What Country is CAC Futures From?
What country is CAC futures? When it comes to trading financial futures, it’s important to understand where the market originates from. One of the …
Read Article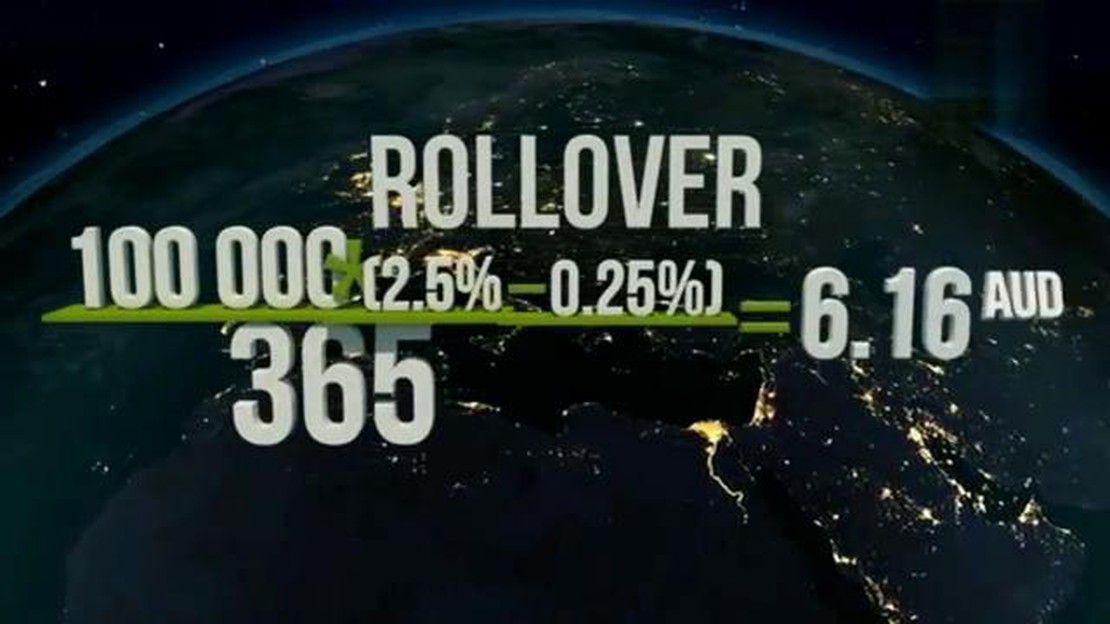
In the world of foreign exchange (FX) trading, one strategy that often comes up is rolling forward FX. This strategy is used by traders to extend the expiration date of a currency contract, allowing them to maintain their market position. It can be a useful tool for managing risk and taking advantage of potential market opportunities.
Rolling forward FX involves closing out an existing currency contract and entering into a new contract with a later expiration date. This can be done for various reasons, such as when the original contract is nearing its expiration and the trader wants to maintain their exposure to a particular currency pair.
The process of rolling forward FX typically involves paying or receiving a rollover fee, which is the difference in interest rates between the two currencies in the currency pair. For example, if a trader is rolling forward a long position in a currency pair with a higher interest rate and rolling it into a new contract with a lower interest rate, they would be required to pay a rollover fee.
Traders need to carefully consider the costs and benefits of rolling forward FX. While it can be a way to extend a trading position and potentially profit from further market movements, it also comes with costs in the form of rollover fees. It’s important for traders to assess their individual risk tolerance and market outlook before deciding whether to roll forward their FX positions.
In conclusion, rolling forward FX is a strategy used by traders to extend the expiration date of a currency contract. It can be a useful tool for managing risk and taking advantage of market opportunities. However, traders need to carefully consider the costs and benefits before deciding to roll forward their FX positions. By understanding the intricacies of rolling forward FX, traders can make informed decisions and better navigate the world of foreign exchange trading.
Rolling forward FX is a strategy used in foreign exchange (FX) trading to extend the maturity date of a futures contract. It allows traders to maintain their positions beyond the original expiration date, giving them more time to capture potential gains or hedge against currency fluctuations.
When a futures contract is nearing its expiration, traders have three options: close the position, roll it forward, or use physical delivery. While closing the position ends any further exposure to the contract, it may not be the desired outcome if there is still profit potential. Physical delivery requires the actual delivery of the underlying currency, which may not be practical or cost-effective.
Rolling forward, on the other hand, involves closing the existing futures contract and simultaneously opening a new contract with a later maturity date. This allows traders to maintain their exposure to the underlying currency without the need for physical delivery. The new contract will have its own expiration date, which can be chosen based on the trader’s preferred timeframe.
One of the main reasons traders choose to roll forward FX contracts is to avoid disruption in their trading strategies. By extending the maturity date, they can continue to benefit from favorable exchange rate movements or protect against potential losses. Rolling forward also provides flexibility in adjusting positions based on changing market conditions or new information.
