Understanding the ESOP 30% Rule: What You Need to Know
Understanding the ESOP 30% Rule: A Comprehensive Guide Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) have become a popular way for companies to provide their …
Read Article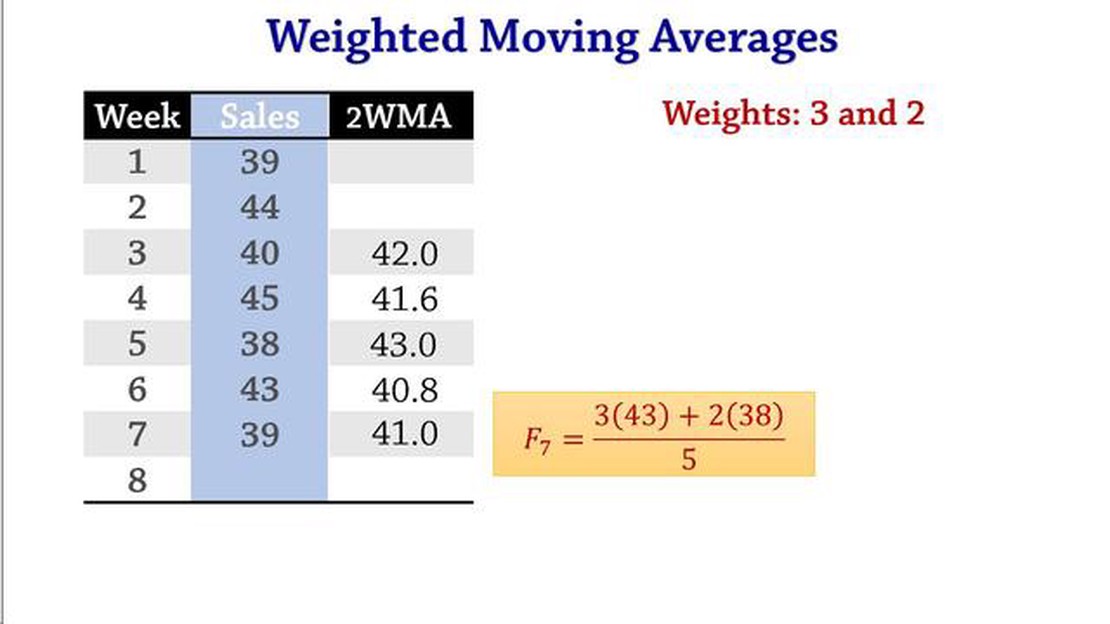
In demand forecasting, weighted moving averages are a commonly used technique to analyze and predict future demand patterns. This method takes into account historical data and assigns weights to different time periods, giving more importance to recent data points.
The concept behind weighted moving averages is that recent data is more relevant in determining future demand trends. By assigning higher weights to recent data, the model can capture and respond to changes in demand more quickly and accurately. This is especially useful in industries with fluctuating demand patterns and short product lifecycles.
Weighted moving averages can be calculated using various methods, such as exponential smoothing or linear regression. The choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the forecasting problem and the nature of the data being analyzed.
One of the advantages of weighted moving averages is their ability to adapt to changing demand patterns. As the weights assigned to different time periods can be adjusted, the model can respond to shifts in demand and incorporate new patterns or trends. This flexibility makes weighted moving averages a valuable tool in demand forecasting and can help businesses make more informed decisions about inventory management, production scheduling, and resource allocation.
In demand forecasting, a weighted moving average is a commonly used technique that allows for the evaluation of past data to predict future demand. Unlike a simple moving average, a weighted moving average assigns different weights to different periods within the data set, giving more importance to more recent data points. This approach is especially useful when there is a need to capture short-term trends and fluctuations in demand, while still considering the overall historical pattern.
The calculation of a weighted moving average involves multiplying each data point by its assigned weight, summing these products, and then dividing the sum by the total weight. The weights are typically assigned based on a predefined pattern or formula, such as an exponential decay function or a linearly decreasing pattern.
