5 Ways AI Can Revolutionize Trading
Using AI for Trading: A Comprehensive Guide Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer in various industries, and the field of trading is …
Read Article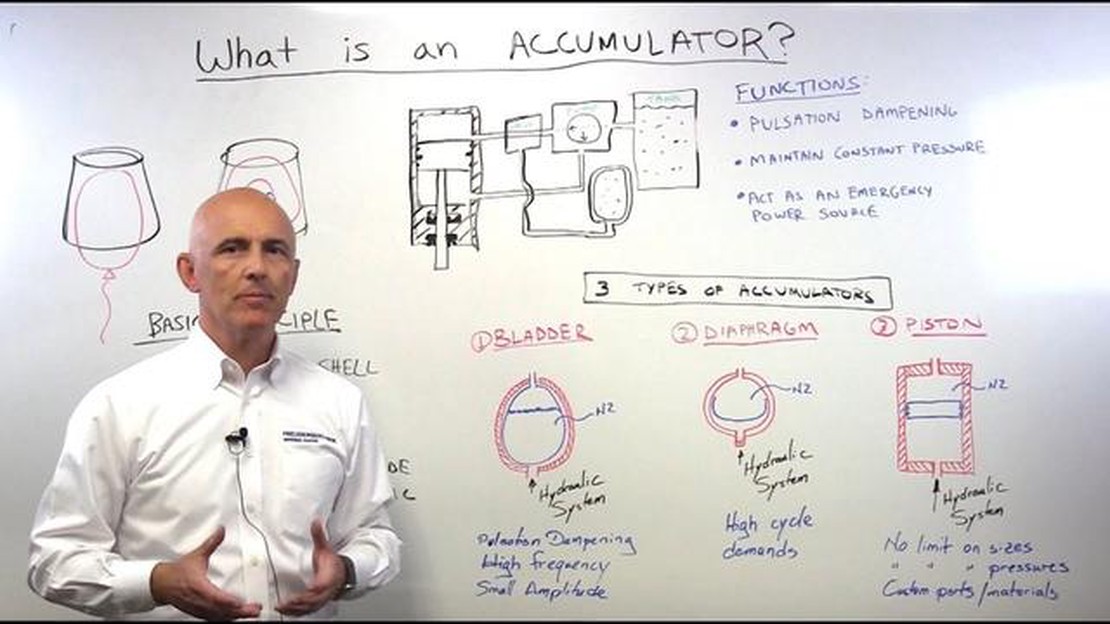
An accumulator is a device or mechanism used to store and accumulate energy in various forms. It is commonly used in a wide range of industrial applications, including hydraulic systems, electrical circuits, and mechanical systems.
There are several types of accumulators available, each designed to suit specific requirements. One example is a hydraulic accumulator, which stores energy in the form of a compressed gas or fluid. It is commonly used in hydraulic systems to enhance system performance, reduce shock and vibration, and store energy for emergency scenarios.
Another example is an electrical accumulator, also known as a battery. It stores energy in the form of chemical potential, which can be converted into electrical energy when needed. Batteries are widely used in portable electronic devices, vehicles, and renewable energy systems.
Mechanical accumulators are also utilized in various applications. One such example is a flywheel accumulator, which stores energy in the rotational motion of a spinning flywheel. This energy can be released whenever needed, providing a stable and consistent power source for machines and equipment.
Accumulators play a crucial role in many industries, offering numerous benefits such as energy storage, enhanced system performance, and emergency backup solutions. Understanding the different types of accumulators and their applications can help in selecting the most suitable option for a particular system or project.
There are various types of accumulators that are used in different industries and applications. Here are some examples:
1. Hydraulic Accumulator: This type of accumulator stores hydraulic energy by using a compressible gas or fluid. It is commonly used in hydraulic systems to store energy and maintain pressure stability.
2. Electrical Accumulator: An electrical accumulator is used in electrical systems to store electric energy. It is typically a battery or a capacitor that stores and releases electrical energy as needed.
3. Steam Accumulator: In steam power plants or industrial processes that use steam, a steam accumulator is used to store excess steam. The stored steam can then be used during peak demand periods or when there is a temporary interruption in steam supply.
4. Thermal Accumulator: This type of accumulator stores thermal energy and is commonly used in heating and cooling systems. It can store excess heat or cold and release it as needed to maintain a comfortable temperature in a building.
5. Gas Accumulator: A gas accumulator is used to store gases under pressure. It is commonly used in gas supply systems to provide a steady flow of gas when the demand exceeds the supply rate.
6. Mechanical Accumulator: This type of accumulator stores mechanical energy and is commonly used in mechanical systems like springs, flywheels, or weight-driven systems. It can store energy and release it as needed to perform mechanical tasks.
