Options vs. Futures: Understanding the Difference for Beginners
Options vs. Futures: A Beginner’s Guide to the Differences Options and futures are both popular financial instruments that can be used for speculative …
Read Article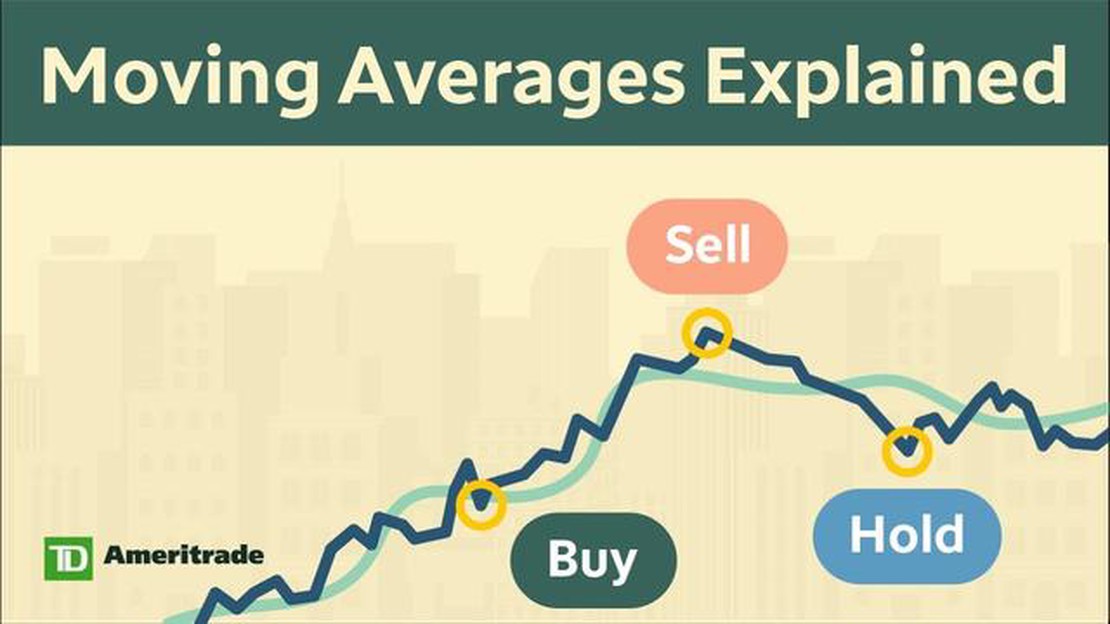
The weighted moving average is a commonly used tool in technical analysis that helps traders and investors make sense of price trends. It is a variation of the simple moving average that assigns different weights to different data points, giving more importance to recent data.
The weighted moving average is calculated by multiplying each data point by a weight factor, which is determined by the trader or investor based on their analysis and preference. The weighted moving average gives more weight to recent data points, making it more responsive to price changes and trends.
Traders and investors use the weighted moving average to identify the direction and strength of price trends. By looking at the slope and position of the weighted moving average line on a price chart, they can determine whether the price is trending upwards, downwards, or sideways. This information can help them make informed decisions about buying or selling assets.
The weighted moving average is particularly useful when applied to longer time frames, as it helps smoothen out short-term price fluctuations and noise. By focusing on the overall trend rather than individual price movements, traders and investors can reduce the impact of market volatility and make more accurate predictions about future price movements.
A weighted moving average is a type of moving average where different weights are assigned to the data points in the time series. Unlike a simple moving average where all the data points have equal weights, a weighted moving average assigns higher weights to more recent data points and lower weights to older data points.
The weights assigned to the data points can vary depending on the specific requirements of the analysis. Typically, the weights are assigned in such a way that the most recent data points have the highest weight, gradually decreasing as we move further back in time.
By giving more importance to recent data points, a weighted moving average can provide a more accurate representation of the underlying trend or pattern in the time series, especially if there are sudden fluctuations or outliers in the data.
The calculation of a weighted moving average involves multiplying each data point by its corresponding weight, summing up the results, and then dividing by the sum of the weights. This weighted average value is then used as the moving average for the given time period.
