What Causes Underpricing in IPO? Understanding the Phenomenon and its Impact
Factors Contributing to Underpricing in IPO Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) are one of the most common ways for companies to raise capital and enter …
Read Article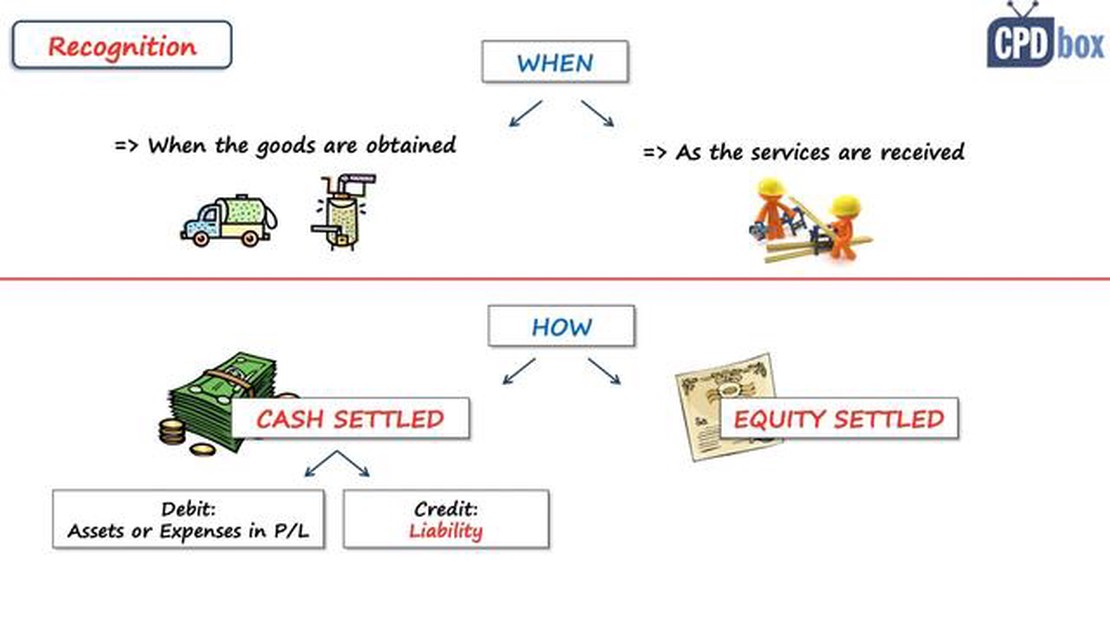
Valuing share options is a complex and critical task for companies that offer these plans to their employees. Under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) 2, companies must accurately calculate the fair value of share options for accounting purposes. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step overview of the valuation process, helping companies navigate the complexities of IFRS 2 and ensure compliance with financial reporting requirements.
IFRS 2 requires companies to recognize share option expenses as part of their financial statements. The fair value of share options must be determined at the grant date and recognized as an expense over the vesting period. In addition to providing a comprehensive explanation of the valuation process, this guide also explores the various factors that can influence the fair value of share options, such as the exercise price, expected volatility, and risk-free interest rate.
Furthermore, this guide covers the different valuation methods that companies can use to determine the fair value of their share options, including the Black-Scholes model, binomial model, and lattice model. Each method is explained in detail, with step-by-step instructions and examples to illustrate the calculations involved. The guide also discusses the key assumptions and inputs required for each valuation method, and how companies can ensure the accuracy and reliability of their valuations.
Valuing share options can be a challenging task, but with the guidance provided in this comprehensive guide, companies can navigate the complexities of IFRS 2 and ensure accurate and compliant financial reporting. Whether you are an accountant, auditor, or financial professional, this guide will serve as a valuable resource in understanding and implementing the valuation requirements of IFRS 2.
IFRS 2 is the International Financial Reporting Standard that deals with share-based payment transactions. It is important because it sets out the accounting treatment for share-based compensation plans, such as share option plans, which are commonly used by companies as a way to incentivize their employees and align their interests with the company’s shareholders.
Share option plans are valued under IFRS 2 using an option pricing model, such as the Black-Scholes-Merton model. This model takes into account various factors, such as the exercise price of the options, the expected term of the options, the volatility of the company’s share price, the risk-free interest rate, and the expected dividend yield. The resulting fair value of the options is then recognized as an expense in the company’s financial statements.
Valuing share option plans under IFRS 2 can be challenging due to several factors. Firstly, there is often uncertainty around the expected term of the options, as employees may exercise their options earlier or later than anticipated. Secondly, estimating the volatility of the company’s share price can be difficult, especially for companies in volatile industries or those with limited historical data. Lastly, determining the appropriate risk-free interest rate and expected dividend yield can require judgment.
The valuation of share option plans has a significant impact on a company’s financial statements. The fair value of the options is recognized as an expense in the company’s income statement, which reduces its reported profits. Additionally, the fair value of the options is recorded as a liability on the company’s balance sheet, which can affect its financial position and financial ratios. Therefore, careful and accurate valuation of share option plans is vital for the transparency and accuracy of a company’s financial reporting.
While the option pricing model, such as the Black-Scholes-Merton model, is the most commonly used method for valuing share option plans under IFRS 2, there are alternative methods that can be used. These include the binomial lattice model and the Monte Carlo simulation. However, these alternative methods may require more sophisticated software and data inputs, and may also be more time-consuming to apply. Therefore, companies should carefully consider the most appropriate method for valuing their share option plans, taking into account their specific circumstances and resources.
IFRS 2 is an international accounting standard that outlines the accounting treatment for share-based payment transactions, including share option plans.
Factors Contributing to Underpricing in IPO Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) are one of the most common ways for companies to raise capital and enter …
Read ArticleWhat is the optimal time of day for trading options? If you’re an options trader, you know that timing is everything. Knowing the optimal time of day …
Read ArticleUnderstanding EFX Trading: A Comprehensive Guide EFX Trading, also known as Electronic Foreign Exchange Trading, is a popular method of trading …
Read ArticleHow much is 1 VGX worth in dollars? Are you interested in knowing the current value of 1 VGX in dollars? Look no further! In this article, we will …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Pullback Entry in Trading In the world of trading and investing, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of market corrections and …
Read ArticleCalculating Stock Options Outstanding Stock options are a popular form of compensation for employees, providing them with the opportunity to purchase …
Read Article