Everything you need to know about paying tax on vested shares in the UK
Do I pay tax on vested shares UK? When it comes to employee compensation, one common form of reward is through the issuance of shares in the company. …
Read Article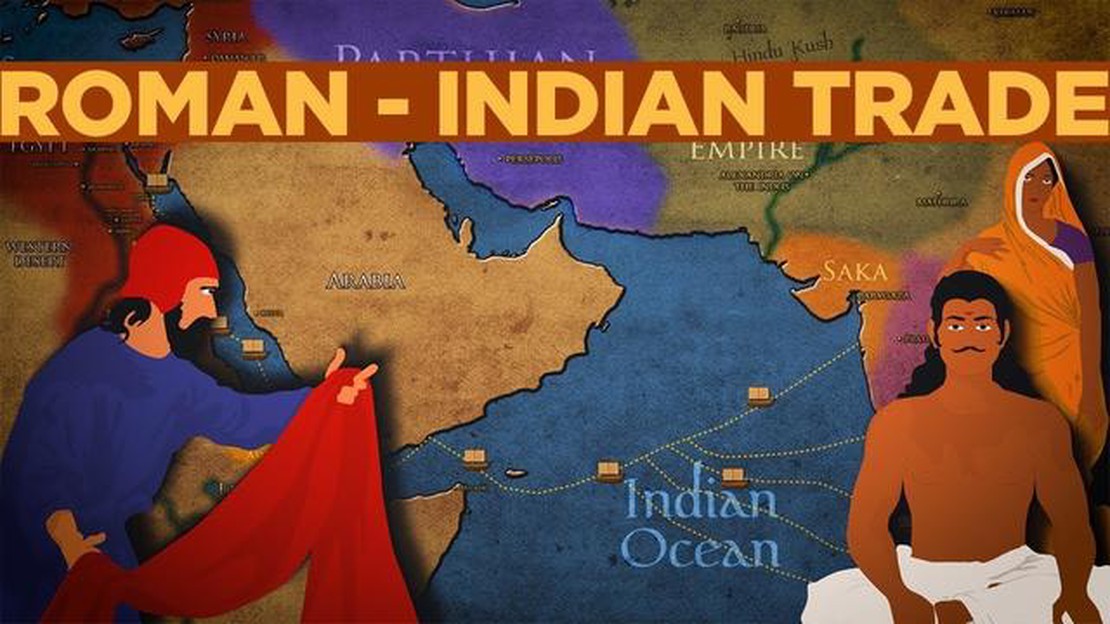
India has a long and rich history of trade, dating back thousands of years. The ancient trade system in India was not only significant for the economy, but also played a crucial role in shaping the country’s cultural and social fabric. This article explores the intricacies of the trade system in ancient India and highlights its impact on the development of the region.
The trade routes in ancient India, known as the “Silk Road of the Sea,” connected the country to various parts of the world. These trade routes stretched from the Arabian Sea in the west to the Bay of Bengal in the east, and were instrumental in facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. The Indian Ocean was a hub of maritime trade, with ships carrying silk, spices, precious metals, and other commodities.
One of the key factors that contributed to the success of the ancient trade system in India was the country’s geographical location. Situated in the heart of Asia, India served as a gateway between the East and the West. This strategic position allowed Indian merchants to establish trade links with neighboring countries such as China, Persia, and Egypt, as well as with distant lands like Rome and Greece.
The trade system in ancient India was not limited to maritime trade alone. Overland trade routes, known as the “Silk Road of the Land,” traversed the Indian subcontinent, connecting it to Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. These routes were used to transport goods such as textiles, spices, and precious stones. The trade routes also facilitated the exchange of knowledge and ideas, as traders, scholars, and travelers from different regions interacted with each other.
India has a rich history of trade that dates back thousands of years. The ancient trade system in India played a significant role in shaping the country’s economy, society, and culture.
One major influence of ancient trade in India was the introduction of new goods and technologies. Through trade, India established connections with various civilizations, leading to the exchange of commodities such as spices, textiles, and precious metals. These new goods not only enriched the Indian economy but also influenced the way of life of its people.
Ancient trade in India also had a profound impact on the social structure of the country. As trade routes expanded, cities grew and became centers of commerce and cultural exchange. This led to the emergence of a merchant class, which played a crucial role in the economy. Traders from different parts of the world settled in India, contributing to the diversity and cosmopolitan nature of the society.
Furthermore, trade in ancient India promoted the growth of urban settlements and infrastructure. To accommodate the increasing flow of goods, ports and markets were developed along coastal areas. This stimulated the construction of roads, bridges, warehouses, and other infrastructure, creating a more efficient and interconnected transport network. These developments not only facilitated trade but also fostered economic growth and regional integration.
The influence of ancient trade in India extended beyond the economic and social domains. It also had a profound impact on the cultural exchange and diffusion of ideas. As traders came into contact with people from different regions, they shared knowledge, traditions, and beliefs. This resulted in a blending of cultures and the spread of religious, artistic, and intellectual practices. For example, Indian mathematics and astronomy were greatly influenced by the knowledge brought by foreign traders.
In conclusion, the ancient trade system in India had a wide-ranging influence on the country. Through the exchange of goods and ideas, it enriched the economy, shaped society, and fostered cultural exchange. The legacy of ancient trade can still be seen in present-day India, where trade continues to be a vital component of the country’s growth and development.
