Owner of Ossia International - Revealed!
Owner of Ossia International Ossia International, a global leader in wireless power technology, has finally revealed the identity of its secretive …
Read Article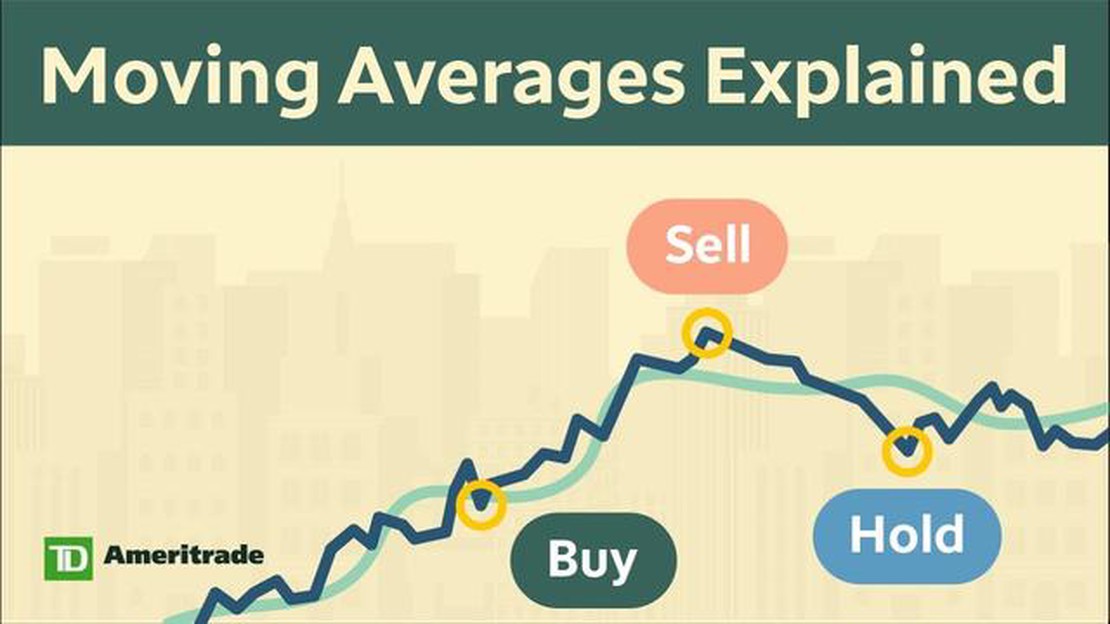
In the world of trading and investing, understanding moving averages is essential for making informed decisions. Moving averages are powerful tools that help traders identify trends, spot potential entry and exit points, and manage risk. In this complete guide, we will break down the concept of moving averages, explore the different types, and learn how to effectively use them in quantitative analysis.
What are Moving Averages?
Moving averages are statistical calculations that are used to analyze the average value of a security or index over a specific period of time. They smooth out price data, making it easier to identify trends and patterns. By calculating the average price over a set period, moving averages can provide traders with a clearer picture of where a stock or index is headed.
Types of Moving Averages
There are different types of moving averages, each with its own benefits and limitations. The most commonly used are the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). SMA calculates the average price over a specific period equally, while EMA assigns more weight to recent data points. Both types have their advantages and are used in different trading strategies.
How to Use Moving Averages in Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis involves the use of mathematical and statistical techniques to analyze market data. Moving averages are a key component of this analysis, helping traders identify trends and make data-driven decisions. By comparing different moving averages, traders can spot potential price reversals or confirm the strength of a trend. Additionally, moving averages can be used in conjunction with other technical indicators to generate trading signals and build trading strategies.
A moving average is a commonly used technical analysis tool in the field of finance. It is a calculation that is used to analyze the trend of a given price over a specified period of time. By calculating an average price over a particular time frame, moving averages can help reduce the noise in price data and provide a clearer view of the overall trend.
There are different types of moving averages, but the most commonly used are the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). The SMA calculates the average price over a specific number of periods, while the EMA puts more weight on recent prices. Both types of moving averages can be used to identify support and resistance levels, as well as potential entry and exit points for traders.
Moving averages can also be used to generate trading signals. For example, when the price of an asset crosses above its moving average, it is considered a bullish signal, indicating that the price may continue to rise. On the other hand, when the price crosses below its moving average, it is seen as a bearish signal, suggesting that the price may decline.
