The Secret Strategy of Forex Trading: Unveiling the Key to Success
What is the Secret Strategy of Forex Trading? Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the largest and most liquid financial market …
Read Article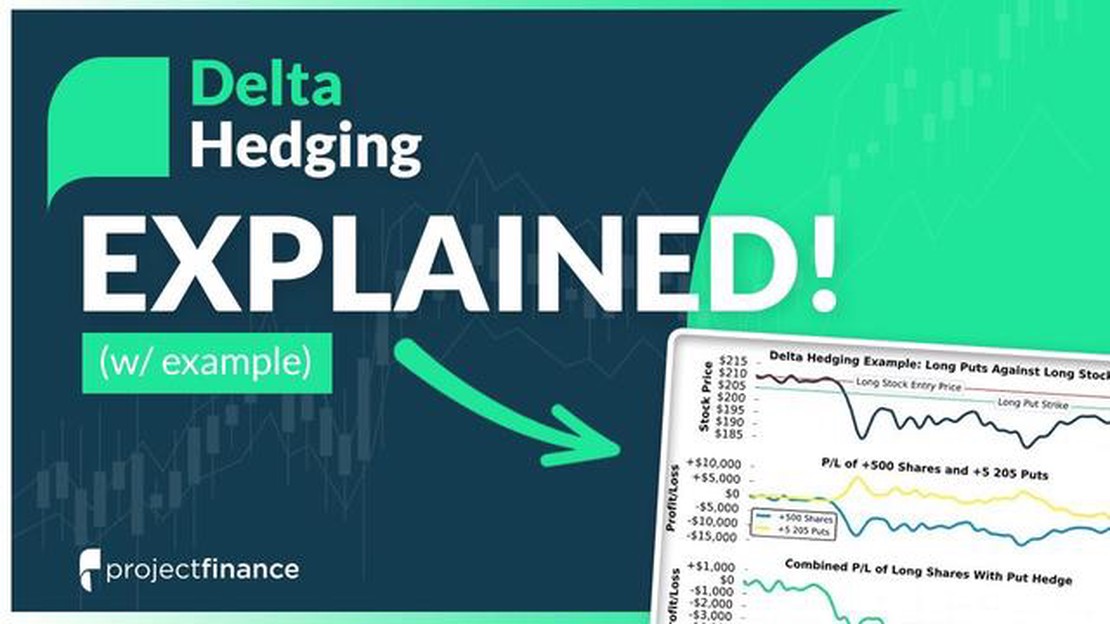
Options are financial derivatives that give their holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. Delta hedging is a risk management strategy used by options traders to neutralize the risk of price fluctuations in the underlying asset.
The delta of an option measures the sensitivity of its price to changes in the price of the underlying asset. Delta is expressed as a value between -1 and 1. A delta of 1 means that the option price will move in perfect correlation with the price of the underlying asset, while a delta of -1 means they will move in opposite directions.
To hedge against price fluctuations, options traders can adjust their portfolio by buying or selling shares of the underlying asset in proportion to the options’ delta. By maintaining a delta-neutral portfolio, traders can reduce the risk of losses due to changes in the underlying asset’s price.
Let’s take an example to illustrate delta hedging. Suppose a trader has purchased call options on a stock with a delta of 0.5. This means that for every $1 increase in the stock’s price, the option price will increase by $0.5. To hedge against potential losses if the stock price falls, the trader will sell 0.5 shares of the stock for every call option purchased. This way, the change in the option price due to the change in the stock price will be offset by the change in the value of the shares.
“Delta hedging allows options traders to manage their risk by maintaining a delta-neutral position, thereby reducing the impact of price fluctuations in the underlying asset. It is an important tool for options traders to protect their investments and optimize their portfolio performance.”
Delta hedging is a risk management strategy commonly used by options traders to offset or minimize the risk associated with changes in the price of the underlying asset. This technique involves taking positions in the underlying asset and its corresponding options in order to create a neutral position, where the overall change in value is minimal regardless of the direction of price movements.
The delta of an option measures the sensitivity of its price to changes in the price of the underlying asset. By understanding the delta value, options traders can estimate the risk exposure of their positions and take appropriate actions to hedge against potential losses.
Delta hedging involves continuously adjusting the position in the underlying asset to maintain a neutral delta. When the delta of an option becomes positive, indicating that the position is exposed to price increases, traders may hedge by buying a certain quantity of the underlying asset. Conversely, when the delta becomes negative, indicating exposure to price decreases, traders may hedge by selling a certain quantity of the underlying asset.
