How to profit from triangular arbitrage and maximize your earnings
Making money from triangular arbitrage: A comprehensive guide Triangular arbitrage is a trading strategy that takes advantage of price differences …
Read Article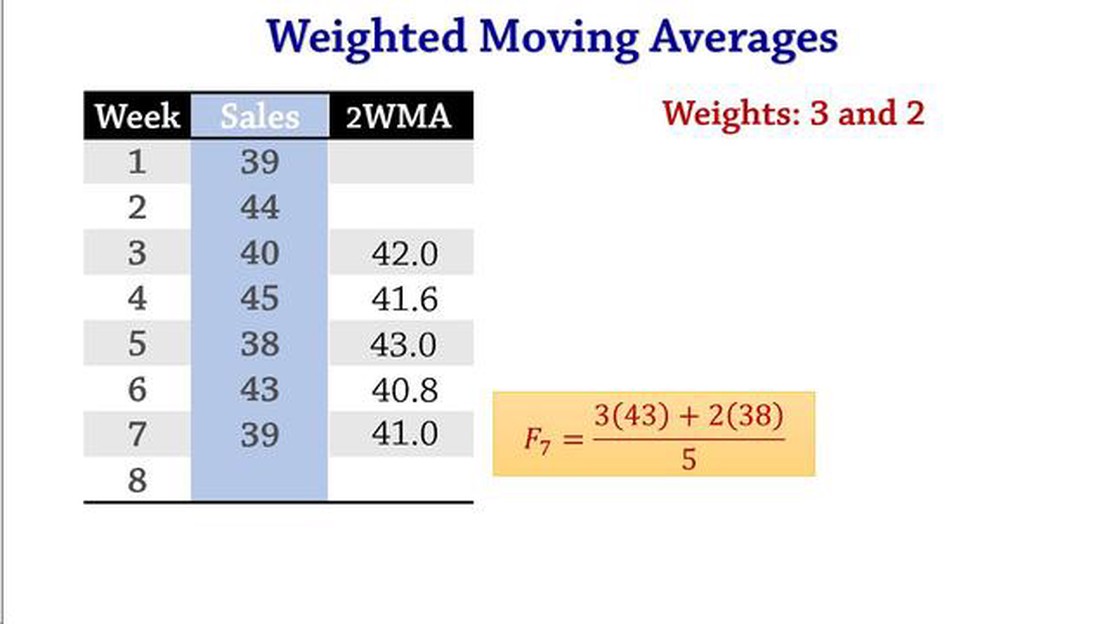
The weighted moving average is a widely used statistical technique that provides valuable insights for analyzing trends and making predictions in various fields. It is a variation of the simple moving average, with the key difference being that the weighted moving average assigns different weights to different data points within the time series. These weights are typically determined based on their significance or relevance to the analysis being conducted.
By assigning different weights to the data points, the weighted moving average places more importance on recent observations, while still considering the overall trend of the data. This makes it particularly useful for smoothing out fluctuations and identifying underlying patterns in the time series.
One of the main advantages of using the weighted moving average is its ability to adapt to changing trends over time. The weights can be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the analysis, allowing for greater flexibility and accuracy in capturing the relevant information. This makes it a powerful tool for forecasting future values and identifying potential turning points in the data.
“The weighted moving average is an effective method for filtering out noise and uncovering the underlying trend in a time series.”
Furthermore, the weighted moving average can be easily combined with other statistical techniques, such as exponential smoothing or trend analysis, to enhance its predictive capabilities. By leveraging the strengths of different methods, analysts can achieve more accurate and reliable forecasts, improving decision-making and planning in various domains, including finance, economics, and operations management.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of the weighted moving average is crucial for data analysts and decision-makers alike. By utilizing this powerful statistical technique, they can gain valuable insights into trends, make informed predictions, and improve the accuracy of their forecasts. The weighted moving average offers a versatile and adaptable approach for analyzing time series data, making it an indispensable tool in the field of data analytics.
A weighted moving average (WMA) is a commonly used statistical method for analyzing and forecasting time series data. It is a variation of the simple moving average (SMA), which assigns equal weights to each data point in the calculation.
In contrast, a WMA assigns different weights to different data points, with the most recent data points given more weight. This means that the WMA places greater emphasis on recent data, making it more responsive to changes in the underlying trend.
The weights assigned to each data point in a WMA are typically determined by a weighted distribution, such as a triangular or exponential distribution. These distributions can be customized based on the specific requirements of the analysis.
One of the main advantages of using a WMA is its ability to provide a more accurate representation of the underlying trend in time series data. By giving greater weight to recent data, the WMA can better capture short-term fluctuations and changes in the data.
Additionally, the WMA can be used to generate forecasts and predictions for future data points. By analyzing the historical trends and patterns in the data, the WMA can be used to extrapolate future values and make informed predictions.
