Regulation of Forex Trading in South Africa: Find Out Who Oversees the Industry
Regulation of Forex Trading in South Africa Forex trading is a popular investment option for individuals in South Africa, as it offers the potential …
Read Article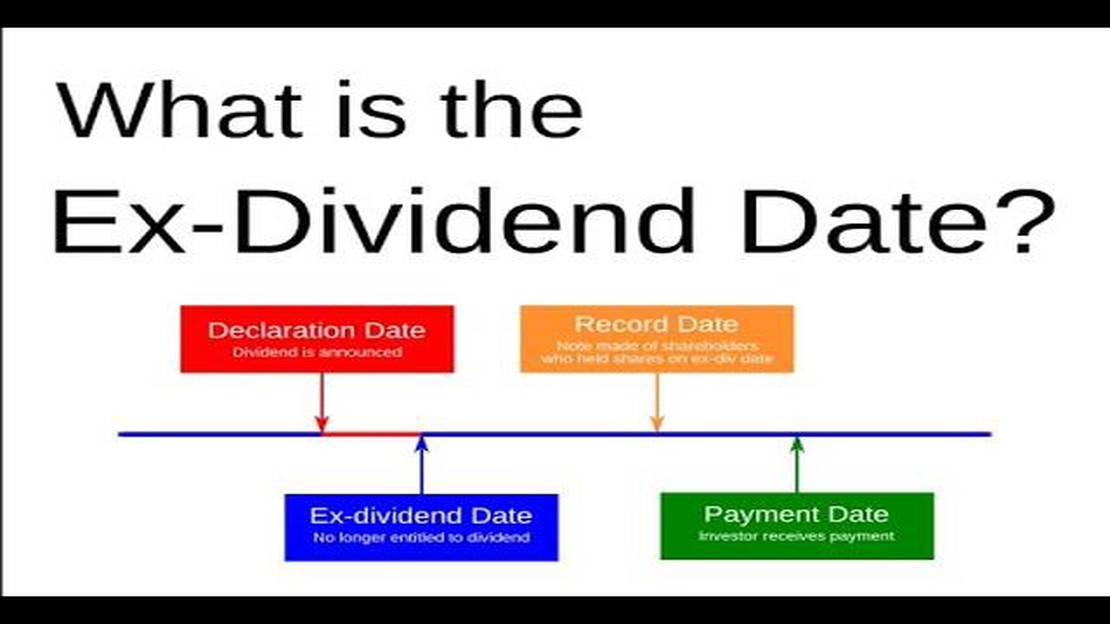
When investing in stocks, one of the important factors to consider is the dividend payment. Dividends are the portion of a company’s profits that are distributed to its shareholders, and they can be a significant source of income for investors. However, deciding whether to sell a stock before or after the ex-dividend date can be a challenging decision.
Before we delve into the best time to sell a stock in relation to the ex-dividend date, let’s first understand what exactly this date represents. The ex-dividend date is the date on which a stock begins trading without the financial benefits of the upcoming dividend. In other words, if you sell a stock on or after the ex-dividend date, you will not receive the dividend payment.
Selling a stock before the ex-dividend date may seem like the logical choice if you want to secure the dividend payment. After all, why sell a stock before receiving the additional income? However, it’s essential to consider the bigger picture and evaluate the potential impact on the stock price.
Some investors believe that the stock price tends to decline by the amount of the dividend payment on the ex-dividend date. This phenomenon is known as the “dividend capture strategy.” Investors who follow this strategy sell their shares right after the ex-dividend date to benefit from the dividend payment while minimizing any potential loss in stock price. However, it’s important to note that this strategy does not guarantee profits and can be risky.
Deciding when to sell a stock can be a crucial part of an investor’s strategy. One factor to consider is the ex-dividend date, which is the date on or after which a buyer of the stock is no longer entitled to the most recently declared dividend payment. Some investors believe that it is best to sell a stock before the ex-dividend date, while others prefer to sell it after.
Selling a stock before the ex-dividend date means that the investor will not receive the upcoming dividend payment. However, there are some potential benefits to selling before the ex-dividend date. By selling before the ex-dividend date, investors may be able to avoid any fluctuations in the stock price that often occur after the dividend is paid. This can be particularly beneficial if the stock has a high dividend yield or if the investor is looking to quickly exit their position.
