How Much Start-Up Capital Do You Need for Trading?
How much start-up capital do you need for trading? Starting a trading business can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture, but it requires …
Read Article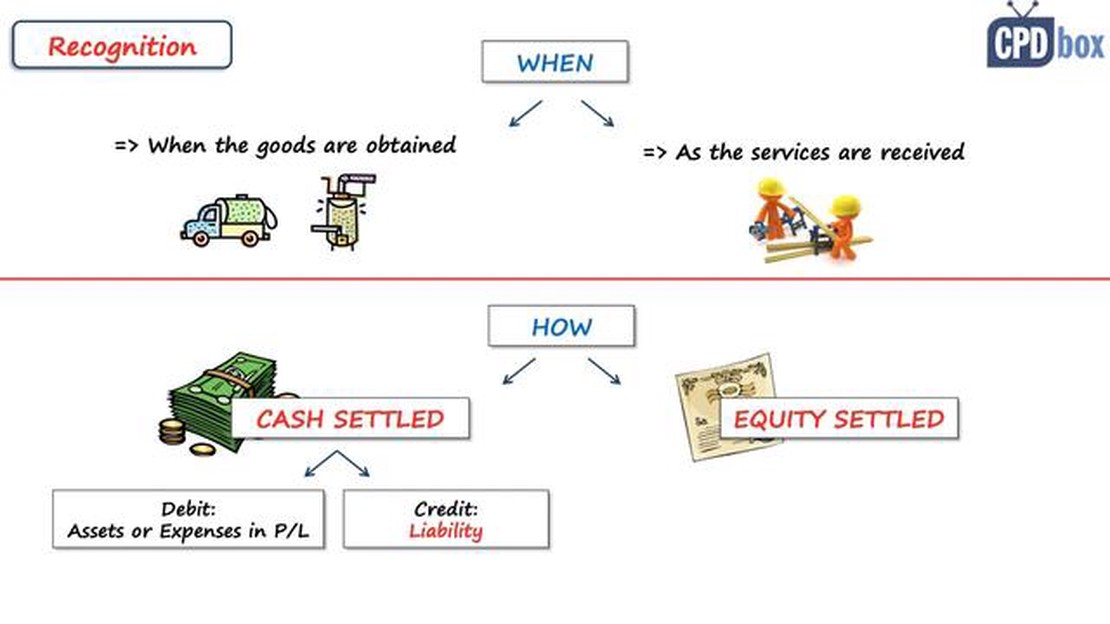
IFRS 2, which stands for International Financial Reporting Standard 2, provides guidance on the accounting treatment for employee share-based compensation. This standard aims to ensure transparency and accuracy in reporting the cost of employee services received in exchange for equity instruments, such as stock options or shares.
Employee share-based compensation is a common practice used by companies to attract and retain talent. It refers to the granting of equity instruments to employees as part of their remuneration package. These equity instruments can be in the form of stock options, restricted shares, or other similar instruments.
Under IFRS 2, companies are required to recognize the fair value of employee services received in exchange for equity instruments as an expense in their financial statements. This expense is recognized over the vesting period, which is the period over which employees become entitled to the equity instruments granted to them.
The fair value of the equity instruments granted is determined at the grant date, taking into account any conditions or restrictions attached to the instruments. Companies are required to estimate the fair value using appropriate valuation techniques, such as option pricing models.
In conclusion, IFRS 2 provides important guidance on how companies should account for employee share-based compensation. By following this standard, companies can ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect the cost of employee services received in exchange for equity instruments. This promotes transparency and helps investors and other stakeholders make informed decisions.
IFRS 2 provides guidance on accounting for share-based compensation arrangements in which an entity receives goods or services from its employees or other parties as a form of consideration for equity instruments (including shares or share options). The standard aims to ensure that companies recognize the cost of employee services received in exchange for equity instruments and to provide relevant information about such transactions in the financial statements.
Under IFRS 2, the fair value of the equity instruments granted is recognized as an expense over the vesting period, which is the period during which an employee is required to provide services to earn the equity instruments. The expense is recognized in the income statement and credited to equity. The accounting treatment varies depending on whether the equity instruments are classified as equity-settled or cash-settled.
Equity-settled share-based payment transactions are those in which an entity receives goods or services as consideration for equity instruments of the entity, where the entity has no choice as to the settlement method. When the equity instruments are equity-settled, the fair value of the goods or services received is recognized as an expense over the vesting period.
