Best Forex Trading Platforms in Malaysia
Best Forex Trading Platforms in Malaysia Forex trading has grown in popularity in Malaysia, with more and more individuals looking to invest in this …
Read Article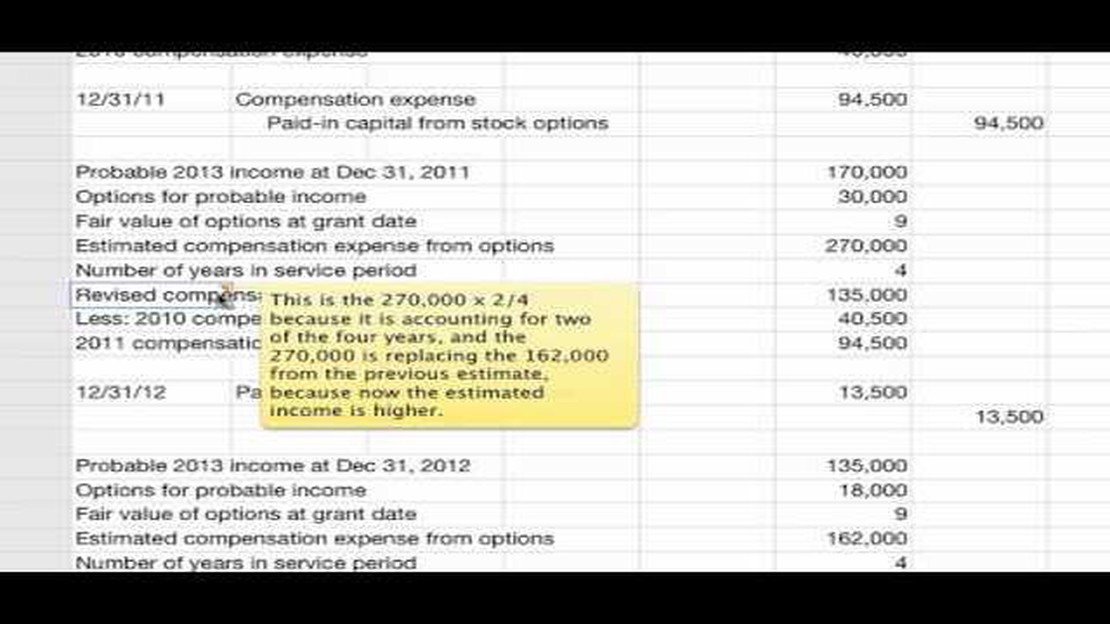
Stock options are a common form of compensation for employees, particularly in the tech industry. They offer employees the opportunity to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. When the stock price goes up, employees can exercise their options, buy the stock at the lower strike price, and then sell it at the higher market price, making a profit. Stock options can have a significant impact on a company’s net income, both positively and negatively.
When employees exercise their stock options and sell the stock, the company is required to record an expense equal to the difference between the strike price and the fair market value of the stock at the time of exercise. This expense is typically spread out over the vesting period, which is the period of time that employees must wait before they can exercise their options. This means that the expense is recognized gradually over time, reducing net income in each reporting period.
While stock options can reduce net income in the short term due to the expense recognition, they can also have a positive impact on net income in the long term. This is because the company’s stock price is likely to increase as employees exercise their options and demonstrate their confidence in the company’s future prospects. A higher stock price can lead to increased market capitalization, attracting investors and potentially boosting the company’s net income.
In addition to the impact on net income, stock options can also affect other financial metrics such as earnings per share (EPS) and diluted earnings per share (Diluted EPS). When stock options are exercised, the number of shares outstanding increases, potentially diluting the ownership stake of existing shareholders. This can result in a decrease in EPS and Diluted EPS, which are measures of a company’s profitability per share.
Stock options are a type of financial instrument that gives individuals the right to buy or sell a specific amount of stock at a predetermined price within a specified time period. They provide the holder with the opportunity to profit from the changes in a company’s stock price without actually owning the stock.
There are two types of stock options: call options and put options. Call options give the holder the right to buy stock at the predetermined price, while put options give the holder the right to sell stock at the predetermined price. The predetermined price is known as the strike price.
Stock options are typically granted to employees as a part of their compensation package. They are also commonly used as an incentive for executives and key employees to align their interests with the company’s performance. By offering stock options, companies can motivate employees to work harder and contribute to the company’s success, as they will directly benefit from an increase in the stock price.
When an employee exercises their stock options, they typically have to pay the strike price to acquire the underlying shares. If the stock price at the time of exercise is higher than the strike price, the employee can then sell the shares at the higher market price, resulting in a profit. However, if the stock price is lower than the strike price, the employee may choose not to exercise the options, as it would result in a loss.
Stock options can have a significant impact on a company’s net income. When employees exercise their options and sell the shares, the company may need to recognize the difference between the strike price and the market price as an expense. This expense is known as the stock-based compensation expense and is subtracted from the company’s net income, thus reducing its profitability.
It is important for investors and stakeholders to understand the impact of stock options on a company’s financial statements and profitability. By carefully analyzing the amount of stock-based compensation expense and its potential effect on net income, investors can make more informed decisions about the company’s financial performance and future prospects.
