Is the London Session More Volatile Than New York? Exploring Forex Market Dynamics
Is London Session More Volatile Than New York? Forex market trading sessions play a crucial role in determining the overall volatility of currency …
Read Article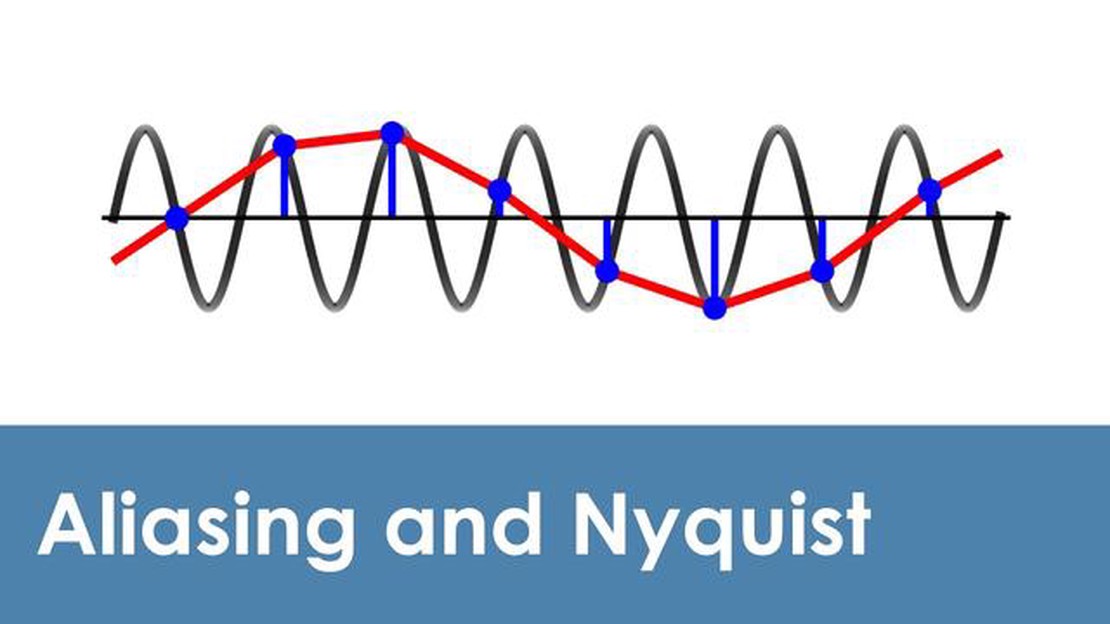
In the field of digital signal processing, the Nyquist rule plays a vital role in ensuring accurate and high-quality signal representation. The rule is named after Harry Nyquist, a prominent engineer, and mathematician who first introduced the concept in the 1920s. But what exactly is the Nyquist rule, and why is it so important?
At its core, the Nyquist rule states that in order to accurately reconstruct a continuous signal from its discrete samples, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency component of the signal. This means that for a digital system to faithfully capture and represent a signal, the sampling rate must cover a wide enough frequency range to include all the relevant information contained within the signal.
When the sampling rate is lower than the Nyquist rate, a phenomenon known as aliasing occurs. This is when higher-frequency components of the signal are incorrectly represented as lower-frequency components, leading to distortion and loss of important information. To avoid aliasing, it is crucial to ensure that the sampling rate is sufficiently high to accurately capture the signal’s frequency content.
The importance of the Nyquist rule goes beyond just avoiding aliasing. It also impacts the overall fidelity and quality of the signal reconstruction. By adhering to the Nyquist rule and using a proper sampling rate, digital signal processing systems can accurately capture and reproduce signals, enabling various applications such as audio and video processing, telecommunications, and medical imaging.
Understanding the Nyquist rule is fundamental for any engineer or scientist working in the field of digital signal processing. By applying this rule and ensuring an adequate sampling rate, we can avoid aliasing and achieve high-fidelity signal representation, ultimately leading to improved system performance and better user experiences.
The Nyquist Rule is a fundamental concept in digital signal processing that governs the sampling rate required for accurate representation of an analog signal in the digital domain. It states that in order to faithfully reconstruct a continuous signal from its samples, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency component of the signal.
This rule is based on the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem, which was developed in the 1940s by engineers Harry Nyquist and Claude Shannon. The theorem mathematically proves that if a signal has no frequency components above a certain limit, known as the Nyquist frequency, then it can be completely reconstructed from its samples taken at a rate higher than twice the Nyquist frequency.
