Understanding the Calculation Method for Bollinger Bands
Understanding the Calculation of Bollinger Bands Bollinger Bands are a widely used technical indicator in financial markets. They were created by John …
Read Article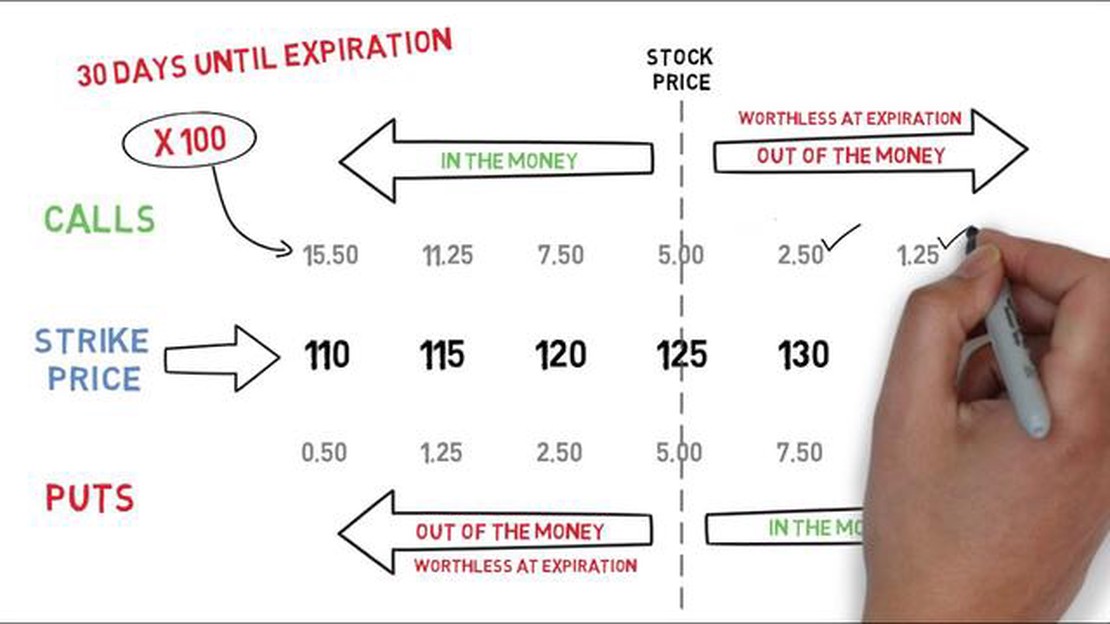
A call option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a specified price within a predetermined period of time. Understanding how to calculate call options is essential for investors and traders who want to make informed decisions in the options market.
To calculate the value of a call option, several factors must be taken into consideration. These include the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price of the option, the time until expiration, the volatility of the underlying asset, and the risk-free interest rate.
One of the most widely used methods for calculating call options is the Black-Scholes model. This mathematical model takes into account the variables mentioned above to determine the fair value of the call option. The Black-Scholes model considers not only the current price of the underlying asset, but also its expected future price movement.
Another method for calculating call options is the binomial model. This model uses a tree-like structure to simulate the different possible outcomes of the underlying asset’s price over time. By calculating the expected value at each node of the tree, the fair value of the call option can be determined.
It is important to note that while these models provide a theoretical value for a call option, market prices may differ due to factors such as supply and demand dynamics. Therefore, it is essential for investors and traders to not solely rely on these calculations, but also consider market conditions and other relevant factors.
In conclusion, calculating call options requires the consideration of various factors and the use of mathematical models such as the Black-Scholes model or the binomial model. These calculations provide a theoretical value for a call option, but market prices may differ. Understanding how to calculate call options is crucial for making informed decisions in the options market.
A call option is a financial contract that provides the holder with the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specified amount of an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time.
Call options are widely used in the financial markets as a way to speculate on the future price movement of an underlying asset or to hedge against potential losses. They are commonly used in options trading, where traders can take advantage of price fluctuations without actually owning the underlying asset.
One of the key features of a call option is the strike price, which is the price at which the holder can buy the underlying asset. If the current market price of the asset is higher than the strike price, the option is said to be “in the money” and the holder can exercise the option to buy the asset at a lower price. If the market price is lower than the strike price, the option is “out of the money” and the holder will not exercise the option.