Read Also: Understanding Nonqualified Stock Options: What You Need to Know
The goal of delta hedging is to eliminate or reduce directional risk, allowing traders to focus on other factors that may influence the value of their options positions, such as time decay or volatility. While delta hedging does not provide a perfect hedge, as option prices and delta values can change over time, it can help mitigate the impact of price movements and improve risk management.
Overall, delta hedging options is a complex yet important strategy in options trading. It requires a thorough understanding of the relationship between the underlying asset and its options, as well as ongoing monitoring and adjustment of positions to maintain a neutral delta. By implementing delta hedging techniques, options traders can better manage their risk and potentially improve their overall trading performance.
Delta hedging is a risk management strategy used by investors and financial institutions to reduce or eliminate the risk associated with changes in the price of an underlying asset. It involves making offsetting trades or adjustments to the portfolio in order to maintain a delta-neutral position.
The delta of an option represents the sensitivity of its price to changes in the price of the underlying asset. By maintaining a delta-neutral position, investors can protect themselves against price movements in the underlying asset.
Delta hedging involves continuously adjusting the portfolio by buying or selling the underlying asset or its derivatives. This allows the investor to lock in profits or minimize losses caused by price changes. The goal is to keep the delta of the portfolio as close to zero as possible.
Delta hedging is commonly used in options trading. When an investor purchases an option, they are exposed to the risk of price changes in the underlying asset. By delta hedging, they can reduce this risk by adjusting their position to offset the changes in the option’s delta.
Read Also: Exchange Rate: How much is $1000 Canadian in pesos?
To implement delta hedging, investors need to have access to accurate and up-to-date information about the delta of their options and the underlying asset. They also need to have the ability to execute trades quickly and efficiently.
In conclusion, delta hedging is a valuable risk management strategy that allows investors to reduce or eliminate the risk associated with changes in the price of an underlying asset. By maintaining a delta-neutral position, investors can protect themselves against price movements and increase the stability of their portfolio.
Delta hedging is a risk management technique used in options trading to reduce or eliminate the risk associated with changes in the price of the underlying asset. It involves adjusting the position in the underlying asset in such a way that the overall delta of the options portfolio becomes neutral or zero. Delta represents the sensitivity of the option price to changes in the underlying asset price. By delta hedging, traders can minimize their exposure to directional risk and ensure that the value of their options portfolio remains relatively stable.
Sure! Let’s say an options trader has a portfolio of call options on a stock with a delta of 0.6. This means that for every $1 increase in the stock price, the call options will increase in value by $0.60. To delta hedge the portfolio, the trader would need to sell short 0.6 shares of the underlying stock for every call option in the portfolio. This ensures that the overall delta of the portfolio remains close to zero, reducing the trader’s exposure to changes in the stock price.
Not delta hedging options can expose traders to directional risk, also known as delta risk. If the price of the underlying asset moves against the trader’s position, the value of their options portfolio can significantly decrease. This can result in substantial losses. By delta hedging, traders can minimize this risk and protect their portfolio from adverse price movements. Delta hedging is especially important for options traders who want to maintain a neutral stance towards the market and focus on volatility trading strategies.
Delta hedging can be beneficial for all types of options traders, but its suitability depends on the trader’s objectives and risk tolerance. Delta hedging is particularly useful for traders who want to hedge their directional exposure and maintain a neutral stance towards the market. It can also be useful for traders who want to manage their risk and protect their options portfolio from adverse price movements. However, delta hedging requires constant monitoring and adjustment of positions, which can be time-consuming and may not be suitable for all traders.
What is the Secret Strategy of Forex Trading? Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the largest and most liquid financial market …
Read ArticleForex Market Opening Time on Sunday in the UK The forex market is a decentralized global market for the trading of currencies. It operates 24 hours a …
Read ArticleInvestigating the Reliability of the 200-day Moving Average The 200-day moving average is a widely used technical analysis indicator in the financial …
Read ArticleHow to Create an ESOP Creating an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) can be a beneficial strategy for both business owners and employees alike. An …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Social Trading in Forex: A Comprehensive Guide Forex trading can be an overwhelming and complex world, especially for beginners. But …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Seagull Option Structure In the world of investing, there are many different strategies and structures that traders and investors …
Read Article