The ancient trade routes of India were instrumental in the development and growth of the Indian civilization. They connected India with various parts of the world, fostering the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices. These trade routes spanned vast distances and were crucial for the economic prosperity of ancient India.
One of the most significant trade routes was the Silk Road, which connected China, Central Asia, and India. This route played a vital role in the trade of silk, spices, and other luxury goods. It facilitated the cultural exchange between these regions, leading to the spread of Buddhism from India to other parts of Asia.
Read Also: Is the World Trade Organization (WTO) a Trading Organization?
Another important trade route was the maritime route, which connected India with the countries of Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Arabian Peninsula. This route enabled the trade of goods like spices, textiles, and precious metals. The Indian Ocean served as a major hub for maritime trade, with ports like Kaveripattinam and Muziris flourishing as vibrant trading centers.
The ancient trade routes of India also extended to the west, with the overland route to the Mediterranean. This route connected India with the Roman Empire and allowed for the exchange of goods like spices, textiles, and precious metals. The trade between India and Rome was highly lucrative and greatly enriched both civilizations.
The trade routes of ancient India not only facilitated the movement of goods but also led to the exchange of ideas and knowledge. It promoted cultural diversity and fostered the growth of Indian civilization. Moreover, these trade routes played a crucial role in the spread of Buddhism and Hinduism to other parts of the world.
In conclusion, the ancient trade routes of India were essential for its economic prosperity and cultural development. They connected India with different regions of the world and facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas. These trade routes played a significant role in shaping the history and civilization of ancient India.
India’s ancient trade system played a crucial role in shaping its economy and had far-reaching impacts on both the domestic and international fronts.
One of the most significant economic impacts of India’s trade system was the influx of wealth and resources into the country. Through its trade routes, India established robust commercial connections with various regions and nations, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences. This resulted in a flow of commodities such as spices, textiles, precious metals, and gems into India, enhancing the country’s wealth and contributing to its economic prosperity.
Read Also: Using ChatGPT for Forex Trading: Exploring the Possibilities
In addition to the acquisition of wealth, India’s trade system also spurred the development of industries and manufacturing. Through trade, Indian artisans and craftsmen were exposed to new techniques and designs, leading to the evolution of local industries and the production of high-quality goods. This led to an increase in trade specialization and the emergence of renowned Indian products, such as silk and cotton textiles, which attracted demand from both domestic and foreign markets.
Moreover, India’s trade system had a profound impact on employment and livelihoods. As trade routes expanded, more individuals were engaged in diverse economic activities along these routes. Traders, merchants, and skilled workers found new opportunities and employment prospects, resulting in the growth of urban centers and the establishment of trade hubs. This led to an increase in economic activities, innovation, and productivity, improving the overall standard of living for many.
India’s trade also played a central role in fostering cultural exchange and the diffusion of knowledge and ideas. As merchants traveled across vast distances, they inadvertently brought with them not just goods but also cultural influences, customs, beliefs, and intellectual knowledge. This exchange of ideas and cultural practices enriched India’s society, leading to the growth of arts, literature, and architecture. It also resulted in the spread of Indian ideas and philosophies to other regions of the world, contributing to the global intellectual heritage.
In conclusion, the ancient trade system of India had a profound economic impact on the country. It led to an influx of wealth, the growth of industries, the expansion of employment opportunities, and the exchange of cultural and intellectual ideas. The effects of India’s trade system can still be felt today, as the nation continues to engage in global trade and harness its rich historical legacy.
The major trade routes in ancient India were the Silk Route, the Spice Route, the Incense Route, and the Gangetic trade route.
The ancient Indian trade system was based on a barter system, where goods were exchanged for other goods. Merchants traveled long distances along trade routes, carrying goods such as textiles, spices, precious stones, and metals. These goods were then traded with other regions or exported to foreign countries.
Ancient India traded a wide range of goods. Some of the main goods traded were textiles, spices like pepper and cinnamon, precious stones like diamonds and emeralds, metals like gold and silver, and luxury items like perfumes and silk.
The ancient Indian trade system played a crucial role in the economy. It created opportunities for economic growth, stimulated the production of goods, and facilitated cultural exchange between different regions. The trade also helped in the spread of knowledge and ideas, contributing to the overall development of the society.
Merchants in ancient India faced various challenges. They had to travel long distances through difficult terrains and face the risk of bandits or natural disasters. The lack of proper infrastructure and transportation also posed challenges. Additionally, merchants had to deal with different languages, currencies, and customs in the regions they traded with.
The ancient trade system in India was highly developed and complex. It involved both internal and external trade routes, with a wide variety of goods being traded.
Do I pay tax on vested shares UK? When it comes to employee compensation, one common form of reward is through the issuance of shares in the company. …
Read ArticleQuick Ways to Earn 500 Coins in Dragon Adventures Dragon Adventures is an exciting game where players get to explore a magical world filled with …
Read ArticleTD Ameritrade Forex Spread: Complete Guide and Analysis Forex trading is a popular investment option for those looking to diversify their portfolio …
Read ArticleHow to trade in Vanguard? Are you new to investing and looking for a reliable platform to start your trading journey? Look no further than Vanguard. …
Read ArticleForex Factory Operating Hours Forex trading is a decentralized global market where traders buy and sell currencies. As the market is open 24/5, it is …
Read ArticleCreating a Basic Trading Strategy: Step-by-Step Guide Trading in the financial markets can be a complex and daunting task, especially for beginners. …
Read Article