How to display spread in MetaTrader 4: A step-by-step guide
How to Display Spread in MetaTrader 4 MetaTrader 4 is a popular trading platform used by traders all over the world. It offers a wide range of tools …
Read Article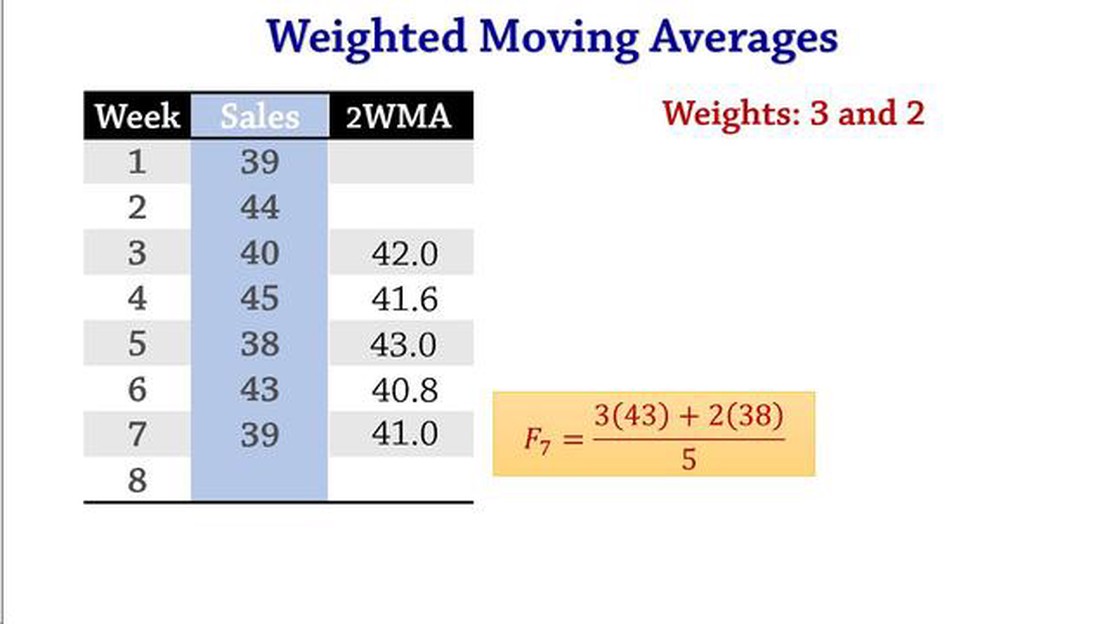
Accurate forecasting is crucial for businesses in making informed decisions and planning for the future. One popular method used for forecasting is the weighted moving average, which takes into account the importance or weight of each data point. By assigning weights to the data points, the weighted moving average gives more weight to recent data, reflecting the changing trends and patterns in the data.
The weighted moving average is especially useful when there are anomalies or outliers in the data, as it helps smooth out the fluctuations and provides a more accurate forecast. This method is widely used in various industries, such as finance, sales, marketing, and supply chain management, to predict future trends and make strategic decisions.
In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of using the weighted moving average for accurate forecasting. We will cover how to determine the weights for each data point, how to calculate the weighted moving average, and how to interpret the results. With this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge and skills to make more accurate forecasts for your business.
Note: It is important to note that the weighted moving average is just one method for forecasting and may not be suitable for all types of data. It is essential to assess the characteristics of your data and consider other forecasting methods as well. Additionally, the accuracy of the forecast depends on the quality and completeness of the data used.
Accurate forecasting is crucial for businesses and individuals alike, as it helps in making informed decisions and planning for the future. One commonly used method for forecasting is the weighted moving average, which takes into account the importance or weight of different data points. In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of using the weighted moving average technique for accurate forecasting.
Before diving into the implementation, it is essential to grasp the concept of weighted moving average. Unlike the simple moving average, where all data points have equal importance, the weighted moving average assigns different weights to each data point depending on their significance. This allows for more accurate forecasting, as it focuses on the recent and relevant data points.
The next step is to collect the relevant data that you want to forecast. Ensure that you have a sufficient amount of historical data points to make accurate predictions. Organize the data in a spreadsheet or any other suitable format for analysis.
Assign different weights to each data point based on their importance. The weights can be determined based on expert knowledge, historical performance, or any other relevant factors. The sum of the weights should be equal to 1 to ensure that the forecast remains accurate.
