Understanding Your Options: Do You Have to Sell Shares if a Company Goes Private?
What Happens to Your Shares When a Company Goes Private? Investing in the stock market can be a thrilling and sometimes unpredictable endeavor. As a …
Read Article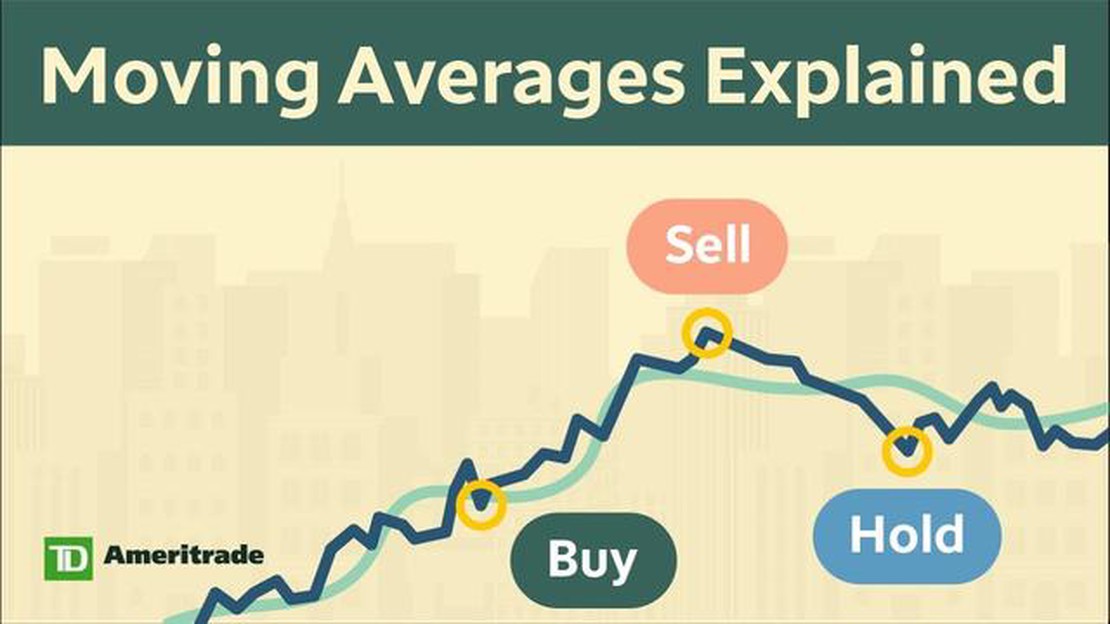
In today’s fast-paced world, where data is constantly being generated and analyzed, it is crucial to have a good understanding of statistical concepts such as rolling average. Whether you are an analyst, a data scientist, or simply someone who wants to make sense of the numbers, knowing how to calculate and interpret rolling averages can be immensely helpful.
A rolling average, also known as a moving average or a rolling mean, is a statistical calculation that allows you to analyze the trend of a data set over a specific period of time. Unlike a simple average, which takes into account all the data points equally, a rolling average focuses on a set of consecutive data points and calculates their average. This approach helps reduce the impact of outliers and smoothes out the fluctuations in the data, making it easier to identify long-term trends.
For example, imagine you are analyzing stock prices over a 30-day period. Instead of looking at the daily fluctuations, you can calculate the 30-day rolling average to see the overall trend. This can help you identify whether the stock is generally increasing or decreasing in value, and potentially predict future movements.
Calculating a rolling average involves taking a set of data points, determining the desired period of time, and continuously updating the average as new data points become available. This rolling window moves along the data set, removing the oldest data point and including the newest one in the calculation. The size of the rolling window can vary depending on the specific analysis, but it is typically chosen based on the desired level of smoothing and the frequency of the data.
By understanding and utilizing rolling averages, you can gain valuable insights from time-series data, monitor trends, and make more informed decisions. Whether you are analyzing financial data, tracking sales performance, or evaluating website traffic, rolling averages provide a powerful tool for understanding patterns and making predictions in real time.
A rolling average, also known as a moving average, is a statistical calculation that is used to analyze patterns or trends in data over a certain period of time. It is often used in fields such as finance, economics, and data analysis.
Rolling averages are calculated by taking the average of a set of data points over a specific time window, and then shifting the window by one data point and recalculating the average. This process is repeated until the entire dataset has been analyzed.
The main purpose of using rolling averages is to smooth out short-term fluctuations or noise in the data and highlight the underlying trends or patterns. By calculating the average over a longer period of time, the rolling average provides a more stable representation of the data.
A common application of rolling averages is in financial markets, where they are used to analyze price trends. For example, a 50-day rolling average of a stock’s closing price can help identify whether the stock is trending up or down over a longer time period.
Rolling averages can also be used to forecast future trends or predict future values based on historical data. By analyzing the trend of the rolling average, analysts can make informed predictions about the future behavior of the data.