On the other hand, some investors prefer to sell a stock after the ex-dividend date. This is because the stock price may decrease by the amount of the dividend payment on the ex-dividend date. By waiting to sell until after the ex-dividend date, investors may be able to sell their shares at a higher price and still receive the dividend. However, it is worth noting that this strategy carries some risk, as the stock price may continue to decline after the ex-dividend date.
Ultimately, the decision of when to sell a stock, whether before or after the ex-dividend date, will depend on a variety of factors, including the investor’s individual goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions. It can be helpful for investors to carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks of each approach before making a decision.
Before selling your stock, it is important to carefully consider a few key factors that can impact your decision. These factors include:
Read Also: How to pronounce bulgur: a simple guide for beginners
5. Portfolio Diversification: Consider your overall investment portfolio. Assess if your stock is overweighted compared to other investments. Diversification can help reduce risk, so it might be necessary to sell some shares to maintain a balanced portfolio. 6. Long-term Goals: Determine your long-term goals and investment strategy. Consider whether selling the stock aligns with your investment objectives. If you believe in the company’s growth prospects and have a long-term investment horizon, it might be beneficial to hold onto the stock.
Remember, before making any investment decisions, consider consulting with a financial advisor who can provide personalized advice based on your individual circumstances.
When it comes to investing in stocks, understanding the concept of ex-dividend is crucial. Ex-dividend refers to the period of time during which a stock buyer does not earn the upcoming dividend payment.
Read Also: Understanding the Key Differences Between Warrants and Options
Generally, when a company declares a dividend, it sets a record date. This record date is the date on which an investor must be on the company’s record as a shareholder in order to be eligible to receive the dividend payment. The ex-dividend date, on the other hand, is typically set two business days before the record date. This means that in order to receive the dividend, an investor must buy the stock before the ex-dividend date.
On the ex-dividend date, the stock price usually drops by the amount of the dividend as the company pays out the dividend to the eligible shareholders. This drop in stock price can be attributed to the fact that investors purchasing the stock on or after the ex-dividend date will not be entitled to receive the upcoming dividend payment.
So, if you are planning to sell a stock, it is generally advisable to sell it after the ex-dividend date. By doing so, you can still enjoy the dividend payment and potentially sell the stock at a higher price. However, it is important to note that this strategy may not always guarantee a profit, as stock prices can fluctuate due to various factors.
The ex-dividend date is the date on which the buyer of a stock is not entitled to the upcoming dividend payment. If you buy the stock on or after this date, you will not receive the dividend.
The decision to sell a stock before or after the ex-dividend date depends on various factors. If you sell before the ex-dividend date, you will still receive the dividend as long as you held the stock on the record date. However, selling after the ex-dividend date may result in a lower stock price due to the absence of the dividend, so it’s important to consider the potential impact on the stock’s value.
Stock prices may experience a drop after the ex-dividend date, but it’s not a guarantee. The drop in price can be attributed to investors who bought the stock for the sole purpose of receiving the dividend selling off their shares. However, other market factors can also influence the stock price, so it’s important to analyze the specific stock and market conditions.
Selling a stock before the ex-dividend date does not necessarily result in a higher profit. While you may receive the dividend if you sell before the ex-dividend date, the stock price may also be influenced by other factors. It’s important to consider the overall market conditions, company performance, and future prospects before making a decision to sell a stock.
Regulation of Forex Trading in South Africa Forex trading is a popular investment option for individuals in South Africa, as it offers the potential …
Read ArticleDoes HSBC Work with Brokers? If you’re in the market for a mortgage or other financial product, you may be wondering if HSBC works with brokers. The …
Read ArticleTrading Options Before Earnings: Pros and Cons Earnings season is a highly anticipated time for both investors and traders. It is during this period …
Read ArticleLearn how to code a trading strategy If you’re interested in the world of finance and have a passion for coding, then mastering the art of coding a …
Read ArticleRisks of Credit Spread Options Credit spread options are a popular financial instrument that allow investors to speculate on the movement of credit …
Read ArticleWhat Does RSS Stand For? RSS stands for Really Simple Syndication, which is a way to easily distribute and access website content. RSS allows users to …
Read Article