Understanding additive models in time series analysis: a comprehensive guide
Understanding the Additive Model in Time Series Analysis When analyzing time series data, it is often important to understand and predict the …
Read Article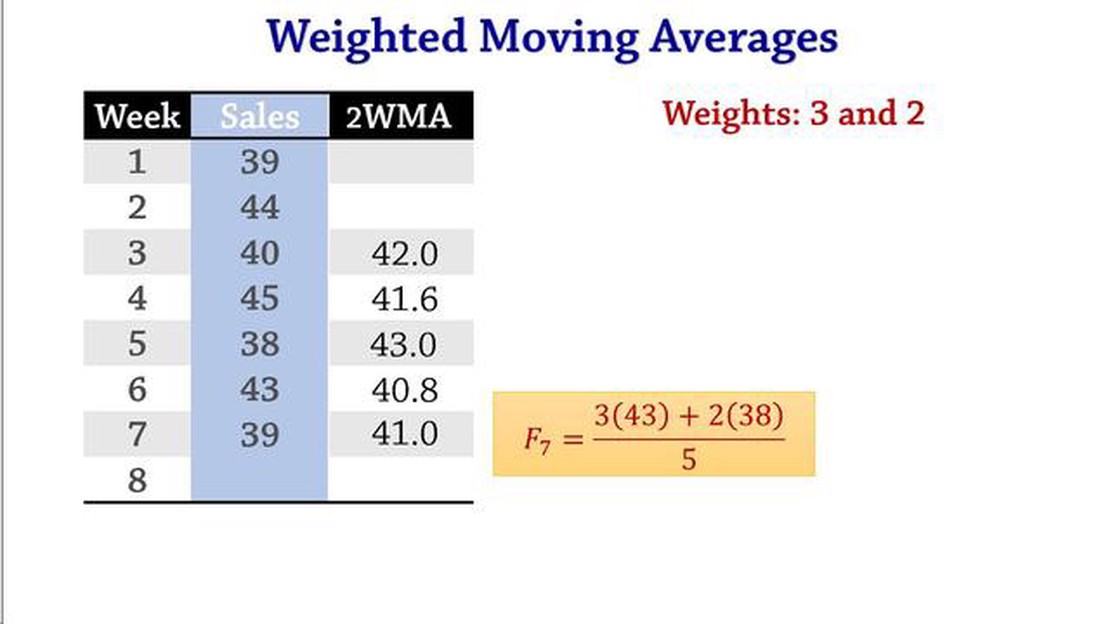
When it comes to analyzing data trends and making forecasts, moving averages are a popular tool used by analysts and investors. But what exactly is a moving average, and is it a weighted average or a simple average?
At its core, a moving average is a calculation that allows us to smooth out fluctuations and identify the underlying trends present in a dataset. It is commonly used to analyze stock prices, economic indicators, and other time series data.
A simple moving average (SMA) is the most basic form of moving average. It calculates the average of a set of data points over a specified period of time. Each data point has the same weight in the calculation, hence the term “simple” average.
A weighted moving average (WMA), on the other hand, assigns different weights to each data point in the calculation. This means that recent data points have a higher impact on the average than older data points. The weights are typically based on a predefined formula or subjective judgment.
So, to answer the question, a moving average can be either a weighted average or a simple average. The choice depends on the specific needs and objectives of the analysis. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to understand and consider these factors when applying moving averages in your analysis.
When it comes to analyzing data trends and patterns, moving averages are a commonly used statistical tool. Moving averages help smooth out fluctuations in data and provide a clearer picture of the overall trend. However, there are different types of moving averages, and one of the main distinctions is between weighted and simple averages.
A moving average is a calculation that takes the average of a set of data points over a specific period of time. The period of time could be daily, weekly, monthly, or any other interval depending on the data being analyzed. The moving average is recalculated for each new data point, creating a moving window of averages that shift along the timeline.
A simple moving average, as the name suggests, is calculated by taking the arithmetic mean of the data points over the specified period. Each data point is given equal weight in the calculation, regardless of its position in the time series. This means that the oldest and newest data points have the same influence on the moving average.
For example, if we have a 5-day SMA, we would add up the data points from the past 5 days and divide by 5 to get the average. The process is repeated for each new data point, using the most recent 5 days of data. This simple algorithm provides a straightforward and easy-to-understand calculation for the moving average.
