When Does the Global Forex Market Open in India? Find Out Here!
When does the global forex market open in India? As a global financial hub, India plays a significant role in the forex market. Traders and investors …
Read Article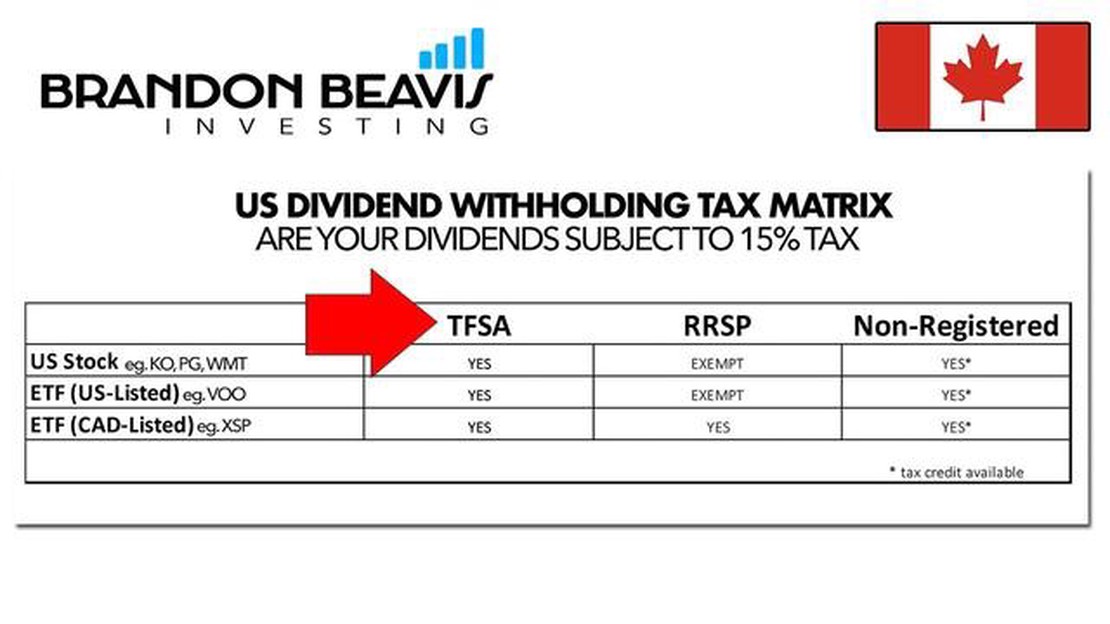
Investing in shares can be a profitable venture, but it is important to understand the various taxes that may be associated with your investment. One such tax is the withholding tax on shares in the United States. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with an in-depth understanding of what US withholding tax is, how it is calculated, and what steps you can take to minimize its impact on your investments.
US withholding tax is a tax imposed by the United States government on certain types of income, including dividends and interest paid to non-US residents. When it comes to shares, US companies are required to withhold a portion of the dividends paid to foreign investors as tax. This withholding tax is deducted at the source, which means it is taken out of the dividend payment before it reaches the investor.
The rate of withholding tax on shares in the US can vary depending on the investor’s country of residence and the tax treaty between that country and the United States. Generally, foreign investors are subject to a 30% withholding tax on dividends from US stocks. However, this rate can be reduced or eliminated if a tax treaty between the investor’s country of residence and the US allows for a lower rate or exemption. It is essential to consult the relevant tax treaty or seek professional advice to determine the applicable rate.
To minimize the impact of US withholding tax on your investments, there are several strategies you can employ. One approach is to invest in tax-efficient vehicles such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that hold a diversified portfolio of shares. These funds may have lower dividend yields, which can result in reduced withholding tax. Additionally, holding shares through tax-advantaged accounts, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs), can also help reduce or defer US withholding tax.
Bottom Line: Understanding US withholding tax on shares is crucial for investors looking to maximize their returns. By familiarizing yourself with the applicable rates and exploring tax-efficient investment strategies, you can effectively navigate the complexities of US tax regulations and optimize your investment portfolio.
US withholding tax refers to the tax that is deducted or withheld from certain types of income, such as dividends and interest, before it is paid to non-US residents or foreign entities. This tax is collected by the US government in order to ensure that taxable income earned within the US by foreign individuals or entities is reported and taxed appropriately.
The withholding tax applies to a wide range of income sources, including but not limited to:
The tax is typically deducted by the payer of the income, such as a US corporation or financial institution, before the payment is made to the non-US resident or foreign entity. The rate at which the withholding tax is applied can vary depending on the type of income and the tax treaty between the US and the country of the recipient.