Overall, rolling averages are a powerful tool for understanding patterns and trends in data. They can help analysts make data-driven decisions, identify anomalies or outliers, and make predictions about the future based on historical trends.
A rolling average, also known as a moving average, is a statistical calculation used to analyze data over a specific time period. It is a technique that helps smooth out the fluctuations or variations in data by calculating the average of a set of values within a given window. The window size determines the number of data points included in the calculation.
To calculate a rolling average, you take the average of the current and previous data points, and then repeat this process for each subsequent data point within the window. As new data points are added, the oldest data points are dropped from the calculation.
The rolling average is commonly used to identify trends and patterns in time series data. By smoothing out short-term fluctuations, it provides a clearer picture of the underlying long-term trend. This makes it a useful tool for forecasting future values or identifying turning points in the data.
Read Also: What is the formula for running average?
The choice of window size for the rolling average depends on the specific application and the characteristics of the data. A larger window size can smooth out more fluctuations but may result in a delay in identifying changes. Conversely, a smaller window size can respond quickly to changes but may be susceptible to noise.
Overall, the rolling average is a valuable technique for understanding and interpreting data in real time. It allows for the identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies, helping in making informed decisions and predictions.
A rolling average has a wide range of benefits and applications in real-time data analysis. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Smoothing Out Fluctuations: A rolling average helps in smoothing out random fluctuations in data by averaging a certain number of past observations. This can help in identifying trends and patterns more easily.
Read Also: Is a 1 pip spread good? Exploring the impact of tight spreads on forex trading
2. Forecasting: By using a rolling average, analysts can make more accurate predictions and forecasts. The smoothed data provides a clearer picture of the overall trend, making it easier to project future values.
3. Identifying Anomalies: Rolling averages can help in identifying anomalies or outliers in the data. These anomalies may indicate unusual events or errors in the data collection process.
4. Time Series Analysis: Rolling averages are commonly used in time series analysis to study the patterns and trends over time. By looking at the rolling average, analysts can gain insights into the cyclicality or seasonality of the data.
5. Comparing Performance: Rolling averages can be used to compare the performance of different entities or variables over a period of time. This can help in evaluating and ranking the performance of various factors or entities.
6. Smoothing Volatility: In financial markets, rolling averages are often used to smooth out volatility and identify long-term trends. This can help investors in making more informed decisions based on the overall market direction.
7. Monitoring Real-Time Data: Rolling averages are useful for monitoring real-time data by providing a continuous and updated view of the trend. This can be especially valuable in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
8. Seasonal Adjustment: Rolling averages can be used to adjust for seasonal fluctuations in data. By calculating the rolling average over a seasonal period, analysts can remove the seasonal component and focus on the underlying trend.
Overall, the concept of rolling average offers numerous benefits and applications in analyzing real-time data. Its versatility and usefulness make it a valuable tool for various industries and domains.
A rolling average is a statistical calculation that takes a series of data points and calculates the average over a specified time period. It continuously updates the average as new data points become available.
Rolling averages are commonly used in real-time data analysis because they provide a smoother representation of data trends and help to filter out short-term fluctuations or noise. They help in identifying long-term patterns and making predictions.
A rolling average takes into account a specific time period and adjusts the average as new data points are added. A simple average, on the other hand, calculates the average of all data points without considering any time period. Rolling average provides a more dynamic and up-to-date representation of the data.
Using rolling averages in real-time data analysis allows for a more accurate understanding of the trends and patterns in the data. It helps to filter out short-term fluctuations and provides a smoother representation of the data. Additionally, rolling averages enable better forecasting and prediction based on the data.
The specific time period for calculating a rolling average depends on the data being analyzed and the desired level of analysis. Shorter time periods, such as 7 or 14 days, are commonly used for more frequent updates, while longer time periods, such as 30 or 60 days, are used for broader trends and patterns. The choice of time period should be based on the specific requirements and goals of the analysis.
What Happens to Your Shares When a Company Goes Private? Investing in the stock market can be a thrilling and sometimes unpredictable endeavor. As a …
Read ArticleTop Option Trading Bots in India If you’re an investor or trader in India looking to maximize your profits in the options market, then it’s time to …
Read ArticleCost of 1 Micro Lot In forex trading, a micro lot refers to a unit of measurement for the trading volume of a currency pair. It is equivalent to 1,000 …
Read ArticleCan I borrow against my private company stock? Many entrepreneurs and business owners may find themselves in need of additional capital to fund the …
Read ArticleBenefits of Selling a Put Option vs Buying a Call Option Options trading can be a complex and intricate strategy for investors looking to profit from …
Read ArticleWho is a Pro Forex Trader? If you’ve ever wondered what it takes to become a professional forex trader, you’re in the right place. Forex trading is …
Read Article