Is OANDA a good forex broker? Find out in our comprehensive review
Is OANDA a good forex broker? When it comes to choosing a forex broker, it’s important to find one that meets your needs and provides reliable and …
Read Article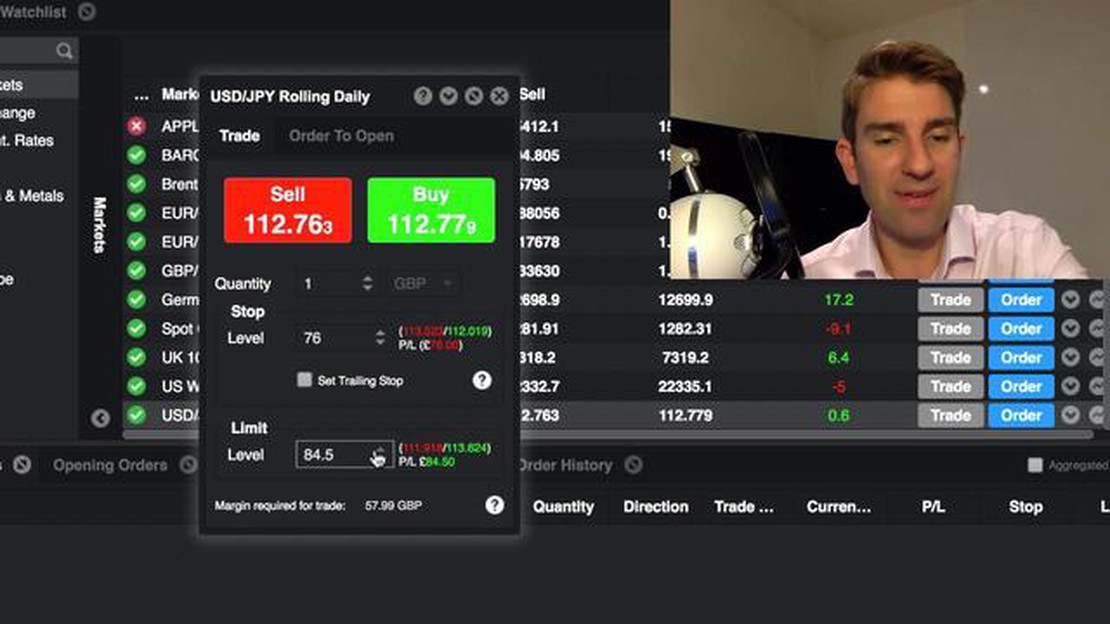
When it comes to trading orders, there are various options available to traders to manage their positions and minimize risks. Two common types of trading orders that traders often use are OTO (One Triggers Other) and OCO (One Cancels Other) orders. While both orders serve similar purposes, they have distinct features and functions.
An OTO order is a combination of multiple orders that are executed in a specific sequence based on predetermined conditions. This means that when the first order is triggered, it will automatically trigger the execution of the subsequent orders in the predefined sequence. Traders use OTO orders to manage multiple trades simultaneously, allowing them to set profit targets and stop losses for each individual trade.
On the other hand, an OCO order is a set of two or more orders that are linked together. In an OCO order, if one order is executed, it will automatically cancel the remaining orders. The purpose of an OCO order is to provide traders with a way to manage their positions in case the market moves in an unexpected direction. Traders commonly use OCO orders to set up both a stop loss order and a take profit order simultaneously.
It is important for traders to understand the key differences between OTO and OCO orders to effectively use them in their trading strategies. OTO orders allow for a sequence of orders to be executed based on predetermined conditions, while OCO orders provide a way to manage positions by linking multiple orders together. Both order types offer traders the ability to manage risks and maximize profits, but the choice between the two depends on the trader’s specific trading style and objectives.
Understanding the differences between OTO and OCO orders can greatly enhance a trader’s ability to execute their trading strategies with precision and efficiency. By utilizing these order types effectively, traders can have more control over their positions and react to market movements in a timely manner.
