Discover the Number of Tracks at Goteborg Central Station | Goteborg Central Tracks
Number of tracks at Goteborg Central Station: Explained Goteborg Central Station, located in the heart of Sweden’s second largest city, is a bustling …
Read Article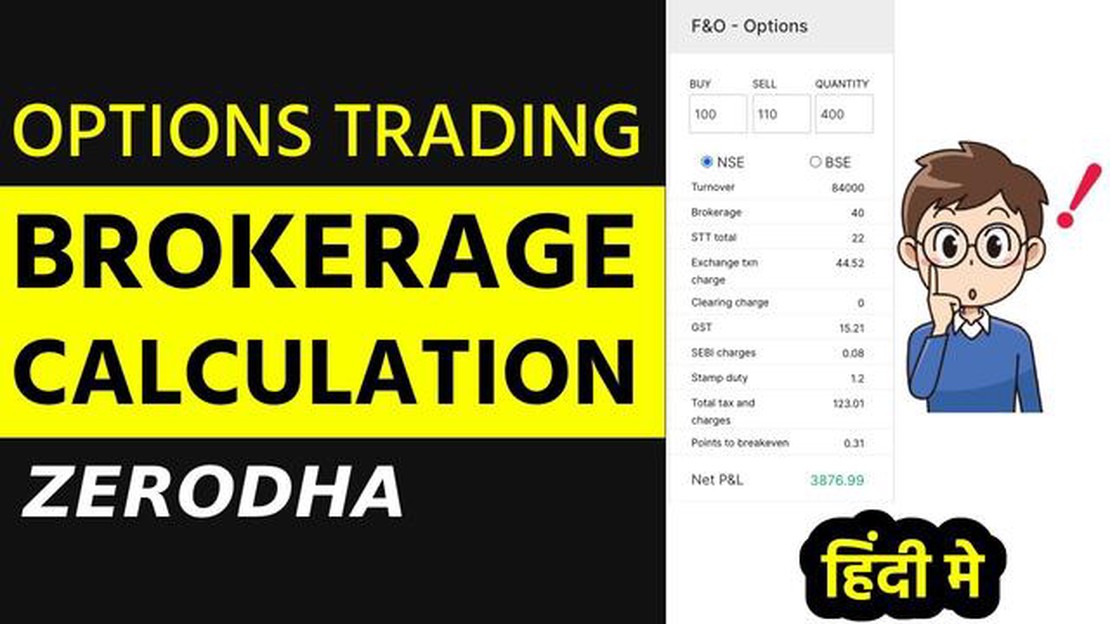
Options trading can be a lucrative investment strategy, but it’s important to understand the various costs involved before diving in. One such cost is the brokerage fee, which is the commission charged by a brokerage firm for executing a trade on your behalf. This fee can vary based on a number of factors, and calculating it accurately is essential for managing your options trading expenses.
When it comes to options, brokerage fees are typically calculated based on the number of contracts traded. A contract represents a specific number of shares of the underlying security, and the brokerage fee is charged per contract. It’s important to note that the fee is charged for both buying and selling options contracts, so it can add up quickly if you’re an active options trader.
In addition to the per-contract fee, brokerage firms may also charge a minimum fee for options trades. This means that even if you’re trading a small number of contracts, you’ll still be charged a minimum amount. It’s important to consider this minimum fee when calculating your total brokerage costs, as it can significantly impact your overall profitability.
Furthermore, some brokerage firms have a tiered fee structure for options trades. This means that the fee per contract decreases as the number of contracts traded increases. Understanding the tiered fee structure is crucial, as it allows you to optimize your trading strategy to minimize costs.
Overall, understanding the calculation of brokerage on options is essential for managing your trading expenses and maximizing your profitability. By considering factors such as the per-contract fee, minimum fee, and tiered fee structure, you can make informed decisions and ensure that your options trading strategy remains cost-effective.
Understanding the calculation of brokerage on options is crucial for any investor or trader. Brokerage refers to the fee that a brokerage firm charges for facilitating trades on behalf of the investor. It is important to have a clear understanding of how this fee is calculated as it can significantly impact the profitability of options trading.
