Understanding Bollinger Band Breakouts: Everything You Need to Know
Understanding Bollinger Band Breakouts When it comes to technical analysis in the financial markets, Bollinger Bands are a popular tool used by …
Read Article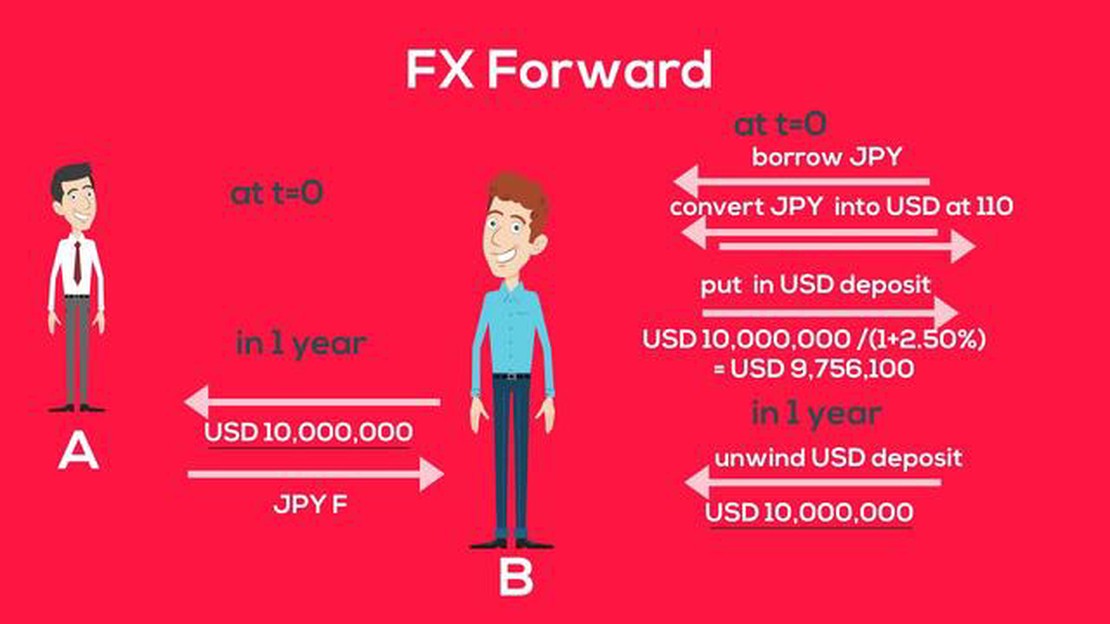
Foreign exchange (FX) forwards are a vital tool in managing currency risk for companies and individuals involved in international trade. They allow parties to lock in the future exchange rate for a specific currency pair, providing predictability and protection against potential losses.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the mechanism of FX forwards, providing a clear understanding of how they work and their key features. We will explore the concept of a forward contract, its purpose, and the different components involved.
One of the essential aspects of FX forwards is the notion of the spot rate, which refers to the current exchange rate between two currencies. We will delve into how the spot rate affects the pricing of forward contracts and explore the determinants of exchange rates.
Furthermore, this guide will explain the mechanics behind entering into an FX forward contract, including the calculation of the forward rate, the settlement process, and the potential risks and benefits involved. We will also discuss the various hedging strategies that can be employed to mitigate currency risk.
Whether you are a novice or seasoned participant in the foreign exchange market, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights necessary to navigate the complexities of FX forwards and make informed decisions in managing your currency exposure.
Foreign exchange (FX) forwards are a popular derivative instrument used by companies and investors to manage their currency risk. In this article, we will take a closer look at the mechanism of FX forwards and how they work.
FX forwards are essentially agreements between two parties to exchange a specified amount of one currency for another at a predetermined date in the future. The exchange rate at which the currencies will be swapped is fixed at the time of the agreement, known as the forward rate. This allows both parties to lock in the exchange rate, providing certainty and protection against potential future currency fluctuations.
The mechanism of FX forwards involves several key components. Firstly, there is the agreement between the two parties, known as the forward contract. This contract outlines the details of the transaction, including the currencies being exchanged, the amount of currency to be exchanged, the forward rate, and the settlement date.
Read Also: Understanding ISOs: What Does ISO Mean in Stock Options?
Once the forward contract is established, the parties involved are obligated to fulfill the terms of the agreement. This means that at the specified settlement date, the buyer of the forward contract is required to purchase the agreed upon amount of currency at the fixed forward rate, while the seller is obligated to sell the currency at that rate.
The settlement of the forward contract can occur through physical delivery of the currencies, but more commonly, it is settled by a cash payment based on the difference between the forward rate and the prevailing spot rate at the time of settlement. This settlement process allows the parties to avoid the costs and logistics associated with physically exchanging the currencies.
FX forwards are commonly used by companies and investors to manage their currency risk. For example, a company that has exposure to foreign exchange risk may enter into an FX forward contract to lock in the exchange rate for a future payment or receipt in a foreign currency. This helps the company to hedge against potential currency fluctuations and provides certainty in their cash flows.
In conclusion, FX forwards are a mechanism used to manage currency risk by locking in an exchange rate for a future transaction. By understanding the mechanism and workings of FX forwards, companies and investors can effectively manage their currency exposure and mitigate potential financial risks.
In the world of finance, foreign exchange (FX) forwards are commonly used to manage currency risk. These contracts allow market participants to buy or sell a currency at a future date, at a predetermined exchange rate. Understanding the key concepts of FX forwards is crucial for effectively using these instruments:
These concepts are fundamental to understanding and utilizing FX forwards effectively. By comprehending these key elements, market participants can make informed decisions when managing currency risk and achieving their financial objectives.
Read Also: Understanding the Taxability of Employee Stock Options: A Comprehensive Guide
An FX forward is a financial contract that allows two parties to exchange currencies at a specified exchange rate on a future date.
FX forwards work by locking in an exchange rate today for a currency exchange that will occur in the future. This helps parties mitigate the risk of currency fluctuations.
The advantages of using FX forwards include hedging against currency risk, minimizing uncertainty in international transactions, and stabilizing cash flows for businesses.
FX forwards are commonly used by corporations involved in international trade, banks, investors, and speculators.
Some key factors to consider when entering into an FX forward include the currency pair involved, the forward rate, the expiration date, the counterparty risk, and any associated fees.
An FX forward is a financial contract that allows two parties to exchange currencies at a specific exchange rate at a future date.
Understanding Bollinger Band Breakouts When it comes to technical analysis in the financial markets, Bollinger Bands are a popular tool used by …
Read ArticleChoosing the Best EMA for 5 Minute Trading When it comes to executing successful trading strategies, using the right indicators can make a significant …
Read ArticleWhat are the 4 major trading currencies? When it comes to international trade and finance, certain currencies have emerged as dominant players on the …
Read ArticleExploring the Forex Market: Understanding How it Works The forex market, also known as the foreign exchange market, is a decentralized global …
Read ArticleBest Free Ways to Learn Forex Trading Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is a popular market where individuals and institutions …
Read ArticleWhat Do Villagers Want to Trade in Minecraft? If you’re a dedicated Minecraft player, you’ve probably encountered villagers at some point. These …
Read Article