US withholding tax can have an impact on investors who hold US shares, as it affects the amount of dividends they receive. Non-US residents and foreign entities may be subject to a higher withholding tax rate compared to US residents. However, tax treaties between the US and certain countries may provide reduced or exempt rates for qualified individuals or entities.
Understanding US withholding tax is crucial for investors and foreign entities who receive income from US sources, as it determines the amount of tax that will be deducted from their payments. It is important to consult with a tax professional or advisor to ensure compliance with US tax regulations and to optimize tax planning strategies.
Read Also: Understanding the World Trade System: A Comprehensive Guide
The US withholding tax on shares is a tax that is deducted at source on income derived from US sources. It applies to non-US individuals or entities who receive dividend or interest payments from US corporations, as well as to certain capital gains from the sale of US assets.
The withholding tax rate on dividends is generally 30%, but it can be reduced or eliminated in certain cases through tax treaties between the US and other countries. To claim a reduced rate, the recipient must provide the payer with a valid Form W-8BEN or similar documentation.
The withholding tax on interest income is generally 30% for non-US individuals or entities, unless a reduced rate applies under a tax treaty. Interest income is generally not subject to US withholding tax if it is effectively connected with a US trade or business.
When it comes to capital gains, the US imposes withholding tax on non-US investors who sell shares in US companies. The withholding tax rate is generally 15%, unless a reduced rate applies under a tax treaty. However, if the non-US investor has a permanent establishment in the US, the gain may be subject to regular US income tax instead of withholding tax.
Read Also: Is Plus500 a Trustworthy Trading Platform? Find Out Here!
It is important to note that US withholding tax is deducted by the payer, which is usually the US custodian or broker. The tax is then remitted to the IRS on behalf of the non-US recipient. Non-US individuals or entities can claim a refund of any excess withholding tax by filing a US tax return.
Overall, understanding US withholding tax on shares is crucial for non-US investors as it can significantly impact the returns on their investments. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure compliance with US tax regulations and to optimize tax efficiency.
| Income Type | Withholding Tax Rate | Conditions and Exceptions |
|---|---|---|
| Dividends | 30% (potentially reduced through tax treaties) | Valid Form W-8BEN or similar documentation required |
| Interest | 30% (potentially reduced through tax treaties) | Generally not subject to withholding tax if effectively connected with US trade or business |
| Capital Gains | 15% (potentially reduced through tax treaties) | May be subject to regular US income tax if non-US investor has a permanent establishment in the US |
US withholding tax on shares is a tax that is imposed by the US government on dividends and interest income earned by foreign investors in US stocks. It is deducted at the source before the investor receives the payment.
The US withholding tax on shares is typically 30% of the dividends and interest income earned by foreign investors. However, the rate may be reduced or eliminated altogether depending on the tax treaty between the investor’s home country and the US.
Yes, the US withholding tax on shares is refundable in certain cases. If the investor’s home country has a tax treaty with the US that provides for a reduced rate or exemption from withholding tax, the investor can claim a refund of the excess tax withheld.
There are a few ways to reduce the US withholding tax on shares. One way is to invest in US stocks through a tax-efficient structure, such as a retirement account or a tax-exempt entity. Another way is to take advantage of tax treaty benefits by providing the necessary documentation to the withholding agent.
Yes, there are some exemptions from the US withholding tax on shares. For example, dividends paid by US corporations to foreign corporations are generally exempt from withholding tax. Additionally, certain types of interest income, such as portfolio interest, may also be exempt.
When does the global forex market open in India? As a global financial hub, India plays a significant role in the forex market. Traders and investors …
Read ArticleCurrency Exchange at Sydney Airport: Everything You Need to Know When traveling abroad, it’s important to understand how to handle your currency …
Read ArticleThe Indus Valley Trade Economy: A Comprehensive Overview The Indus Valley civilization, which flourished from 2600 to 1900 BCE, was one of the world’s …
Read ArticleWill copper prices rise again? The price of copper has been subject to significant volatility in recent years, with sharp fluctuations in response to …
Read ArticleMy Life Transformed by Forex Trading Have you ever wondered if there is a way to break free from the mundane 9-5 routine and achieve both personal …
Read ArticleCan a Raspberry Pi run a trading bot? The Raspberry Pi is a versatile and affordable single-board computer that can be used for a wide range of …
Read Article