Read Also: What is P&? All You Need to Know
When rolling forward FX contracts, traders should consider several factors. These include the cost of rolling, which can vary depending on the interest rate differentials between the two currencies involved. Traders should also consider any potential market impact from the roll as well as the overall cost-effectiveness of the strategy.
In conclusion, rolling forward FX contracts is a useful strategy for extending the maturity date of futures contracts in foreign exchange trading. It allows traders to maintain exposure to the underlying currency without physical delivery and provides flexibility in adapting to market conditions. Understanding the factors involved and carefully considering the costs and benefits can help traders make informed decisions when rolling forward their FX positions.
Forward exchange rates are an important concept in the world of foreign exchange. They refer to the exchange rate at which a currency can be bought or sold for delivery at a future date. Unlike spot exchange rates, which are for immediate delivery, forward exchange rates allow for hedging against potential currency fluctuations in the future.
Understanding Forward Exchange Rates:
Forward exchange rates are determined by the interplay of several factors, including interest rates, inflation rates, economic indicators, and market expectations. These rates are quoted for different time periods, such as one month, three months, or even a year in the future.
Forward exchange rates are quoted as a premium or discount to the spot exchange rate. A currency is said to be trading at a premium if the forward exchange rate is higher than the spot rate, indicating that the future value of the currency is expected to be higher. On the other hand, a currency is trading at a discount if the forward exchange rate is lower than the spot rate, suggesting that the future value of the currency is expected to be lower.
Uses of Forward Exchange Rates:
Forward exchange rates play a crucial role in managing currency risk for businesses and investors. By entering into a forward contract, they can lock in a specific rate at which they can buy or sell a currency in the future. This helps them mitigate any potential losses due to adverse exchange rate movements.
Read Also: Will the Iraqi Dinar Revalue? Exploring the Possibility of a Currency Revaluation
Forward exchange rates are also used by speculators and arbitrageurs to take advantage of differences in exchange rates between different markets. They can buy a currency at a lower forward rate in one market and sell it at a higher spot rate in another market, making a profit from the difference.
Risks Associated with Forward Exchange Rates:
While forward exchange rates provide a valuable tool for managing currency risk, they also come with their own set of risks. If the market expectations turn out to be incorrect, businesses and investors may end up losing money. Additionally, there may be unforeseen events or changes in economic conditions that can significantly impact exchange rates, making forward contracts less effective.
In conclusion, forward exchange rates are an essential aspect of the foreign exchange market. They allow businesses and investors to hedge against potential currency fluctuations and manage their currency risk effectively. However, it’s important to carefully assess the factors and risks associated with forward exchange rates before making any decisions.
Rolling forward in the FX market refers to the process of extending the maturity date of a forward contract. It allows market participants to extend the time frame of their foreign exchange transaction, usually to avoid physical delivery of the currency.
Market participants use rolling forward in the FX market for various reasons. One common reason is to manage their currency exposure by extending the hedging period of their forward contracts. By rolling forward, they can continue to protect themselves from adverse currency movements. Additionally, rolling forward can help market participants align the maturity dates of their forward contracts with their cash flow needs.
Rolling forward in the FX market is typically done through a rollover or swap transaction. In a rollover, the existing forward contract is closed out at the current market rate, and a new forward contract is entered into with a new maturity date. The cost or benefit of the rollover is determined by the interest rate differential between the two currencies involved in the transaction. Market participants can also roll forward their positions through a swap transaction, where they exchange one currency for another at the current spot rate and simultaneously enter into a new forward contract.
Yes, there can be costs associated with rolling forward in the FX market. The cost or benefit of rolling forward is determined by the interest rate differential between the two currencies involved in the transaction. If the interest rate of the currency being bought is higher than the interest rate of the currency being sold, market participants may receive a benefit from rolling forward. Conversely, if the interest rate of the currency being sold is higher, market participants may incur a cost for rolling forward. Additionally, there may be transaction costs involved in executing the rollover or swap transaction.
What country is CAC futures? When it comes to trading financial futures, it’s important to understand where the market originates from. One of the …
Read ArticleGuide to Nifty Trading: Tips and Strategies Interested in the stock market but not sure where to start? Look no further! This comprehensive guide will …
Read ArticleCan you make money just trading spy? Trading the SPY, or the S&P 500 Index fund, has become increasingly popular among individual investors. With its …
Read ArticleOptions Trading in the UK: Everything You Need to Know Options trading is a popular investment strategy in the UK, offering individuals the …
Read ArticleIs Covered Call a bullish strategy? When it comes to investing, there are various strategies that traders employ to maximize returns and minimize …
Read ArticleUnderstanding 25 Delta Skew: A Complete Guide Options trading is a complex and dynamic field that requires traders to constantly adapt to changing …
Read Article