Best Platforms to Observe Exchange Rates: A Comprehensive Guide
The Best Places to Observe Exchange Rates Exchange rates are a crucial aspect of the global economy. They determine the value of one currency in …
Read Article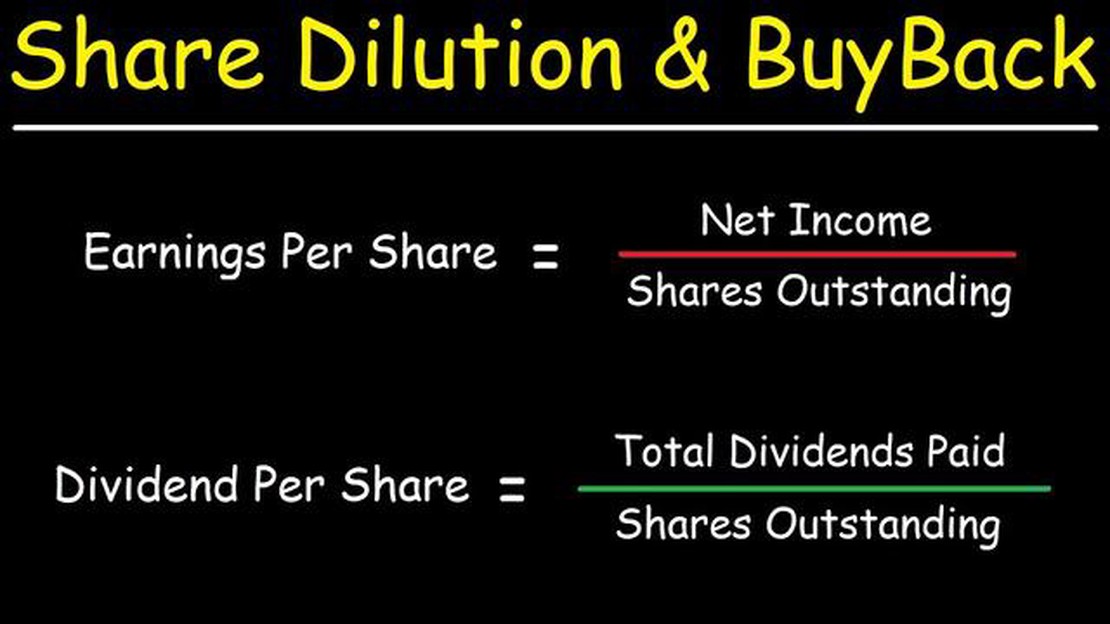
Earnings per share (EPS) is a financial ratio that measures the profitability of a company. It is calculated by dividing the company’s net income by the number of outstanding shares. EPS is an important metric for investors as it helps them assess the company’s profitability and compare it to other companies in the same industry.
Dividends, on the other hand, are the payments made by a company to its shareholders as a portion of its profits. They are usually paid in the form of cash or additional shares. Dividends can impact the EPS of a company in several ways.
First, when a company pays dividends, it reduces its retained earnings. Retained earnings are the portion of a company’s net income that is reinvested back into the business. Since EPS is calculated by dividing net income by the number of outstanding shares, a decrease in net income will result in a lower EPS.
Second, dividends can also impact the number of outstanding shares. When a company pays dividends in the form of additional shares, it increases the total number of outstanding shares. This increase in shares will dilute the EPS, as the earnings will be spread across a larger number of shares.
In conclusion, dividends can have a significant impact on earnings per share. A decrease in net income due to dividend payments will result in a lower EPS, and the issuance of additional shares as dividends will dilute the EPS. Therefore, it is important for investors to consider the impact of dividends when analyzing a company’s financial performance.
Dividends are a form of distribution of a company’s earnings to its shareholders. When a company declares and pays dividends, it affects its earnings per share (EPS).
EPS is a financial metric used to assess a company’s profitability and is calculated by dividing the company’s net income by the total number of outstanding shares. EPS is an important measure for investors as it indicates the company’s profitability on a per-share basis.
When a company pays dividends, it reduces its retained earnings, which are used to calculate the net income. As a result, the net income decreases, leading to a decrease in the EPS. This decrease in the EPS occurs because the company’s earnings are being distributed to shareholders rather than being retained within the business.
| Scenario | Net Income | Shares Outstanding | EPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Dividend | $1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | $1.00 |
| After Dividend | $900,000 | 1,000,000 | $0.90 |
As shown in the table above, before the dividend payment, the company had a net income of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding, resulting in an EPS of $1.00. After deducting the dividend payment from the net income, the company’s net income decreases to $900,000, while the number of shares outstanding remains the same. This leads to a decrease in the EPS to $0.90.
It is important for investors to consider the impact of dividends on a company’s earnings per share when making investment decisions. A decrease in EPS may indicate a decrease in profitability, which could affect the company’s stock price. On the other hand, some investors may see dividends as a positive sign, as it indicates that the company is sharing its profits with shareholders.
In conclusion, dividends have an impact on a company’s earnings per share. When a company pays dividends, it reduces its retained earnings, resulting in a decrease in the net income and subsequently the EPS. Investors should consider the impact of dividends on a company’s profitability and make informed investment decisions based on their own investment goals and risk tolerance.