For example, if we have a demand data set for a specific product over the course of 12 months, we may assign a weight of 0.3 to the most recent month, 0.2 to the second most recent month, and so on, with the oldest month receiving a weight of 0.1. By multiplying each month’s demand by its assigned weight, summing the products, and dividing by the total weight (in this case, 1), we can calculate the weighted moving average.
| Month | Demand | Weight | Weighted Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 100 | 0.1 | 10 |
| February | 120 | 0.2 | 24 |
| March | 150 | 0.3 | 45 |
| April | 130 | 0.4 | 52 |
| May | 110 | 0.2 | 22 |
| June | 90 | 0.1 | 9 |
| Total | 1.0 | 162 |
In this example, the calculated weighted moving average is 162. This value represents the forecasted demand for the next period, based on the past 12 months of data.
Weighted moving averages can be adjusted to accommodate different business needs, such as focusing on recent data or giving more weight to certain periods of the year. By fine-tuning the weights and adjusting the periods considered, demand forecasters can create models that effectively capture and predict demand patterns, helping businesses make more informed decisions in production planning, inventory management, and resource allocation.
Demand forecasting is a crucial aspect of business planning and inventory management. By accurately predicting the future demand for a product or service, companies can optimize their production processes, minimize costs, and ensure customer satisfaction.
Read Also: Put Spread: Understanding the Bullish and Bearish Aspects
The goal of demand forecasting is to identify patterns and trends in historical data to make informed predictions about future demand. One commonly used technique in demand forecasting is the weighted moving average (WMA) method.
The WMA method assigns different weights to different time periods, reflecting the relative importance of each period in the forecast. The most recent periods usually receive higher weights, as they are considered more relevant to the current market conditions.
Read Also: Discover the biggest loss ever recorded by the Swiss National Bank
The weighted moving average formula is calculated by multiplying each data point by its corresponding weight, summing up these values, and then dividing by the sum of the weights. This calculation provides a weighted average that takes into account the most recent data points.
By using weighted moving averages in demand forecasting, companies can capture short-term fluctuations in demand while still accounting for longer-term trends. This method allows for a more accurate representation of current market conditions and can help companies make more informed decisions about production and inventory levels.
However, it is important to note that demand forecasting is not an exact science. External factors such as seasonality, economic conditions, and competitor actions can all impact demand and disrupt the accuracy of forecasts. Therefore, demand forecasting should be seen as a tool to guide decision-making rather than a guarantee of future outcomes.
In conclusion, demand forecasting plays a vital role in business planning and inventory management. The weighted moving average method is a powerful technique that allows companies to make more accurate predictions by taking into account the most recent data points. While not foolproof, demand forecasting can help companies optimize their operations and stay ahead of market fluctuations.
A weighted moving average is a type of forecasting method that assigns different weights to different periods in the data. These weights determine the importance or significance of each period in the calculation of the forecasted value.
A weighted moving average differs from a simple moving average in that it assigns different weights to different periods, whereas a simple moving average assigns equal weights to all periods. This means that a weighted moving average gives more importance to recent periods, while a simple moving average treats all periods equally.
The purpose of using a weighted moving average in demand forecasting is to give more importance to recent periods and less importance to older periods, as recent periods are generally more indicative of future demand patterns. By assigning different weights, the weighted moving average captures the underlying trends and patterns in the demand data more accurately.
The weights in a weighted moving average can be determined in different ways. One common method is to assign higher weights to more recent periods and decreasing weights to older periods. The specific weights can be determined based on factors such as the judgment of the forecaster or statistical analysis of the data.
The advantages of using a weighted moving average in demand forecasting include the ability to give more importance to recent periods, which allows for better capturing of short-term trends and seasonality. Additionally, a weighted moving average can provide a smoother forecast compared to a simple moving average, as it adjusts for the changing nature of the demand patterns.
A weighted moving average is a forecasting technique that assigns different weights to different time periods. These weights are used to calculate the average, giving more importance to recent data.
Understanding the ESOP 30% Rule: A Comprehensive Guide Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) have become a popular way for companies to provide their …
Read ArticleIs Binary or Forex Trading More Risky? Investing in financial markets can be a lucrative endeavor for those who are willing to take on some risk. Two …
Read ArticleMastercard Currency Conversion Fees: How Much Does It Charge? When it comes to using your Mastercard for international transactions, one thing you …
Read ArticleIs Investopedia stock simulator safe? One of the most important aspects of trading stocks is learning how to manage risk. The Investopedia Stock …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Price Action after an Inverted Hammer Candlestick Pattern An inverted hammer pattern is a popular candlestick pattern used in …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Williams %R Indicator: A Powerful Technical Analysis Tool When it comes to trading and investing, having the right tools and …
Read Article