A weighted moving average, on the other hand, assigns different weights to the data points based on their position in the time series. The weights are usually determined by a predefined weighting scheme, such as an exponential or triangular weighting.
With a weighted average, more recent data points are given greater importance, while older data points have less influence on the moving average. This makes the weighted moving average more responsive to recent changes in the data and can help capture short-term trends more effectively.
Read Also: Can Non-Employees Receive Incentive Stock Options? Exploring the Possibility
For example, a 5-day WMA might assign weights of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1 to the most recent 5 data points, with the highest weight given to the newest data point. The weighted moving average is then calculated by summing up the products of each data point and its corresponding weight, and dividing by the sum of the weights.
While both weighted and simple moving averages have their merits, the choice between the two depends on the specific data being analyzed and the desired outcome. Simple moving averages are easier to calculate and understand, making them ideal for beginners or situations where simplicity is key.
Weighted moving averages, on the other hand, provide a more accurate representation of recent changes in the data and are more suitable for capturing short-term trends. They require a more complex calculation but can offer more insights for experienced analysts.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between weighted and simple moving averages is crucial for making informed decisions when analyzing data trends. Both types of moving averages have their applications and provide valuable insights, so it is important to choose the right one based on the specific data set and analysis goals.
Moving Average is a statistical calculation used to analyze data points over a certain period of time. It provides a smoothed representation of the data by calculating the average value of a set of data points within a specified time frame. The Moving Average is widely used in various fields, including finance, economics, and signal processing.
The Moving Average helps to identify trends and patterns in the data by removing short-term fluctuations and noise. It is particularly useful in situations where the data is noisy or contains random variations, as it provides a clearer and more stable picture of the underlying trend.
Read Also: Reasons executives are given stock options and their benefits
There are different types of Moving Averages, including the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and the Weighted Moving Average (WMA). The Simple Moving Average calculates the average by equally weighting all data points within the time frame. On the other hand, the Weighted Moving Average assigns different weights to each data point, giving more importance to recent data.
| Type | Calculation Method | Equal Weighting | Weighted by Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Moving Average (SMA) | Sum of data points / Number of data points | Yes | No |
| Weighted Moving Average (WMA) | (Sum of (data point * weight)) / Sum of weights | No | Yes |
Both types of Moving Averages have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use depends on the specific requirements of the analysis. In general, the Simple Moving Average is simpler to calculate and provides a smoother representation of the data, while the Weighted Moving Average gives more weight to recent data points, making it more responsive to changes in the underlying trend.
A moving average is a statistical calculation that is used to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set. It is a commonly used technique in technical analysis to identify trends and patterns in data.
A moving average can be either a weighted average or a simple average, depending on the specific method used. Simple moving average (SMA) gives equal weightage to all data points, while exponential moving average (EMA) assigns more weight to recent data points and less weight to older data points.
The formula for calculating a simple moving average involves summing up a certain number of data points and dividing the total by the number of data points. For example, to calculate a 10-day simple moving average, you would add up the closing prices of the last 10 days and divide the sum by 10.
A weighted moving average assigns different weights to different data points, whereas a simple moving average gives equal weightage to all data points. This means that recent data points have a greater impact on the weighted moving average compared to older data points.
Using a moving average can help to smooth out fluctuations in data and highlight trends or patterns. It can also be used to generate trading signals in financial markets and is a popular tool for technical analysts.
A moving average is a calculation used to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different subsets of the full data set. Moving averages can be calculated using a weighted average or a simple average.
Understanding the Additive Model in Time Series Analysis When analyzing time series data, it is often important to understand and predict the …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the 4 Week Rule in Forex Trading Forex trading is an exciting and challenging market that offers numerous opportunities for profit. With …
Read ArticleImpact of Option Trading on Index Price Option trading plays a critical role in influencing the overall price movement of stock market indices. As …
Read ArticleHow to Purchase Digital Currency in SBI If you’re interested in buying digital currency and are a customer of the State Bank of India (SBI), you’re in …
Read ArticleWhat indicators do banks use? Banks are complex financial institutions that play a crucial role in the economy. They provide a wide range of financial …
Read ArticleIs IG trading platform safe? The safety and security of an online trading platform are paramount concerns for any investor. With the increasing …
Read Article