Weighted moving averages are commonly used in finance, economics, and other fields where the recent data points are considered more relevant or informative than the older ones. They can be used to smooth out the noise in the data, identify trends, and make predictions.
Overall, a weighted moving average is a powerful tool for analyzing time series data, providing a more accurate and timely representation of the underlying patterns and trends.
Read Also: Understanding the Fair Value Method of Stock Options: A Comprehensive Guide
The weighted moving average is an important tool in data analysis and forecasting. It allows you to give more weight to recent data points while still considering older data points, making it a more accurate representation of trends and patterns in the data.
One of the key advantages of using the weighted moving average is that it can help smooth out random fluctuations in the data, which can be particularly helpful when dealing with noisy or volatile datasets. By assigning different weights to different data points, you can give more importance to the data that is more relevant or recent, while still incorporating the historical information.
The weighted moving average is widely used in various fields such as finance, economics, and stock market analysis. It is particularly useful for tracking and predicting short-term trends, as it can provide a more responsive indication of changes in the data compared to other smoothing techniques.
Another reason why the weighted moving average is important is its simplicity and ease of use. It is a straightforward calculation that can be easily applied to a wide range of datasets. This makes it accessible to beginners in data analysis and forecasting, as well as for those who may not have access to more advanced statistical tools.
Overall, the weighted moving average is an essential tool for anyone looking to analyze and forecast data. By incorporating both recent and historical information, it provides a more accurate representation of trends and patterns, while also helping to smooth out random fluctuations. Whether you are analyzing financial data or trying to predict future trends, the weighted moving average can be a valuable tool in your toolkit.
To calculate the weighted moving average, you need to follow these steps:
Here is an example to illustrate the calculation:
| Data Point | Weight | Weighted Value |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 15 | 0.3 | 4.5 |
| 20 | 0.5 | 10 |
Read Also: Is RadioShack Involved in Cryptocurrency? | Exploring the Connection
In this example, the data points are 10, 15, and 20, and the corresponding weights are 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5, respectively. The weighted values are calculated by multiplying the data points with their corresponding weights. The sum of the weighted values is 2 + 4.5 + 10 = 16.5. The sum of the weights is 0.2 + 0.3 + 0.5 = 1. Finally, the weighted moving average is obtained by dividing the sum of the weighted values by the sum of the weights: 16.5 / 1 = 16.5.
This calculation can be performed for any number of data points, and the weights can be adjusted according to your requirements. The weighted moving average is a useful tool for smoothing out noisy data and identifying trends over a specific period of time.
A weighted moving average is a type of moving average that assigns different weights to different data points. It gives more importance, or weight, to recent data points and less importance to older data points.
A weighted moving average is calculated by multiplying each data point by a weight, summing up these products, and then dividing the sum by the sum of the weights. The weights are typically assigned in a way that gives more weight to recent data points.
A weighted moving average is useful because it helps to smooth out fluctuations in data by giving more importance to recent data points. It can be used to identify trends and make predictions based on historical data.
The advantages of using a weighted moving average over a simple moving average include the ability to give more weight to recent data points, which can make the average more responsive to changes in trends. This can result in a more accurate representation of the underlying data.
Yes, a weighted moving average can be used to forecast future data. By analyzing the historical data and identifying trends, it is possible to make predictions based on the weighted moving average. However, it is important to note that this method does not guarantee accurate forecasts and should be used in conjunction with other analysis techniques.
A weighted moving average is a type of moving average that assigns different weights to the data points in the average.
Options vs. Futures: A Beginner’s Guide to the Differences Options and futures are both popular financial instruments that can be used for speculative …
Read ArticleIs Bloomberg a Good Platform for Forex Trading? When it comes to forex trading platforms, reliability is a crucial factor to consider. Bloomberg, a …
Read ArticleIs the trading floor worth it? Trading on a physical exchange, also known as a trading floor, has been a staple of the financial industry for decades. …
Read ArticleWhat is the equation for the moving average ma? In the world of finance and statistics, the moving average (MA) is a commonly used indicator to …
Read ArticleWhere to Place Your Initial Stop When Taking a Box Breakout Trade A box breakout strategy is a popular trading strategy used by both beginner and …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Exponentially Weighted Moving Average Filter In signal processing, the Exponentially Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) filter is a …
Read Article