December Forex Market Schedule: Closing Days and Holidays
Forex Market Closing Days in December December is a month filled with anticipation and excitement as the holiday season is in full swing. However, for …
Read Article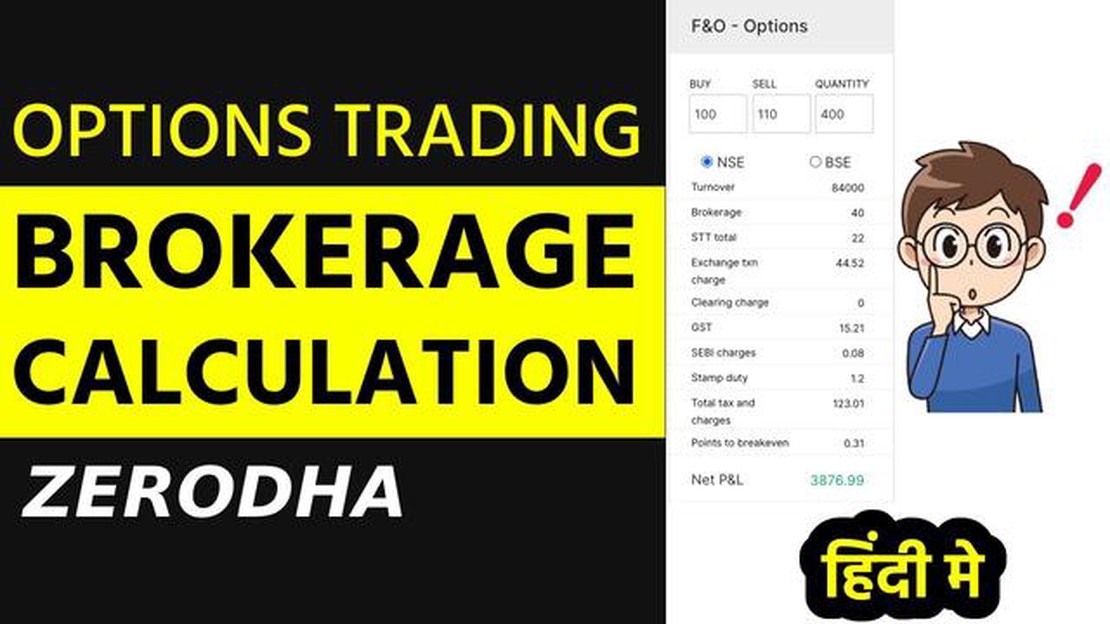
Options trading can be a lucrative investment strategy, offering investors the opportunity to profit from changes in the price of underlying assets. However, before diving into options trading, it is important to understand the various costs involved, including brokerage fees. Brokerage fees are charges levied by brokers for facilitating the buying and selling of options contracts. These fees can vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of option, the number of contracts traded, and the broker’s fee structure.
Calculating brokerage fees for options trading
Calculating brokerage fees for options trading can be complex, as they are typically based on a percentage of the contract’s value or a flat fee per contract. To calculate the brokerage fees, investors need to multiply the fee rate by the total contract value or the number of contracts traded. For example, if the brokerage fee is 1% and the total contract value is $10,000, the brokerage fee would be $100.
It is important to note that brokerage fees for options trading can vary significantly between brokers. Some brokers may offer a lower fee structure for high-volume traders or provide discounted rates for frequent traders. Additionally, some brokers may have a minimum fee per trade, which means that even if the calculation based on the fee rate results in a lower amount, the minimum fee still applies.
Understanding the calculation of brokerage fees in options trading is essential for investors to make informed decisions and manage their costs effectively. By comparing the fee structures of different brokers and considering factors such as trading frequency and contract size, investors can minimize their overall trading costs and maximize their potential profits.
Options trading is a type of investment strategy that involves buying and selling options contracts on various financial instruments, such as stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies. An option is a derivative contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time period.
There are two types of options: calls and puts. A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date, while a put option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date.
