Are stocks given by company taxable?
Are Stocks Given by Company Taxable? Stocks are a common form of compensation given by companies to their employees. They can be an attractive …
Read Article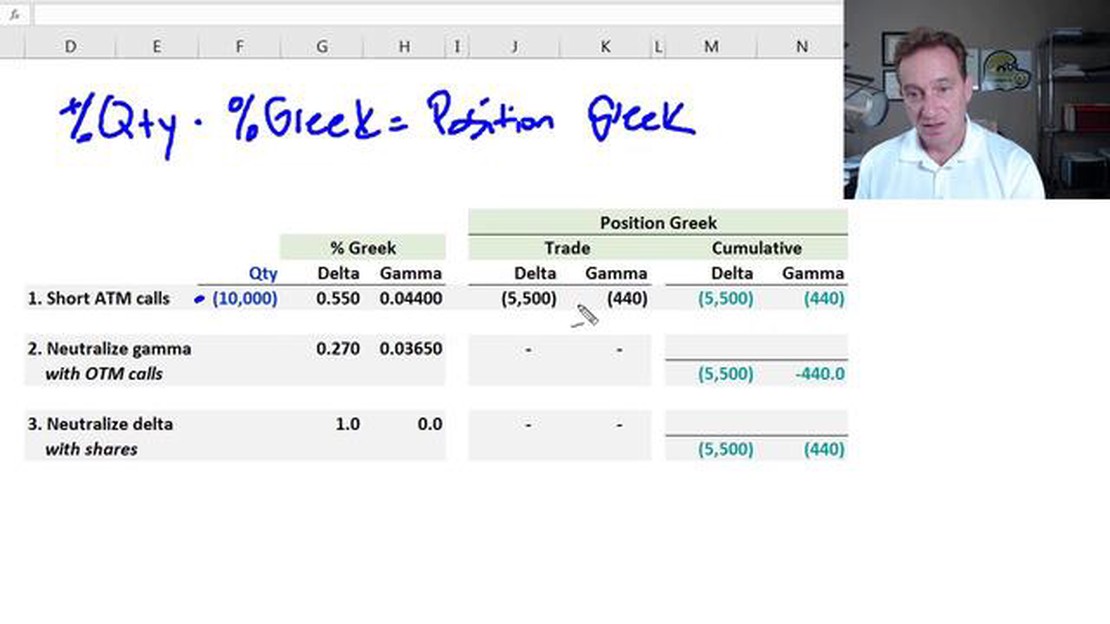
Gamma options are an important tool for investors looking to protect their portfolios and manage risk. They refer to the rate of change in an option’s delta in response to a change in the underlying asset’s price. By understanding and hedging gamma options, investors can navigate market volatility and maximize their overall returns.
One popular strategy for hedging gamma options is the use of delta-neutral portfolios. This involves creating a portfolio that has a delta of zero, ensuring that the value of the portfolio remains relatively stable regardless of changes in the underlying asset’s price. To achieve this, investors engage in dynamic hedging, where they continually adjust the composition of their portfolio to maintain a delta-neutral position.
Another approach to hedging gamma options is through the use of options spreads. An options spread involves simultaneously buying and selling different options contracts with different strike prices and expiration dates. This strategy can help investors manage their exposure to gamma risk and limit potential losses.
Furthermore, investors can hedge gamma options by using futures contracts. By taking a position in a futures contract that tracks the underlying asset, investors can offset potential losses from their options positions. This allows them to mitigate the impact of changes in the underlying asset’s price on their portfolio.
Overall, understanding how to hedge gamma options is crucial for investors looking to protect their portfolios and manage risk. Whether through delta-neutral portfolios, options spreads, or futures contracts, different hedging strategies can help investors navigate market volatility and maximize their overall returns.
Gamma is one of the options Greeks and it measures the rate at which the option’s delta changes in relation to the underlying asset’s price movement. In simpler terms, gamma can be seen as the sensitivity of an option’s delta to changes in the price of the underlying asset.
Gamma plays a crucial role in options trading because it helps traders understand how the value of an option may change as the underlying asset’s price moves. High gamma means that the option’s delta can change significantly with even small movements in the underlying asset, while low gamma indicates that the option’s delta is less affected by price changes.