Overall, moving averages are a valuable tool for traders and analysts in identifying trends, filtering out noise, and making informed trading decisions. They provide a visual representation of price movement over time and can help traders determine the overall direction of the market.
Moving averages are widely used in technical analysis to identify trends and provide signals for potential trading opportunities. A moving average is a calculation that takes the average price of a security over a specific period of time.
There are different types of moving averages that vary in their calculation method:
Read Also: How to Hedge Gamma Options: A Comprehensive Guide
| Type | Calculation Method |
|---|---|
| Simple Moving Average (SMA) | The SMA is calculated by summing up the closing prices over a specific period and dividing the sum by the number of periods. |
| Exponential Moving Average (EMA) | The EMA gives more weight to recent prices compared to older prices. It is calculated by using a constant multiplier that decreases exponentially as the time period increases. |
| Weighted Moving Average (WMA) | The WMA assigns different weights to each data point in the time period. The weights decrease linearly from the most recent data point to the oldest. |
| Smoothed Moving Average (SMMA) | The SMMA is similar to the EMA but uses a different smoothing technique. It is calculated by recursively applying an average on the previous SMMA value and the current close price. |
Each type of moving average has its own strengths and weaknesses, and can be used in different ways depending on the trader’s preference and trading strategy.
In quality control, moving averages are used as a statistical tool to analyze data and detect patterns or trends over time. They are commonly applied to monitor and improve processes, identify abnormal variations, and make informed decisions.
1. Smoothing out fluctuations: Moving averages help to remove random or short-term fluctuations in data, allowing quality control professionals to focus on the underlying trends or patterns that are significant to their analysis. By averaging the values over a specific time period, they can identify the overall direction of the process and distinguish it from temporary fluctuations.
Read Also: Understanding the concept of leverage 1:1 in Forex trading
2. Identifying long-term trends: Moving averages provide a clearer picture of the long-term trend in the data, making it easier to identify whether the process is improving, deteriorating, or remaining relatively stable over time. This information is crucial for decision-making and continuous improvement efforts.
3. Comparing actual performance to benchmarks: By comparing the moving average values to established benchmarks or standards, quality control professionals can determine whether the process is meeting performance targets or if there is a need for corrective actions. This allows them to take proactive steps to bring the process back into control and achieve the desired quality levels.
4. Detecting process variability: Moving averages can help identify process variability and potential sources of variation. Sudden changes or shifts in the moving average values can signal issues in the process that may require investigation and intervention to prevent quality problems.
5. Forecasting future performance: By analyzing moving averages, quality control professionals can make informed predictions about the future performance of the process. They can anticipate potential issues or deviations from the expected trend, allowing them to proactively implement measures to maintain or improve product quality.
In conclusion, moving averages are a valuable tool in quality control as they allow professionals to analyze data, smooth out fluctuations, identify trends, compare performance to benchmarks, detect process variability, and forecast future performance. By understanding and utilizing moving averages effectively, quality control professionals can make data-driven decisions to ensure product quality and process improvement.
A moving average is a statistical calculation that is used to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set.
The purpose of using moving averages in quality control is to identify patterns or trends in the data that can help in making informed decisions about process improvement.
There are several types of moving averages, including simple moving average, weighted moving average, exponential moving average, and triangular moving average.
A moving average is calculated by taking the average of a certain number of data points within a given time period, and then moving that window of data points forward by one data point at a time and recalculating the average.
Some limitations of using moving averages in quality control include the fact that it can only provide a general trend rather than specific insights into individual data points, and it may not be suitable for detecting sudden changes or outliers in the data.
A moving average is a statistical calculation used to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set.
Owner of Ossia International Ossia International, a global leader in wireless power technology, has finally revealed the identity of its secretive …
Read ArticleWhat is the interest rate for OCBC? Are you looking for a bank that offers competitive interest rates to grow your savings? Look no further than OCBC! …
Read ArticleWhat is the best combination indicator with RSI? When it comes to trading in the financial markets, having the right tools and indicators can make all …
Read ArticleWhat Causes the Australian Dollar to Weaken Against the Euro? The Australian dollar (AUD) has been experiencing weakness against the Euro (EUR) in …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Social Trading in Forex: A Comprehensive Guide Forex trading can be an overwhelming and complex world, especially for beginners. But …
Read ArticleWhat does Pivot mean? When it comes to making decisions or finding a new direction, the concept of pivot plays a crucial role. In various fields, from …
Read Article