Read Also: Discover the top forex indicator for MT4 and maximize your trading potential
Another key component of a call option is the expiration date, which is the date on which the option expires. After the expiration date, the option becomes worthless and the holder no longer has the right to buy the underlying asset.
The value of a call option is influenced by several factors, including the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time remaining until expiration, and the volatility of the underlying asset. These factors can affect the likelihood that the option will be in the money at expiration and therefore the potential profitability of the option.
It is important for beginners to understand the basics of call options and how they work before engaging in options trading. By understanding these concepts, beginners can make informed decisions about when to buy or sell call options and can better manage their risk and potential returns in the financial markets.
| Key Concepts | Description |
|---|---|
| Call Option | A financial contract that gives the holder the right to buy an underlying asset at a specific price within a specific time period. |
| Strike Price | The price at which the holder of a call option can buy the underlying asset. |
| Expiration Date | The date on which the call option expires and becomes worthless. |
| Value | The potential profitability of a call option, influenced by factors such as the current price of the underlying asset and the time remaining until expiration. |
A call option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specified quantity of a security or other financial instrument at a specified price (known as the strike price) within a specified period of time. It is one of the two main types of options, the other being a put option.
Call options are typically used in stock market trading. They allow investors to profit from an anticipated increase in the price of the underlying asset. When an investor purchases a call option, they are essentially betting that the price of the underlying asset will rise above the strike price before the option expires.
Read Also: Understanding the Mechanism of ICE Currency Exchange: A Comprehensive Guide
When a call option is purchased, the buyer pays a premium to the seller, which gives them the right to buy the asset at the agreed-upon strike price. The seller, also known as the writer of the option, is obligated to sell the asset if the buyer decides to exercise their option. If the price of the asset does not rise above the strike price during the specified time period, the buyer’s option will expire worthless and they will lose the premium they paid.
Call options can be used for various purposes, including speculation, hedging, and generating income. Investors who believe that a particular stock or other asset will increase in value may choose to buy call options as a way to profit from the anticipated price increase. Traders may also use call options to hedge their positions or to generate income by selling call options and collecting premiums.
| Advantages of Call Options | Disadvantages of Call Options |
|---|---|
| Provide leverage: Call options allow investors to control a large amount of assets with a relatively small upfront investment. | Potential loss of premium: If the price of the underlying asset does not rise above the strike price, the buyer of a call option may lose the premium they paid. |
| Potential for high returns: If the price of the underlying asset increases significantly, the buyer of a call option can make a substantial profit. | Limited timeframe: Call options have expiration dates, which means that the buyer must be correct about the direction and timing of the price movement. |
| Flexibility: Call options can be bought and sold on various financial exchanges, providing investors with flexibility in their trading strategies. | Risk of assignment: If the price of the underlying asset rises above the strike price and the buyer exercises their option, the seller is obligated to sell the asset, which may not always be desirable. |
A call option is a financial contract between two parties, where the buyer has the right but not the obligation to buy an asset at a specified price within a specified time period.
The price of a call option, also known as the option premium, is determined by several factors including the current price of the underlying asset, the strike price, the time to expiration, the volatility of the asset, and the interest rate.
The strike price of a call option is the price at which the buyer has the right to buy the underlying asset if they choose to exercise the option.
The profit on a call option can be calculated by subtracting the initial cost of the option from the difference between the market price of the underlying asset and the strike price at the time of exercise.
The maximum loss on a call option is the initial cost of the option. If the option expires out of the money, meaning the market price of the underlying asset is below the strike price, the buyer will lose the entire premium paid for the option.
Understanding the Calculation of Bollinger Bands Bollinger Bands are a widely used technical indicator in financial markets. They were created by John …
Read ArticleTrading Gold in Binary Options: A Comprehensive Guide Trading gold in binary options can be a lucrative venture, especially for those who are …
Read ArticleBest Brokers for Binary Options Trading Binary options trading has gained popularity in recent years, with many traders looking to capitalize on the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Moving Averages: Examples and Benefits A moving average is a statistical calculation used to analyze data over a certain period of time. …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Foundation of Bollinger Bands Bollinger Bands are a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to help identify possible price …
Read ArticleTrade Forex the Halal Way: A Guide for Muslims Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is a popular financial market where individuals …
Read Article