Cash-settled share-based payment transactions are those in which an entity receives goods or services as consideration for equity instruments of the entity, where the entity has a choice as to the settlement method. In these transactions, the fair value of the goods or services received is recognized as a liability. The liability is remeasured at each reporting date until settlement, with any changes in fair value recognized in the income statement.
Read Also: Discover the top options newsletter for maximizing your investment potential
IFRS 2 also requires extensive disclosures about share-based payment transactions, including information about the measurement of fair value, the terms and conditions of the arrangements, and the effect on the financial statements.
By providing guidance on employee share-based compensation, IFRS 2 promotes transparency and comparability in financial reporting, helping users of financial statements to make informed decisions about the financial performance and position of an entity.
IFRS 2: Guidance on Employee Share-Based Compensation is a standard issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) that provides guidance on accounting for share-based payment transactions with employees.
Share-based payment transactions are a common method used by companies to compensate their employees. This can include granting share options, shares, or other equity instruments to employees as part of their remuneration package. IFRS 2 aims to provide consistent and transparent accounting treatment for these transactions.
Under IFRS 2, companies are required to recognize the fair value of share-based payments as an expense in their financial statements. The fair value is the amount at which the equity instruments could be exchanged between knowledgeable and willing parties in an arm’s length transaction.
The standard also requires companies to recognize a corresponding increase in equity as a separate component of shareholders’ equity. This ensures that the expense is properly allocated and does not impact the company’s overall profitability.
Read Also: Today's 1 Tola Gold Price in Pakistan - Check Current Rates
IFRS 2 includes detailed guidance on the measurement of share-based payment transactions, including how to determine the fair value of equity instruments. It also provides guidance on the accounting treatment for modifications, cancellations, and settlements of share-based payment transactions.
Furthermore, the standard requires extensive disclosures in the financial statements to provide users with relevant information about the nature and extent of the share-based payment transactions, as well as their impact on the company’s financial position and performance.
In summary, IFRS 2 provides companies with clear guidelines on how to account for share-based payment transactions with employees. By requiring the recognition of the fair value of these transactions, the standard aims to improve transparency and comparability in financial reporting.
IFRS 2 is an accounting standard that provides guidance on how to account for share-based compensation that companies provide to their employees. It outlines the requirements for measuring and recognizing the costs of share-based payment transactions, as well as the disclosure requirements for share-based payment transactions.
IFRS 2 covers a wide range of share-based compensation, including equity-settled share-based payments, where the company grants equity instruments to its employees; cash-settled share-based payments, where the company grants cash to its employees based on the price of its equity instruments; and transactions where the company receives goods or services as consideration for equity instruments.
IFRS 2 requires companies to measure the fair value of the equity instruments granted to employees and recognize this as an expense over the vesting period, which is the period during which the employees become entitled to the instruments. The expense is recognized in the income statement and the corresponding equity is recognized in the statement of changes in equity.
IFRS 2 requires companies to measure the fair value of the liability associated with the cash-settled share-based payment and recognize it as an expense over the vesting period. The liability is re-measured at each reporting date, with any changes in fair value being recognized in the income statement. The corresponding liability and equity are recognized in the statement of financial position and the statement of changes in equity.
IFRS 2 requires companies to disclose information about the nature and extent of share-based payment arrangements, including the accounting policy for share-based payments, key assumptions used in determining the fair value of equity instruments, and the amount of share-based compensation expense recognized in the financial statements. Companies are also required to disclose the number of equity instruments granted during the period, and the terms and conditions of the share-based payment arrangements.
How much start-up capital do you need for trading? Starting a trading business can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture, but it requires …
Read ArticleWhat days does not Opera Forex? Opera Forex is a popular online trading platform used by many traders around the world. While it is known for its …
Read ArticleWhat happens if I don’t exit on option expiry? Option trading can be an exciting and potentially lucrative way to participate in the financial …
Read ArticleAccounting for Stock Compensation: Understanding the Basics Stock compensation is a common practice in today’s business world, where companies offer …
Read ArticleHow to Become a Master in Forex Trading Forex trading can be a highly profitable venture, but it also comes with its fair share of risks. To succeed …
Read ArticlePros and Cons of Stock Warrants Stock warrants are a financial tool that grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a …
Read Article