A dividend is a payment made by a company to its shareholders, usually in the form of cash or additional shares of stock. It is a way for a company to distribute its profits to its investors.
Dividends are typically paid out of a company’s earnings and are usually determined by the company’s board of directors. The board of directors decides on the amount and timing of the dividend payment.
Dividends are often paid on a regular basis, such as quarterly or annually, but some companies may also distribute special dividends or one-time payments.
Read Also: Understanding the Impact of Dilution on Stock Options
Dividends are considered a return on investment for shareholders and can be a significant source of income for investors, particularly those who rely on dividends for retirement or other financial goals.
Investors who own shares of a company’s stock on the dividend record date are eligible to receive the dividend. The dividend is typically paid to shareholders in proportion to their ownership in the company, meaning that shareholders with more shares will receive a larger dividend payment.
Read Also: Do You Have to Buy Options When They Vest? Explained
Dividend and earnings per share (EPS) are both important financial metrics that provide insights into a company’s financial performance and its ability to generate returns for shareholders. Dividend is the portion of a company’s earnings that is distributed to its shareholders, while EPS is a measure of a company’s profitability and represents the earnings generated per outstanding share of stock. The relationship between dividend and EPS can have important implications for investors and the overall valuation of a company.
When a company pays out dividends to its shareholders, it reduces its retained earnings, which in turn impacts EPS. Since EPS is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings by its outstanding shares, a decrease in retained earnings will result in a decrease in EPS, assuming the number of outstanding shares remains constant. Therefore, paying out dividends can lower the EPS of a company.
On the other hand, a higher dividend payout ratio can be seen as a sign of a company’s confidence in its future earnings prospects and can attract more investors. This can potentially drive up the demand for the company’s stock, resulting in an increase in share price. In this case, even though the EPS may decrease due to the dividend payment, the increase in share price can help offset the impact on the overall valuation of the company.
It’s important to note that the relationship between dividend and EPS can vary across different companies and industries. Some companies may prioritize paying out high dividends to attract income-oriented investors, while others may choose to reinvest their earnings into the company’s growth opportunities, resulting in lower dividend payouts and potentially higher EPS. The decision to pay dividends and the amount of dividends paid can be influenced by various factors, including the company’s financial health, cash flow position, growth prospects, and management’s financial strategy.
| Dividend and EPS Relationship | Impact on EPS | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Increase dividend payout ratio | Decrease | Dividend payments reduce retained earnings, which in turn lowers EPS. |
| Decrease dividend payout ratio | Increase | When a company retains more earnings, it can potentially lead to higher EPS. |
| No dividend payments | May vary | Companies that do not pay dividends can use their retained earnings to fund growth initiatives, potentially leading to higher EPS. |
In conclusion, the relationship between dividend and EPS is complex and can depend on various factors. While paying dividends can lower EPS, it can also attract investors and potentially increase the company’s overall valuation. The decision to pay dividends and the impact on EPS should be evaluated in the context of the company’s financial position, growth prospects, and management’s strategic goals.
A dividend is a payment made by a corporation to its shareholders, usually in the form of cash or additional shares of stock. It represents a share of the company’s profits that is distributed to the shareholders.
Dividends can be paid in various ways, such as cash, stock, or property. The most common method of payment is cash, where shareholders receive a certain amount of money for each share they own.
Dividends have a direct impact on earnings per share. When a company declares and pays dividends, it reduces its retained earnings, which in turn reduces the denominator in the earnings per share calculation. As a result, the earnings per share figure increases.
Companies pay dividends as a way to return profits to their shareholders. It can be seen as a form of reward for investing in the company. Paying dividends can also attract more investors, as it signifies that the company is financially stable and has the ability to generate consistent profits.
Dividends can potentially impact the stock price. An announcement of a dividend increase may lead to a rise in the stock price, as it indicates positive financial performance. Conversely, a reduction or elimination of dividends may result in a decrease in the stock price, as it could be interpreted as a negative sign for the company.
A dividend affects earnings per share by reducing the retained earnings of a company. When a dividend is paid to shareholders, it is subtracted from the company’s earnings. This reduction in retained earnings leads to a decrease in the earnings per share, as the same amount of earnings is now distributed among fewer shares.
When a company pays a dividend, the earnings per share decreases. This is because the dividend is paid out of the company’s earnings, reducing the retained earnings. The same amount of earnings is now distributed among fewer shares, resulting in a decrease in the earnings per share.
The Best Places to Observe Exchange Rates Exchange rates are a crucial aspect of the global economy. They determine the value of one currency in …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the 5 Point Moving Average When it comes to analyzing data, there are various techniques that can be employed to identify trends and …
Read Article500 Iraqi Dinar to Indian Rupee Conversion Rate Are you planning a trip to Iraq or India and wondering how much 500 Iraqi dinar is in Indian rupee? …
Read ArticleExploring the 5 20 EMA Crossover Strategy If you are a trader looking to improve your investment strategy, you might want to consider the 5 20 EMA …
Read ArticleIs 1 200 Leverage Good in Forex? In the world of forex trading, leverage is a powerful tool that allows traders to take on larger positions with only …
Read ArticleShould You Use a Stop Loss on Options? Options trading can be a highly lucrative investment strategy, allowing investors to leverage their capital and …
Read Article