Overall, the weighted moving average is a valuable tool in time series analysis, providing a more accurate depiction of the underlying trend and allowing for better forecasting and prediction capabilities.
A weighted moving average (WMA) is a technical analysis tool used to smooth out price data and identify trends over a specified time period.
Read Also: What Sets MT4 Expert Advisors Apart from MT5 Expert Advisors
Unlike a simple moving average (SMA), which gives equal weight to all data points, a weighted moving average assigns different weights to each data point based on their relative importance. This allows the WMA to be more responsive to recent price changes while still taking into account older data.
The weights assigned to each data point in a WMA are determined by a weighting factor or coefficient. The most commonly used weighting factor is the triangular weighting, where the most recent data point is assigned the highest weight, and the weights decrease linearly as we move back in time.
To calculate a WMA, you multiply each data point by its corresponding weight, sum up these weighted values, and then divide the sum by the total weight. This provides a weighted average value that is used to plot the WMA line on a price chart.
The WMA can be used in various ways in technical analysis. Traders and investors often use it to identify short-term trends and generate buy or sell signals. It can also be combined with other technical indicators to confirm signals and improve the accuracy of trading decisions.
In conclusion, a weighted moving average is a useful tool for smoothing out price data and identifying trends. By assigning different weights to each data point, it provides a more accurate reflection of recent price movements. Traders and investors can use the WMA to make informed decisions and improve their trading strategies.
The weighted moving average is a type of moving average that assigns different weights to each data point in the series, giving more importance to certain values over others.
To calculate the weighted moving average, you need to assign weights to each data point based on its position in the series. Typically, the most recent data points are assigned higher weights, while the older ones have lower weights.
The formula for calculating the weighted moving average is:
Read Also: What does ZMK stand for? Find out the meaning of ZMK
Where:
Each weight is assigned based on the relative importance of the corresponding data point in the series. The weights must add up to 1.
The weighted moving average is useful in smoothing out variations in a time series and highlighting trends over a specific period. The higher weights assigned to recent data points make the weighted moving average more responsive to recent changes in the data.
Traders and analysts often use the weighted moving average to generate trading signals and identify support and resistance levels. By comparing the current value of an asset to its weighted moving average, they can determine if it’s overbought or oversold.
In conclusion, the weighted moving average is a powerful tool in analyzing time series data. By assigning different weights to each data point, it provides a more accurate representation of the underlying trends and helps in making informed decisions based on the data.
A weighted moving average is a type of moving average where the weights assigned to each data point in the calculation are different. In a regular moving average, each data point receives equal weight. The weights in a weighted moving average are typically assigned based on the significance or importance of each data point. This allows a weighted moving average to give more weight to recent data or data that is considered more important.
The weighted moving average is calculated by multiplying each data point by its assigned weight, summing up these weighted values, and then dividing by the sum of the weights. The formula for calculating the weighted moving average is: (Data1 * Weight1 + Data2 * Weight2 + … + DataN * WeightN) / (Weight1 + Weight2 + … + WeightN).
The weighted moving average is commonly used in technical analysis of financial markets to smooth out price data and identify trends. It is also used in forecasting and prediction models to give more importance to recent data and reduce the impact of outliers. Additionally, the weighted moving average can be used in inventory management to forecast demand and in supply chain management to track and predict changes in product demand.
Yes, the weights in the weighted moving average can be adjusted to reflect different factors or preferences. For example, if recent data is considered more important, the weights can be adjusted to give it a higher value. Similarly, if certain data points are believed to be more accurate or reliable, their weights can be increased. The choice of weights depends on the specific application and the analyst’s judgement.
One limitation of the weighted moving average is that it is sensitive to changes in the weights assigned to each data point. Small adjustments in the weights can result in significant changes in the calculated average. Additionally, the weighted moving average may not be suitable for all types of data or time series. For example, in cases where there is a high degree of volatility or unpredictability, a different smoothing method may be more appropriate.
A weighted moving average is a type of moving average that assigns different weights to the values in the time series. The weights are used to give more importance to recent values and less importance to older values.
Making money from triangular arbitrage: A comprehensive guide Triangular arbitrage is a trading strategy that takes advantage of price differences …
Read ArticleUnderstanding and Accounting for Stock Appreciation Rights Stock appreciation rights (SARs) are a form of employee compensation that offers financial …
Read ArticleAccounting for Call Options: A Comprehensive Guide Call options are financial instruments that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to …
Read ArticleGuide to Setting a Pending Order in MQL4 Setting a pending order in MQL4 is an essential skill for any forex trader. A pending order allows you to set …
Read ArticleBest Indicator to Use with Stochastic RSI Stochastic RSI is a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to identify overbought and oversold …
Read ArticleChoosing Between a Long Straddle and a Long Strangle: Which Strategy is Better? When it comes to trading options, there are several strategies that …
Read Article