Is FX Pro Offering Copy Trading? All You Need to Know
Is Copy Trading Available on FX Pro? FX Pro is one of the leading online forex brokers in the industry, known for its innovative trading technologies …
Read Article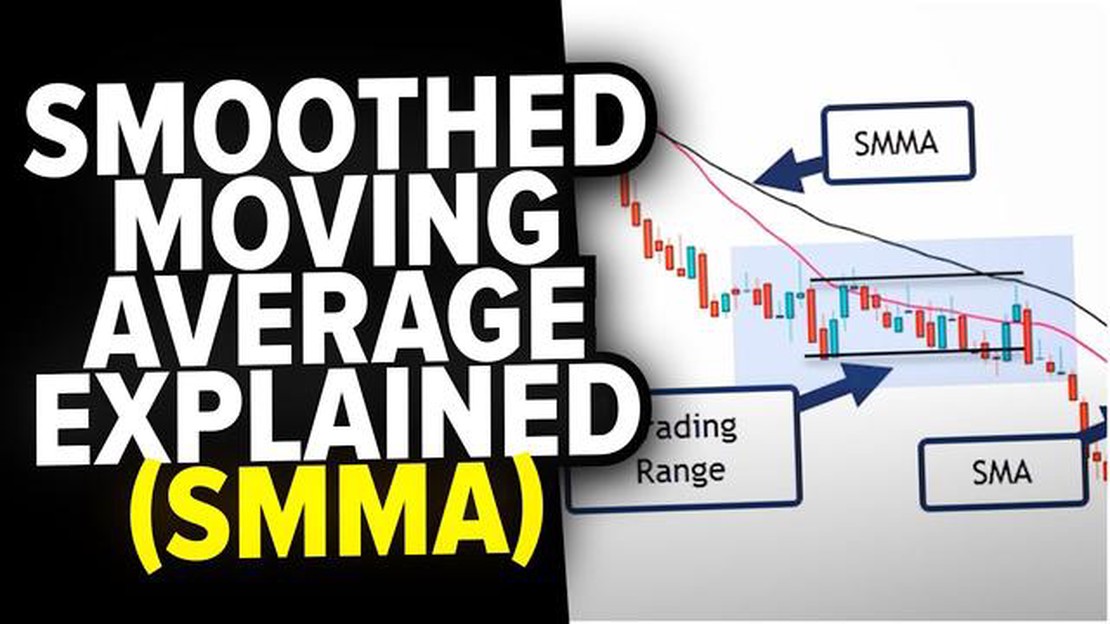
When it comes to financial analysis and forecasting, the smoothed moving average is a popular tool used by analysts and traders. It helps to identify trends and predict future price movements by eliminating short-term fluctuations and noise in the data.
Unlike a simple moving average, which gives equal weight to all data points, a smoothed moving average assigns more weight to the most recent data and less weight to the older data. This makes it more responsive to recent price changes and ensures that it captures the current market sentiment.
One example of a smoothed moving average is the exponential moving average (EMA). The EMA assigns exponentially decreasing weights to the data points, with the most recent data having the highest weight. This results in a smoother line that follows the price trend more closely, without lagging too much behind.
A smoothed moving average can be visually represented on a price chart, with the line plot of the moving average overlaid on the price data. The moving average line smooths out the price fluctuations, allowing traders and analysts to identify the underlying trend more easily. This can help them make better-informed trading decisions and identify potential entry or exit points.
The smoothed moving average is a valuable tool in technical analysis for smoothing out price data and identifying trends. It helps to filter out noise and provides a clearer picture of the market direction. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding and utilizing this indicator can enhance your trading strategies and improve your chances of success.
A smoothed moving average is a type of moving average that reduces the noise or fluctuations often seen in a regular moving average. It is commonly used in technical analysis to identify trends and patterns in financial data.
To calculate a smoothed moving average, you first need a set of data points. The formula for the smoothed moving average differs from that of a simple moving average, as it assigns weights to each data point. The weights decrease exponentially as the data points move further away from the current point.
Here is an example to illustrate the calculation of a smoothed moving average:
The resulting smoothed moving average provides a clearer representation of the underlying trend in the data by reducing the impact of short-term fluctuations. This can be particularly useful in financial analysis and forecasting.
A smoothed moving average is a statistical calculation that is used to analyze time series data. It is often used in finance and economics to identify trends and patterns in data.
The smoothed moving average is derived by taking the average of a set of data points over a specific time period, and then smoothing out the resulting values to create a trend line. This helps to filter out short-term fluctuations and noise in the data, making it easier to identify long-term trends.
For example, let’s say we have a set of stock prices for a particular company over a period of 10 days. To calculate the smoothed moving average, we would take the average of the closing prices for each day over the 10-day period. We would then smooth out the resulting values to create a trend line that represents the overall movement of the stock price over time.
