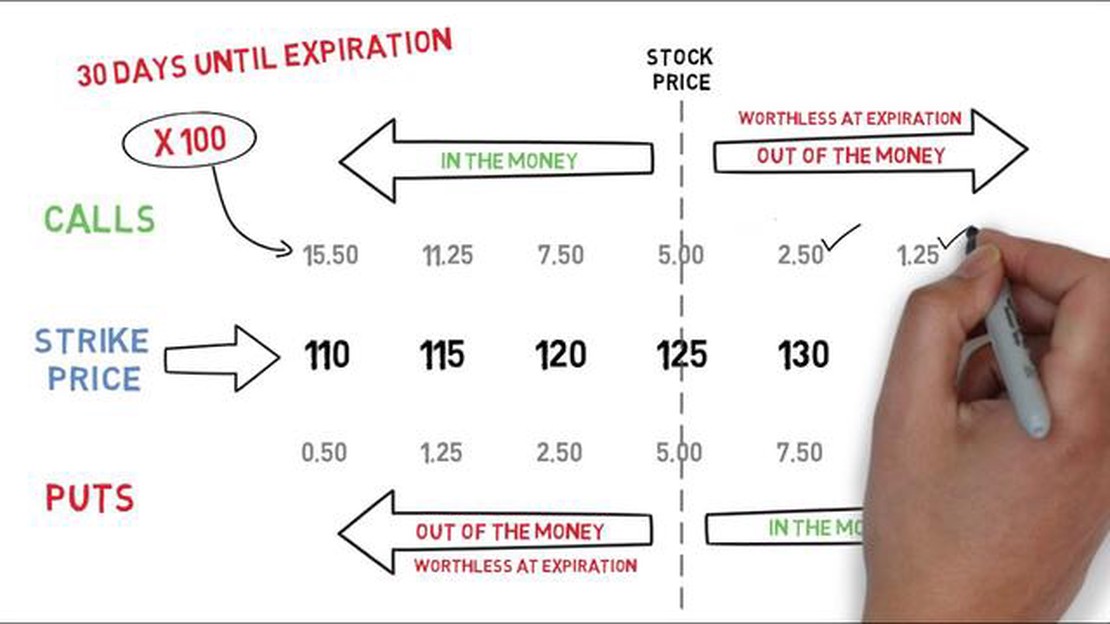
Options are a popular financial instrument that give investors the opportunity to profit from market movements without owning the underlying asset. Whether you’re a professional trader or just getting started, understanding how to calculate option price is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Option pricing involves several factors, including the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time to expiration, and volatility. These variables can make calculating option price seem complex, but with a comprehensive guide, you can master the process.
One widely used model for calculating option price is the Black-Scholes model, named after economists Fischer Black and Myron Scholes. This model takes into account factors such as the risk-free rate of return, the expected volatility of the underlying asset, and the time to expiration to determine the fair value of an option.
Keep in mind that option pricing is not an exact science, and pricing models like the Black-Scholes model have limitations. They are based on certain assumptions about market behavior and may not accurately reflect real-world conditions. Nevertheless, understanding these models can provide valuable insights into option pricing.
In addition to the Black-Scholes model, other models and pricing techniques exist, such as the Binomial Option Pricing Model and the Monte Carlo simulation. These models offer alternative ways to calculate option price and can be useful in different scenarios. It’s important to be familiar with multiple approaches to option pricing to make well-informed investment decisions.
Mastering the art of calculating option price is a valuable skill for any investor looking to navigate the options market. By understanding the key variables and utilizing various pricing models, you can better assess the risk and potential reward of different options contracts. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools necessary to confidently calculate option price and optimize your investment strategy.
An option is a financial derivative that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. Options are commonly used in financial markets for hedging, speculation, and arbitrage purposes.
There are two types of options: call options and put options. A call option gives the holder the right to buy an asset, while a put option gives the holder the right to sell an asset.
When trading options, there are four main components to consider:
Options can be traded on organized exchanges, such as the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), or over-the-counter (OTC) through brokers or dealers.
Understanding options is essential for investors and traders looking to manage risk, generate income, or speculate on price movements. By utilizing options, market participants can take advantage of market volatility and different trading strategies.
1. Underlying Asset Price: The price of the underlying asset is one of the key factors that affects the price of an option. If the price of the underlying asset increases, the price of a call option will generally increase, while the price of a put option will generally decrease.