By following the Nyquist Rule and choosing an appropriate sampling rate, we can avoid aliasing, a phenomenon that occurs when frequencies higher than the Nyquist frequency fold back into the frequency range below it, causing distortion and loss of information. Aliasing leads to artifacts such as “jaggies” in images and “shimmer” in audio.
Understanding the Nyquist Rule is crucial in various fields, such as telecommunications, audio processing, and medical imaging. It allows us to determine the minimum sampling rate needed to accurately capture and analyze signals, ensuring that the digital representation remains faithful to the original analog signal.
Read Also: How much is $1 USD in PHP? Current exchange rate
It is important to note that while the Nyquist Rule provides a minimum sampling rate requirement, higher sampling rates are often used in practice to provide additional margin and ensure better signal fidelity. The trade-off, however, is increased storage and computational requirements.
In conclusion, the Nyquist Rule is a fundamental concept in digital signal processing that dictates the minimum sampling rate necessary for accurate reconstruction of a continuous signal in the digital domain. By following this rule, we can avoid aliasing and preserve the fidelity of the original analog signal.
In digital signal processing, the sampling rate is a crucial parameter that determines how accurately an analog signal can be represented in a digital form. It refers to the number of samples taken per second from the continuous analog signal, and is typically measured in hertz (Hz).
A higher sampling rate leads to a more precise representation of the original analog signal, as it captures more data points per second. This is especially important when dealing with signals that have high-frequency components, such as audio signals or signals in video processing.
The Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem states that in order to accurately reconstruct a continuous signal from its samples, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency present in the signal. This means that if a signal has a maximum frequency of 10 kHz, it should be sampled at a rate of at least 20 kHz to avoid aliasing and information loss.
Aliasing is a distortion effect that occurs when the sampling rate is too low, resulting in the folding of higher frequency components into lower frequency ranges. This can lead to incorrect interpretation of the signal and loss of important information.
Read Also: ActivTrades Ownership: Discover Who Owns the Company
On the other hand, using a sampling rate higher than necessary can result in increased data storage requirements and computational complexity without providing any additional benefits. Therefore, it is important to choose an appropriate sampling rate that strikes a balance between accuracy and efficiency.
Overall, the sampling rate plays a critical role in digital signal processing, as it directly affects the fidelity and quality of the processed signal. By understanding the importance of sampling rate and applying the Nyquist Rule, we can ensure accurate and reliable digital signal representation.
The Nyquist rule is a fundamental principle in digital signal processing that states that the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency component of the signal being sampled in order to accurately reconstruct the original signal. This is important because if the sampling rate is too low, it can result in aliasing, which is the distortion or loss of information in the sampled signal.
Aliasing is a phenomenon in digital signal processing where high-frequency components of a signal are mistakenly represented as lower-frequency components. This can occur when the sampling rate is not high enough to capture the rapid changes in the original signal. This can lead to distortion and loss of information in the sampled signal, making it difficult to accurately reconstruct the original signal.
If the sampling rate is lower than the Nyquist rate, aliasing can occur. This means that high-frequency components of the original signal will be misrepresented as lower-frequency components in the sampled signal. This can lead to distortion and loss of information, making it difficult to accurately reconstruct the original signal.
The Nyquist rule is particularly important in digital audio and music recording. In order to accurately capture and reproduce the full range of frequencies present in a musical recording, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency present in the audio. If the sampling rate is too low, it can lead to aliasing and distortion in the recorded sound.
Yes, there are techniques to overcome aliasing in digital signal processing. One common approach is to use an anti-aliasing filter before the signal is sampled. This filter removes or reduces high-frequency components of the signal that are above the Nyquist frequency. By doing so, it ensures that only frequencies within the desired range are accurately represented in the sampled signal, avoiding the issues caused by aliasing.
The Nyquist rule states that in order to accurately reproduce a signal, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency present in the signal.
Is London Session More Volatile Than New York? Forex market trading sessions play a crucial role in determining the overall volatility of currency …
Read ArticleOptions as Products in OpenCart: Explained OpenCart is a popular open-source e-commerce platform that provides a wide range of features and options …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Bo in Forex Trading Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is a global decentralized market for trading currencies. It …
Read ArticleAre Forex Profits Subject to Capital Gains Tax? Understanding how foreign exchange trading is taxed can be a challenging endeavor. Forex trading, also …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Spread in Forex Trading In the world of Forex trading, understanding the spread is essential. The spread refers to the difference …
Read ArticleIs Investing in Ubisoft a Good Decision? When it comes to investing in the gaming industry, one company that often comes to mind is Ubisoft. With a …
Read Article