One way to smooth out the data is to use a weighted moving average, where more recent data points are given higher weights. This gives more importance to recent trends and makes the smoothed moving average more responsive to recent changes in the data.
The smoothed moving average is a useful tool for identifying trends and making predictions based on historical data. It helps to remove noise and identify underlying patterns in the data, making it easier to make informed decisions.
To illustrate the concept of a smoothed moving average, let’s consider a set of stock prices over a period of time. Suppose we have the following daily closing prices for a particular stock:
$50, $52, $55, $53, $56, $57, $58, $59, $61, $60
To calculate a smoothed moving average, we can take a simple moving average of a specific period and then apply a smoothing factor to get a smoothed moving average. Let’s say we want to calculate a 3-period smoothed moving average.
First, we calculate the simple moving averages for each period:
(50 + 52 + 55) / 3 = $52.33
Read Also: Understanding Forex Royal: Key Features and Benefits
(52 + 55 + 53) / 3 = $53.33
(55 + 53 + 56) / 3 = $54.67
(53 + 56 + 57) / 3 = $55.33
(56 + 57 + 58) / 3 = $57.00
(57 + 58 + 59) / 3 = $58.00
(58 + 59 + 61) / 3 = $59.33
Read Also: Can I be successful in trading? Tips for achieving trading success
(59 + 61 + 60) / 3 = $60.00
Next, we apply a smoothing factor of our choice, let’s say 0.5, to the simple moving averages:
Smoothed Moving Average for the first period = 0.5 * $52.33 + (1 - 0.5) * $52.33 = $52.33
Smoothed Moving Average for the second period = 0.5 * $53.33 + (1 - 0.5) * $53.33 = $53.33
Smoothed Moving Average for the third period = 0.5 * $54.67 + (1 - 0.5) * $53.33 = $54.00
Smoothed Moving Average for the fourth period = 0.5 * $55.33 + (1 - 0.5) * $54.00 = $54.67
Smoothed Moving Average for the fifth period = 0.5 * $57.00 + (1 - 0.5) * $54.67 = $55.83
Smoothed Moving Average for the sixth period = 0.5 * $58.00 + (1 - 0.5) * $55.83 = $56.92
Smoothed Moving Average for the seventh period = 0.5 * $59.33 + (1 - 0.5) * $56.92 = $58.13
Smoothed Moving Average for the eighth period = 0.5 * $60.00 + (1 - 0.5) * $58.13 = $59.07
The smoothed moving average provides a smoother representation of the underlying data compared to the simple moving average. It helps to reduce the noise and highlights the underlying trend.
A smoothed moving average is a type of moving average that is used to reduce noise and fluctuations in data. It takes into account a set number of periods and calculates the average for that period, then assigns a weight to each period based on its distance from the current period. This weight is used to calculate the average for the current period, resulting in a smoother line.
A smoothed moving average is calculated by taking the simple moving average of a set number of periods, and then applying a weighting factor to each period. The weighting factor is based on the distance of each period from the current period. The moving average is then calculated by summing the weighted values and dividing by the sum of the weights.
An example of a smoothed moving average is the exponential moving average (EMA). The EMA assigns more weight to recent data points and less weight to older data points. This helps to give more emphasis to recent trends and reduce the impact of older data on the average. It is commonly used in technical analysis to analyze stock prices and identify trends.
A smoothed moving average is used instead of a simple moving average because it helps to reduce noise and fluctuations in the data. By assigning weights to each period based on its distance from the current period, a smoothed moving average gives more importance to recent data and less importance to older data. This can help to identify and analyze trends in a more accurate and reliable way.
A smoothed moving average can be illustrated through a line chart that shows the average value of a set number of periods over time. The line will have fewer and smoother fluctuations compared to the original data, and it will help to highlight any overall trends or patterns. This makes it easier to analyze and interpret the data, especially when there is a lot of noise or random fluctuations present.
A smoothed moving average is a calculation used to analyze data points over a certain period of time, reducing the impact of short-term fluctuations. It is commonly used in technical analysis to determine trends and identify potential entry or exit points in the market.
Is Copy Trading Available on FX Pro? FX Pro is one of the leading online forex brokers in the industry, known for its innovative trading technologies …
Read ArticleHow to Promote Forex Affiliate Links As a forex affiliate, your success depends on your ability to effectively promote your affiliate links and drive …
Read ArticleWho owns forex? A closer look at the companies behind the global forex market When it comes to the forex market, one of the most pressing questions is …
Read ArticleWithdrawing Swedish Money on Forex: Is It Possible? Sweden is known for its strong economy and stable currency, making it an attractive destination …
Read ArticleIdentifying Chart Patterns in Forex Trading: A Step-by-Step Guide In the world of forex trading, chart patterns are an essential tool for traders to …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Margin Call in Forex Trading Forex trading involves buying and selling currencies in the foreign exchange market. One of the key aspects …
Read Article