Stock options can have a significant impact on a company’s net income. Net income is the amount of money a company earns after deducting all expenses, including the cost of stock options. Stock options are a form of compensation that companies offer to their employees, allowing them to purchase a certain number of company shares at a predetermined price. When employees exercise their stock options, the company incurs an expense related to the increase in the value of the shares.
Read Also: Understanding the Enron Employee Stock Purchase Plan: Everything You Need to Know
Since stock options are a form of compensation, they are considered an expense, which reduces the company’s net income. This expense is recorded on the company’s income statement, where it is deducted from revenues to calculate the net income. The amount of the expense depends on the number of stock options exercised and the increase in the value of the shares.
When employees exercise their stock options, they can either hold on to the shares or sell them. If they choose to sell the shares, the company may receive cash from the sale, which can offset the expense recorded on the income statement. However, if the employees hold on to the shares, the company will not receive any cash, and the expense will directly reduce the net income.
It’s worth noting that stock options can also have a positive impact on net income. If the increase in the value of the shares is greater than the expense recorded on the income statement, the company may recognize a gain. This gain can increase the net income and improve the overall financial performance of the company.
In conclusion, stock options have a direct impact on a company’s net income. They are considered an expense and are deducted from revenues on the income statement, reducing the net income. However, if the increase in the value of the shares is greater than the expense, the company may recognize a gain, which can increase the net income. Understanding the link between stock options and net income is crucial for analyzing a company’s financial performance.
Stock options are a common form of employee compensation that companies offer to attract and retain talent. They provide employees with the right to purchase company stock at a predetermined price, known as the exercise price or strike price.
Stock options are typically granted as part of an employee’s compensation package and can be used as a tool to align the interests of employees with those of the company’s shareholders. The idea is that by giving employees an ownership stake in the company, they will be more motivated to work hard and contribute to its success.
Read Also: Discover the Daily Exchange Rate for the Dollar to the Australian Dollar
When an employee exercises their stock options, they can purchase shares of company stock at the strike price. If the stock price has increased since the options were granted, the employee can then sell the shares at a higher price and make a profit. On the other hand, if the stock price has decreased, the employee may choose not to exercise their options, as it would be more expensive than buying shares on the open market.
Stock options can be a valuable form of compensation, particularly for employees of high-growth companies. They offer the potential for significant financial gains if the company’s stock price rises. However, they also come with risks, as the value of the options is tied to the performance of the company and the stock market.
From an accounting standpoint, the impact of stock options on a company’s net income can be complex. When stock options are granted, they are typically recorded as an expense on the company’s income statement. This expense is based on the estimated fair value of the options at the time they are granted.
However, the actual cost of the options to the company will depend on whether or not employees exercise them. If employees choose not to exercise their options or if the stock price decreases below the strike price, the expense recorded on the income statement will not reflect the true cost to the company.
Overall, stock options can be a valuable tool for companies to compensate and motivate their employees. However, they also come with risks and can have a significant impact on a company’s net income. It is important for companies to carefully consider the potential costs and benefits of stock options before implementing them as part of their compensation strategy.
Stock options can impact a company’s net income in two main ways. Firstly, when employees exercise their stock options, it increases the outstanding shares of the company. This, in turn, reduces the earnings per share and can lower the net income. Secondly, when stock options are granted to employees, it creates an expense for the company, known as stock-based compensation expense, which is recognized in the income statement and reduces the net income.
Stock options have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements. When stock options are exercised, it affects the balance sheet by increasing the number of outstanding shares and reducing the retained earnings. It also affects the income statement by creating an expense in the form of stock-based compensation, which reduces the net income. Additionally, it impacts the statement of cash flows as cash is used to purchase the shares when options are exercised.
Stock options can have a negative impact on a company’s earnings per share (EPS). When employees exercise their stock options, it increases the number of outstanding shares, which reduces the EPS. This is because the earnings are now spread over a larger number of shares. As a result, the EPS decreases, and it can give a misleading impression of the company’s profitability.
Stock options have several accounting implications. When stock options are granted to employees, it creates an expense for the company, known as stock-based compensation expense. This expense is recognized in the income statement, which reduces the net income. Additionally, when stock options are exercised, it affects the balance sheet by increasing the number of outstanding shares and reducing the retained earnings. These accounting implications need to be properly recorded and disclosed in the company’s financial statements.
Best Forex Trading Platforms in Malaysia Forex trading has grown in popularity in Malaysia, with more and more individuals looking to invest in this …
Read ArticleDiscovering the Role of 360T in the Financial Industry 360T is a leading provider of trading and workflow solutions for financial institutions, …
Read ArticleHow Long Does iRemit Transfer Take? When using iRemit to transfer money, one of the most common questions asked is how long it takes for the transfer …
Read ArticleCan I fund my forex account with a credit card? When it comes to funding a forex trading account, there are several options available. One popular …
Read ArticleDoes gold and silver move together in forex? Gold and silver are two of the most popular precious metals and have been used as a form of currency and …
Read ArticleCan Forex Day Traders Make Money? Forex, or foreign exchange, day trading involves buying and selling currencies within the same trading day, with the …
Read Article