7. Gravity Accumulator: In some industrial processes or systems, a gravity accumulator is used to store potential energy. It works by elevating heavy objects to a higher position and then releasing them to convert potential energy into useful work.
These are just a few examples of accumulators, and there are many more types and variations used in different industries and applications.
There are various types of accumulators available in the market, each designed for specific purposes and industries.
1. Hydraulic Accumulator: This type of accumulator uses a hydraulic-based system to store and release energy. It is commonly used in heavy machinery, such as cranes and construction equipment, to provide additional power and smooth out any fluctuations in hydraulic pressure.
2. Pneumatic Accumulator: Pneumatic accumulators store compressed air to be used as a source of energy. They are commonly used in pneumatic systems, such as in automotive applications, to store energy and provide a steady flow of compressed air for various functions.
Read Also: Understanding the Key Differences between Stock Options and Futures Options
3. Thermal Accumulator: Also known as a thermal storage tank, this type of accumulator is used to store excess thermal energy generated by a heating system or a renewable energy source, such as solar panels or a heat pump. The stored energy can be utilized later when there is a higher demand for heating or hot water.
4. Electrical Accumulator: Electrical accumulators, also known as batteries, store electrical energy in chemical form and convert it back into electrical energy when needed. They are widely used in various applications, from portable devices like smartphones and laptops to high-capacity batteries used in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
5. Gravity Accumulator: Gravity accumulators store potential energy in the form of elevated weights or counterweights. When the weights are released, the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, which can be used to perform tasks or generate power. These accumulators are commonly used in applications where large amounts of energy need to be stored and released quickly, such as in hydroelectric power plants.
Each type of accumulator has its own advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications. The choice of accumulator depends on factors such as energy storage capacity, response time, efficiency, and cost.
Read Also: Is Forex Trading Reputable? Uncovering the Truth About Forex Trading
Accumulators have a wide range of applications in various industries. Some of the common applications of accumulators include:
1. Hydraulic systems: Accumulators are commonly used in hydraulic systems to store and release energy. They help control system pressure, absorb pressure surges, and provide emergency power in case of pump failure. Hydraulic accumulators are used in industries such as construction, mining, and manufacturing.
2. Pneumatic systems: Accumulators are also used in pneumatic systems to store compressed air. They help regulate system pressure, absorb pressure variations, and ensure a consistent air supply. Pneumatic accumulators find applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and food processing.
3. Energy storage: Accumulators are used for energy storage in various renewable energy systems. They help store excess energy generated from renewable sources such as solar and wind, and release it when needed. This helps balance the grid and improve energy efficiency.
4. Automotive industry: Accumulators are used in automotive applications such as energy recovery systems, hybrid vehicles, and suspension systems. They help store energy during braking or deceleration, and release it to provide additional power or improve vehicle stability.
5. Marine industry: Accumulators are used in marine hydraulic systems to control ship movements, stabilize cranes, and assist in launching and recovering vessels. They help improve safety, efficiency, and performance in maritime operations.
6. Industrial automation: Accumulators are often used in industrial automation systems to provide quick bursts of energy for pneumatic or hydraulic actuators. This helps improve productivity, precision, and reliability in manufacturing processes.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of accumulators across different industries. With advancements in technology, new applications continue to emerge, making accumulators an essential component in various systems and equipment.
An accumulator is a device that stores and accumulates energy in the form of mechanical or electrical energy.
Some examples of mechanical accumulators include springs, flywheels, and hydraulic accumulators.
Some examples of electrical accumulators include capacitors and batteries.
The different types of hydraulic accumulators include piston accumulators, diaphragm accumulators, and bladder accumulators.
Some common applications of accumulators include energy storage in renewable energy systems, power backup systems, and hydraulic systems in construction equipment and vehicles.
Some examples of mechanical accumulators include springs, flywheels, and weight-loaded systems.
Some examples of hydraulic accumulators include piston accumulators, bladder accumulators, and diaphragm accumulators.
Using AI for Trading: A Comprehensive Guide Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer in various industries, and the field of trading is …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Poi Zone in Forex Trading Trading in the foreign exchange (Forex) market can be a challenging endeavor. With the constant volatility …
Read ArticleIs there an app for Fresh Forex? Are you tired of being tied to your computer when it comes to trading? Look no further than the Fresh Forex App, the …
Read ArticleWhat is Trident trading? Trident Trading is a financial investment strategy that focuses on taking advantage of short-term market fluctuations. It is …
Read ArticleHow to view extended hours on Etrade Trading in the stock market can be a lucrative endeavor, but timing is crucial. If you’re an Etrade user, you may …
Read ArticlePhilippine Peso Forecast: Will it Rise or Fall? The Philippine Peso, the official currency of the Philippines, has been the subject of intense …
Read Article