2. Strike Price: The strike price is another important factor that affects the price of an option. In general, if the strike price is lower than the current price of the underlying asset, the price of a call option will be higher. Conversely, if the strike price is higher than the current price of the underlying asset, the price of a put option will be higher.
3. Time to Expiration: The time remaining until the option’s expiration date also impacts its price. As the expiration date approaches, the time value of an option decreases, which can cause the price to decline, especially if the option is out of the money.
Read Also: Understanding the Settlement Process of FX Options: A Comprehensive Guide
4. Volatility: Volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuations in the underlying asset. Higher volatility generally results in higher option prices, as there is a greater likelihood of the underlying asset moving significantly in price, increasing the potential for the option to be exercised profitably.
5. Interest Rates: Interest rates can also influence option prices. Higher interest rates can increase the cost of carrying the underlying asset, which in turn may increase the price of a call option. On the other hand, higher interest rates may decrease the price of a put option, as the potential benefits of exercising the option may be reduced.
Read Also: Is There a 100% Winning Strategy in Forex?
6. Dividends: If the underlying asset pays dividends, it can affect the price of an option. Typically, the price of a call option will decrease as the ex-dividend date approaches, as the potential benefits of owning the underlying asset decrease. Conversely, the price of a put option may increase as the ex-dividend date approaches.
7. Market Conditions: Overall market conditions, including supply and demand dynamics, can also impact option prices. Changes in market sentiment and investor expectations can lead to fluctuations in option prices, regardless of the specific factors mentioned above.
It’s important to note that these factors are interrelated and can interact with one another to influence option prices. Traders and investors must carefully consider these factors and their potential effects when evaluating and trading options.
Option price is calculated based on a combination of factors, including the current stock price, the strike price, the time until expiration, the volatility of the underlying stock, and the risk-free interest rate. There are several mathematical models that can be used to calculate option prices, including the Black-Scholes model and the binomial model.
The Black-Scholes model is a widely used formula for pricing options. It takes into account the current stock price, the strike price, the time until expiration, the volatility of the stock, and the risk-free interest rate. The formula calculates the theoretical price of a call option or a put option based on these variables.
The binomial model, on the other hand, is a more flexible model that can be used to price options when the underlying stock price is not constant over time. This model divides the time until expiration into a number of smaller time periods and calculates the option price at each period. The final option price is then calculated by summing the discounted values of the option prices at each period.
When calculating option prices, it is important to keep in mind that these prices are theoretical and may not accurately reflect the market price of the option. Factors such as market demand, supply, and liquidity can affect the actual price of an option.
Option price can be calculated using various financial software programs or online calculators. These tools take into account the required inputs, such as the stock price, strike price, time until expiration, volatility, and risk-free rate, and provide an estimated option price based on the selected pricing model. Traders and investors can use these tools to determine the fair value of an option and make informed decisions about buying or selling options.
An option price is the cost of buying or selling an option contract. It represents the monetary value of the rights and obligations associated with the option.
An option price is calculated using various pricing models, such as the Black-Scholes Model. These models take into account factors such as the current stock price, strike price, time to expiration, volatility, risk-free interest rate, and dividends.
Several factors affect option prices, including the current stock price, strike price, time to expiration, volatility, risk-free interest rate, and dividends. These factors can increase or decrease the price of an option.
Sure! Let’s say you have a call option for a stock with a strike price of $50, the current stock price is $55, the time to expiration is 3 months, the volatility is 20%, the risk-free interest rate is 5%, and there are no dividends. Using the Black-Scholes Model, the calculated option price would be $4.28.
What is the average salary of forex traders in London? When it comes to the world of forex trading, it’s no secret that London is one of the major …
Read ArticleIs Crypto Day Trading Profitable? With the rise of cryptocurrencies, day trading has become an increasingly popular investment strategy. Many traders …
Read ArticleWhat are R1, R2, R3, and Pivot Points? In the world of financial markets, trading is a complex and ever-evolving practice. Traders continuously look …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Moving Average Value In finance and statistics, the moving average value is a widely used tool for analyzing data trends over time. …
Read ArticleHow much money should you bring to London? Planning a trip to London can be an exciting experience, but it’s important to consider how much cash you …
Read ArticleThe Results of BNP Paribas 2023 BNP Paribas, one of the world’s largest international banking groups, has recently announced its impressive results …
Read Article