Options trading can be used for various purposes, such as speculating on the price movements of the underlying asset, hedging against potential losses, and generating income through options selling. It requires a good understanding of the options market, as well as knowledge of various strategies and risk management techniques.
Read Also: Is TeleTrade regulated? Learn all about TeleTrade regulation
When trading options, investors can choose to buy or sell options contracts. Buying options is known as going long, and it allows investors to profit from a rise in the price of the underlying asset or to protect against a decline in its price. Selling options is known as going short, and it allows investors to generate income through the premiums received from selling options contracts.
Options trading is considered more complex and risky than traditional stock trading, as options involve leverage and the potential for significant gains or losses. It is important for investors to thoroughly understand the risks and rewards of options trading before engaging in it.
In conclusion, options trading is a versatile investment strategy that offers potential opportunities for profit and risk management. It involves the buying and selling of options contracts on various financial instruments, and it requires a good understanding of the options market and its associated risks. Like any investment strategy, it is important for investors to do their research and seek advice from financial professionals before getting involved in options trading.
In options trading, brokerage is the fee charged by brokers for executing trades on behalf of investors. It is important for options traders to understand how brokerage is calculated, as it can impact their overall profitability.
Brokerage for options trading is typically calculated based on the number of options contracts traded or the notional value of the trade. The notional value is the total value of the options contract, which is calculated by multiplying the price per share by the number of shares covered by the contract.
The brokerage fee is usually a percentage of the notional value of the trade, with different brokers charging varying rates. For example, a broker might charge 0.1% of the notional value as brokerage fee. In some cases, brokers may also have a minimum brokerage charge.
Let’s consider an example to understand how brokerage is calculated in options trading. Suppose an options trader buys 10 call option contracts with a notional value of $10,000 each, and the brokerage rate is 0.1% with a minimum brokerage charge of $20.
The total notional value of the trade would be $10,000 x 10 = $100,000.
Read Also: Understanding the Distinction: Forex vs. HFX
If the brokerage rate is 0.1%, the brokerage fee would be 0.1% x $100,000 = $100. However, since the minimum brokerage charge is $20, the trader would be required to pay a brokerage fee of $20 in this case.
It is important to note that in addition to brokerage fees, options traders may also incur other charges such as exchange fees, regulatory fees, and taxes. These charges may vary depending on the exchange and the type of options being traded.
Overall, understanding how brokerage is calculated is essential for options traders to accurately assess the cost of their trades and make informed decisions to maximize their profitability.
Brokerage in options trading is calculated based on various factors such as the number of contracts traded, the strike price of the options, and the type of options traded (call or put). Generally, a fixed brokerage fee is charged per contract, but some brokers may also charge a percentage of the contract value.
In fixed brokerage, a fixed amount is charged per contract traded, regardless of the contract value. On the other hand, in percentage-based brokerage, a certain percentage of the contract value is charged as brokerage. This means that higher valued contracts will attract higher brokerage charges.
Yes, apart from brokerage, options traders may also have to pay other charges and fees such as exchange fees, regulatory fees, and transaction charges. These charges may vary depending on the broker and the exchange on which the options are traded.
Yes, many brokers have a minimum brokerage charge for options trading. This means that even if you trade a small number of contracts, you will still have to pay a minimum amount as brokerage. The minimum brokerage charge varies from broker to broker.
Forex Market Closing Days in December December is a month filled with anticipation and excitement as the holiday season is in full swing. However, for …
Read ArticleSecond Quarter Earnings of BNSF 2023 In the world of finance and investments, staying up-to-date with the latest quarterly earnings reports of major …
Read ArticleWill USD Grow Stronger? The US dollar (USD) is one of the most important and widely used currencies in the world. It plays a crucial role in global …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Option Delta Calculation In the world of options trading, understanding the concept of delta is essential. Delta measures the rate of …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Moving Average in Share Price Share price analysis is an essential tool for investors and traders, enabling them to make informed …
Read ArticleWhat is KK in euro? If you have ever traveled to Europe or engaged in international trade, you may have come across the abbreviation “KK” when …
Read Article