Understanding gamma is important for options traders as it can help them assess the risk and potential reward of their trades. Options with high gamma can offer the potential for larger profits, as small movements in the underlying asset’s price can result in substantial changes in the option’s value. However, high gamma also means higher risk, as the option’s value can quickly decline if the underlying asset’s price moves against the trader’s position.
On the other hand, options with low gamma are less sensitive to price movements, which can be beneficial for traders seeking more stable and predictable returns. Low gamma options may be suitable for traders who want to hedge existing positions or use options as a risk management tool.
Read Also: Examples of Corporate Social Responsibility: A Guide to Corporate Giving and Sustainability
In summary, gamma is an important concept in options trading as it provides insight into how the value of an option may change in response to movements in the underlying asset. By understanding and managing gamma, traders can make more informed decisions and optimize their trading strategies.
When it comes to options trading, understanding the basics is crucial. Before diving into the intricacies of gamma hedging, it’s important to have a solid understanding of some fundamental concepts.
Options are financial derivatives that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified period of time. They are often used by traders and investors to speculate on price movements, hedge against risks, or generate income.
Gamma is a key options greek that measures the rate of change of an option’s delta in relation to changes in the price of the underlying asset. It quantifies how the delta of an option will change as the price of the underlying asset moves. A higher gamma indicates that the delta of the option is more sensitive to changes in the underlying asset’s price.
Read Also: Understanding ATR Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
Delta is another options greek that measures the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in the price of the underlying asset. It represents the expected change in the option’s price for a one-unit change in the price of the underlying asset. Delta can be positive for call options (as the option’s price increases with the underlying asset’s price) or negative for put options (as the option’s price decreases with the underlying asset’s price).
Hedging is a risk management strategy that involves taking an offsetting position to minimize potential losses or protect against adverse movements in the market. In options trading, gamma hedging aims to reduce the risk associated with delta changes by adjusting the position to maintain a desired delta level.
Gamma hedging involves buying or selling more of the underlying asset or options contracts to adjust the option’s delta. By gamma hedging, traders can neutralize the delta risk and ensure that the portfolio’s overall delta remains close to zero, regardless of changes in the underlying asset’s price.
By understanding the basics of options, gamma, delta, hedging, and gamma hedging, traders can lay the foundation for successfully navigating the complex world of gamma options trading.
Gamma hedging is a risk management strategy used by options traders to reduce their exposure to changes in the gamma of their options positions. Gamma measures the rate at which an option’s delta changes with respect to changes in the underlying asset’s price. By adjusting the delta of the options positions, traders can hedge against potential losses caused by changes in gamma.
Gamma hedging is important for options traders because it allows them to manage the risk associated with changes in an option’s delta. Since delta determines the change in an option’s value for a given change in the underlying asset’s price, gamma hedging helps traders protect their positions from adverse price movements and minimize potential losses.
There are several common gamma hedging techniques used by options traders, including dynamic hedging, gamma scalping, and delta-neutral hedging. Dynamic hedging involves adjusting the delta of the options positions as the underlying asset’s price changes. Gamma scalping involves actively trading the underlying asset to profit from changes in gamma. Delta-neutral hedging involves maintaining a delta-neutral position by adjusting the delta of the options positions whenever necessary.
To hedge gamma in options trading, you can use various strategies such as adjusting the delta of your options positions, trading the underlying asset to offset changes in gamma, or employing delta-neutral hedging techniques. It is important to monitor the gamma of your options positions and make proactive adjustments to maintain a desired risk profile.
Are Stocks Given by Company Taxable? Stocks are a common form of compensation given by companies to their employees. They can be an attractive …
Read ArticleCVS Stock Payout: Everything You Need to Know If you are a shareholder of CVS, you may be wondering about the payout for the stock. CVS Health is a …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Trend Continuation Factor Indicator When it comes to trading in the financial markets, having the right tools at your disposal can …
Read ArticleDiscover the Best EURUSD Scalping Strategy for Success When it comes to forex trading, the EURUSD currency pair is one of the most popular choices …
Read ArticleMastering Forex Chart Patterns: Expert Tips and Strategies When it comes to forex trading, understanding and analyzing chart patterns is crucial for …
Read ArticleWhat is the triple moving average crossover strategy? When it comes to trading financial markets, there are countless strategies to choose from. One …
Read Article