Here are a few key reasons why understanding brokerage calculation is important:
In conclusion, understanding the calculation of brokerage on options is essential for traders to make informed decisions. It helps in cost management, trade strategy optimization, transparency, and risk management. By having a clear understanding of brokerage calculation, traders can enhance their overall trading experience and achieve better financial outcomes.
When it comes to calculating brokerage on options, there are several factors that can influence the final amount. These factors include:
1. Type of Option: The type of option being traded can have an impact on the brokerage calculation. Different options, such as call options or put options, may have different brokerage rates or fees associated with them.
Read Also: Is MT5 a Good Trading Platform? Pros and Cons of MetaTrader 5
2. Strike Price: The strike price of the option contract can also affect the brokerage calculation. Generally, brokerage charges may vary depending on the strike price of the option.
3. Number of Contracts: The number of option contracts being traded can impact the brokerage calculation. Typically, brokerage charges are based on a per-contract basis, so trading a larger number of contracts may result in higher brokerage fees.
4. Premium Paid: The premium paid for the options contract is another factor that can influence the brokerage calculation. Brokers may charge a percentage of the premium paid as brokerage fees.
5. Brokerage Rate: The brokerage rate or fee charged by the broker is a significant factor in the calculation. Different brokers may have different rate structures, including flat fees, percentage-based fees, or a combination of both.
Read Also: Trade's Impact on the Aztecs: Exploring the Influence of Commerce on an Ancient Civilization
6. Trading Account Type: The type of trading account you have can also affect the brokerage calculation. Some brokers offer different rates or fee structures for different types of accounts, such as individual accounts versus corporate accounts.
7. Additional Fees: Apart from the standard brokerage charges, brokers may impose additional fees that can impact the overall brokerage calculation. These fees may include exchange fees, regulatory fees, transaction fees, or any other charges associated with trading options.
8. Trading Volume: The trading volume can also play a role in the brokerage calculation. Some brokers offer discounts on brokerage fees for high-volume traders or provide tiered fee structures based on the total trading volume over a specific period.
It is essential to carefully consider these factors when calculating brokerage on options to ensure you have a clear understanding of the total costs involved in trading.
Options brokerage refers to the fee charged by a brokerage firm for facilitating options trading. It is the commission or transaction cost that traders need to pay when buying or selling options contracts.
Options brokerage is typically calculated based on the number of options contracts traded or the total value of the options contracts. The brokerage fee can be a fixed amount per contract or a percentage of the total value of the trade. Some brokerage firms may have tiered fee structures based on the volume of options trades.
The options brokerage cost can be influenced by several factors, such as the brokerage firm’s fee structure, the type of options trade (buying or selling), the number of contracts traded, the option’s strike price, the option’s expiration date, the liquidity of the options market, and the trader’s account type.
Yes, apart from the options brokerage, there may be additional fees associated with options trading. These can include exchange fees, regulatory fees, clearing fees, and transaction fees. These fees can vary depending on the exchange and the specific options trade.
Traders can minimize their options brokerage costs by comparing brokerage firms’ fee structures and choosing the one that offers competitive rates. It is recommended to trade larger volumes to take advantage of any tiered fee structures. Additionally, selecting options with lower strike prices or closer expiration dates can also help reduce the overall brokerage cost.
Number of tracks at Goteborg Central Station: Explained Goteborg Central Station, located in the heart of Sweden’s second largest city, is a bustling …
Read ArticleJoining a Trading Group: Step-by-Step Guide and Tips Are you interested in joining a trading group? Whether you are a novice trader or have some …
Read ArticleCalforex fees: Are there any charges? Calforex is a well-known currency exchange service that offers competitive rates and convenient locations across …
Read ArticleWhat is 30 day moving average? The 30-day moving average is a commonly used technical indicator in financial markets. It is a tool that can help …
Read ArticleHow to delete a demo account on XTB? If you’re using XTB’s demo account and want to delete it, this step-by-step guide will walk you through the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding whether RSI is leading or lagging When it comes to technical analysis in the world of trading, one of the most popular indicators is the …
Read Article