To calculate the weighted moving average, multiply each data point by its corresponding weight and sum up the products. For example, if you have three data points with weights of 0.3, 0.4, and 0.3, you would multiply the first data point by 0.3, the second data point by 0.4, and the third data point by 0.3. Then, sum up the three products to get the weighted moving average.
As new data becomes available, update the forecast by incorporating the new data point and adjusting the weights accordingly. This will ensure that the forecast remains accurate and up-to-date.
Regularly evaluate the accuracy of your forecasts by comparing them to the actual outcomes. This will help you assess the performance of the weighted moving average method and make any necessary adjustments to improve future forecasts.
Read Also: Understanding the Timeframe H4 Strategy: A Guide for Forex Traders
By following these step-by-step instructions, you can effectively utilize the weighted moving average technique for accurate forecasting. Remember to regularly review and update your forecasts to ensure their reliability and relevance in an ever-changing business environment.
The weighted moving average is a statistical technique used for forecasting future data points by giving different weights to different periods within a time series. It is an extension of the simple moving average method, where all periods have equal weights.
In a weighted moving average, more recent data points are given higher weights, indicating that they should have a greater influence on the forecast. This is based on the assumption that recent events may have a stronger impact on future trends compared to older events.
The process of calculating the weighted moving average involves assigning weights to each period within a time series and then calculating the average of the weighted values. The weights can be determined based on various factors, such as the importance of recent periods or the expected volatility of the data.
One common method of assigning weights in a weighted moving average is the triangular method, where the weights decrease linearly as the periods move away from the most recent data point. For example, if we are using a 5-period weighted moving average, the weights could be assigned as follows:
| Period | Weight |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 0.1 |
Read Also: Find the Best Exchange Rates in Qatar and Save Money
Once the weights are assigned, the weighted moving average can be calculated by multiplying each data point by its corresponding weight, summing the weighted values, and then dividing by the sum of the weights.
The weighted moving average is beneficial for forecasting when there is a need to give more importance to recent data points or when there is an expectation of changing trends over time. However, it is important to note that the selection of weights can significantly impact the forecast accuracy, and it may require some trial and error or statistical analysis to find the optimal weights for a specific time series.
A weighted moving average is a type of moving average where different weights are assigned to each data point in the average calculation.
The weighted moving average differs from the simple moving average because it assigns different weights to each data point, whereas the simple moving average assigns equal weights to all data points.
You might want to use a weighted moving average for forecasting because it allows you to place more emphasis on certain data points that you believe are more important or relevant to the forecast.
To calculate the weighted moving average, you need to multiply each data point by its assigned weight, sum up the products, and then divide the sum by the total weight assigned. This gives you the weighted moving average.
Sure! Let’s say you have sales data for the past 12 months, and you want to forecast sales for the next month. You can assign higher weights to the more recent months and lower weights to the earlier months. By calculating the weighted moving average using these weights, you can get a more accurate forecast for the next month’s sales.
Weighted moving average is a statistical technique used for forecasting that assigns different weights to different time periods. It gives more importance to recent data points while calculating the average, allowing for accurate predictions in situations where there is a trend or change in the data over time.
To calculate weighted moving average, you need to assign weights to each data point based on the importance of the time period. Multiply each data point by its corresponding weight, sum up the products, and divide by the sum of the weights. The formula is: Weighted Moving Average = (w1 * y1 + w2 * y2 + … + wn * yn) / (w1 + w2 + … + wn), where w represents the weights and y represents the data points.
How to Display Spread in MetaTrader 4 MetaTrader 4 is a popular trading platform used by traders all over the world. It offers a wide range of tools …
Read ArticleItaly: Country of the FTSE MIB Index The FTSE MIB Index is a market index that represents the performance of Italy’s major companies listed on the …
Read ArticleHow to Calculate Movement Inventory Understanding and managing inventory movement is a critical aspect of a successful business. Accurately …
Read ArticleHow to Persuade Clients to Invest in Forex Forex investments have become increasingly popular in recent years, offering individuals the opportunity to …
Read ArticleEffective Advertising Strategies for Trading Are you looking for ways to attract more customers and increase your trading business? Advertising is the …
Read ArticleAre options level 1 or 2? Options trading can be a lucrative way to invest in the financial markets. However, it can also be complex and intimidating …
Read Article