When it comes to trading orders, two commonly used terms are Oto and OCO. While they may sound similar, they represent different types of orders that traders can use to manage their positions and mitigate risks in the financial markets.
Oto, or “one triggers the other,” is an order type that allows traders to place two linked orders simultaneously. When the first order is executed, it triggers the second order to be placed automatically. This can be useful for traders who want to enter a position only if a certain condition is met. For example, a trader may place a buy order for a stock with a limit price above the current market price. They can then set a stop-loss order at a price below their entry price. If the buy order is executed, the stop-loss order will be automatically placed, helping to limit potential losses.
Read Also: Why Having a Mentor is Essential for Trading Success
On the other hand, OCO, or “one cancels the other,” is an order type that allows traders to place two linked orders but with the understanding that only one can be executed. When one order is executed, the other order is automatically canceled. This order type can be useful for traders who want to place both a profit target and a stop-loss order for a position. For example, a trader may enter a buy order for a stock and place a limit order to sell at a specific price to take profits, as well as a stop-loss order to sell at a specific price to limit losses. Once one of these orders is executed, the other order is automatically canceled.
Both Oto and OCO orders can be valuable tools for traders, as they allow for more precise control over their positions and risk management strategies. However, it’s important to note that these order types may not be available on all trading platforms or in all markets. Traders should familiarize themselves with the specific order types offered by their broker and understand how they work before using them in their trading strategies.
Read Also: Exploring the Top Anomaly Detection Algorithms: Choosing the Best One
When it comes to trading orders, two common types that traders use are Oto (One Triggers the Other) and OCO (One Cancels the Other). While both types are used to automate trades and manage risk, there are key differences between the two.
Overall, understanding the key differences between Oto and OCO trading orders is essential for traders to effectively use these order types to manage risk and automate their trading strategies.
An OTO (One Triggers the Other) order is a type of order that combines two or more separate orders. When one order is executed, it triggers the execution of the other orders. On the other hand, an OCO (One Cancels the Other) order is a type of order that combines two or more separate orders, but when one order is executed, it cancels the other orders.
OTO orders can be used in a variety of ways in a trading strategy. One common use is for setting profit targets and stop-loss levels. For example, you can place a buy order with an attached profit target order and a stop-loss order. If the buy order is executed, the profit target and stop-loss orders will be triggered. This allows you to automatically take profits and limit losses without constantly monitoring the market.
There may be limitations or restrictions when using OTO orders depending on the trading platform or broker you are using. Some platforms may have a limit on the number of OTO orders you can place or the interval between each order. It is important to check the specific requirements and limitations of your trading platform or broker before using OTO orders in your trading strategy.
One of the main advantages of using OCO orders is that they allow you to automatically manage your risk. When one order is executed, the other orders are cancelled, which helps to ensure that you have a predefined exit strategy in place. This can be especially helpful in volatile markets where prices can quickly change. OCO orders also help to remove emotion from trading decisions and can save you time as you do not have to manually cancel or adjust orders.
Is OANDA a good forex broker? When it comes to choosing a forex broker, it’s important to find one that meets your needs and provides reliable and …
Read ArticleCan you become a millionaire with forex? Forex trading has become increasingly popular in recent years as more and more people are looking for ways to …
Read ArticleWho is the richest trader in the world in 2023? In 2023, the financial world witnessed the rise of an enigmatic trader who quickly became known as the …
Read ArticleIs ION Group a FinTech company? ION Group is a leading provider of innovative financial technology solutions. With over 2,000 employees in offices …
Read ArticleHow to Check My MCB Balance Are you a customer of the MCB bank and wondering how to check your account balance? Look no further! We have prepared a …
Read ArticleIs black gold real or fake? Black gold is a term that has captured the curiosity and imagination of many. It is often associated with great wealth and …
Read Article