Learn how to buy Novartis shares: a step-by-step guide
How to Purchase Novartis Shares If you are interested in investing in the pharmaceutical industry, Novartis could be a great option to consider. …
Read Article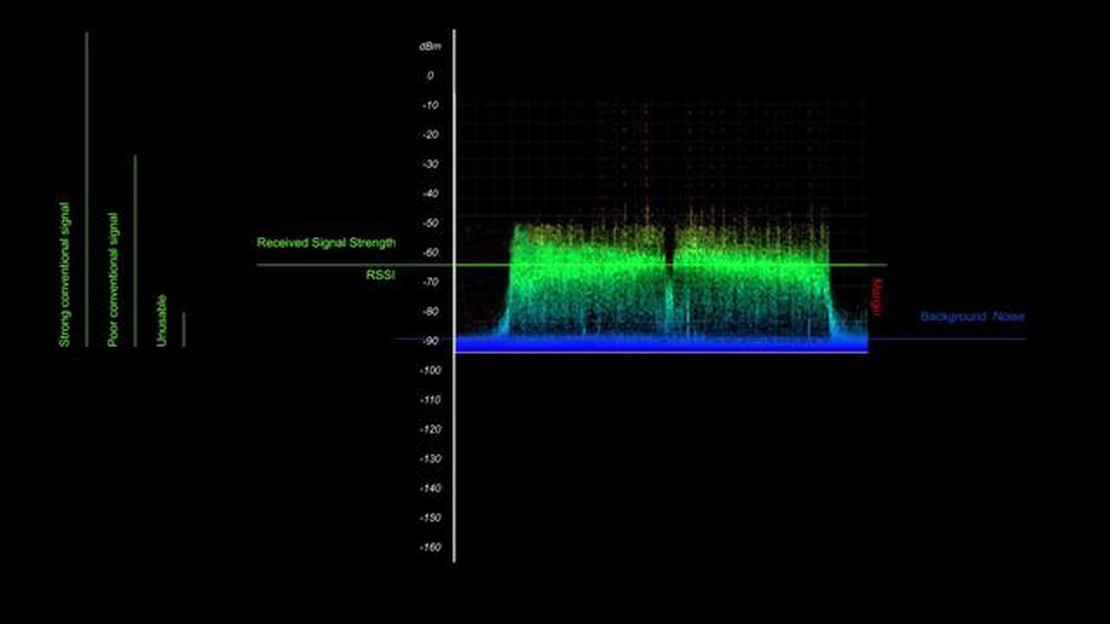
SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) is a measure of the quality and strength of a signal in comparison to the background noise. It is often used in communication systems to determine the reliability and clarity of a transmission. But how much SNR is considered good for optimal performance?
The answer to this question depends on the specific application and the desired level of performance. In general, a higher SNR is desirable because it reduces the impact of noise on the signal and improves the overall quality of the transmission. However, there is no universally accepted threshold for what constitutes a “good” SNR.
For some applications, such as voice communication, a minimum SNR of around 15 dB is often considered sufficient for clear and intelligible audio.
On the other hand, more sensitive applications, such as wireless data transmission or video streaming, may require a higher SNR to ensure reliable and error-free transmission. In these cases, SNR values in the range of 20-25 dB or higher may be necessary to achieve optimal performance.
It’s important to note that achieving a high SNR can be challenging in real-world scenarios, as various factors, such as distance, interference, and environmental conditions, can degrade the signal and introduce noise. Nevertheless, by properly designing and optimizing the communication system, it is possible to maximize the SNR and minimize the impact of noise for optimal performance.
In conclusion, the ideal SNR for optimal performance depends on the specific application and the level of reliability required. However, higher SNR values are generally preferred to ensure clearer and more reliable transmissions.
SNR stands for Signal-to-Noise Ratio, and it is a measure used in telecommunications and signal processing to quantify the ratio of the desired signal to the background noise. It is expressed in decibels (dB) and represents the quality of the signal being transmitted or received.
The signal refers to the information or data being transmitted, while the noise refers to the unwanted disturbances or interference that can be present in the signal. The higher the SNR, the clearer and more reliable the signal is, as there is less noise interfering with the desired signal.
SNR is an important factor in determining the performance of communication systems. It is crucial for ensuring that the signal being transmitted or received is accurately and effectively processed. A higher SNR generally indicates better performance, as it allows for a more accurate and reliable interpretation of the signal.
In telecommunications, a good SNR is necessary for optimum performance, especially in applications where high data rates or long transmission distances are involved. A high SNR can help minimize errors and signal distortions, leading to improved data integrity and overall system efficiency.
SNR also plays a significant role in various fields, such as audio processing, image processing, and wireless communications. It is used to evaluate the performance of audio systems, determine the quality of images, and assess the efficiency of wireless networks.
Read Also: Understanding Income Tax in Romania: A Comprehensive Guide
In summary, SNR is a critical metric that measures the ratio of the desired signal to the background noise in a communication system. It is important for achieving optimal performance, minimizing errors, and ensuring the accuracy and reliability of transmitted or received signals.
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a measure of the strength of a signal compared to the level of background noise. It is commonly used in various fields, including telecommunications, audio engineering, and image processing, to evaluate the quality and performance of a system.
Read Also: How to Calculate a 2-Year Moving Average: Step-by-Step Guide
The SNR is expressed as a ratio or in decibels (dB), where a higher value indicates a better signal quality. A strong signal with a high SNR means that the desired signal is much stronger than the background noise, resulting in clearer and more accurate transmission or processing. On the other hand, a low SNR indicates a weaker signal that is more susceptible to being corrupted or distorted by noise.
In telecommunications, a good SNR is generally considered to be around 20 dB or higher. This ensures minimal signal degradation and a reliable connection. However, the desired SNR may vary depending on the specific application and the level of noise present in the environment.
For audio engineering, a SNR of 90 dB or above is considered excellent, providing a high level of clarity and fidelity. High-quality audio equipment and recording techniques aim to achieve a high SNR to reproduce sound accurately and without unwanted noise.
In image processing, a higher SNR is desirable for better image quality. This enables the preservation of fine details and the reduction of image artifacts caused by noise. The minimum acceptable SNR may vary depending on the specific application, but generally, an SNR of 30 dB or higher is considered good.
It is important to note that SNR alone does not provide a complete measure of system performance. Other factors, such as bandwidth, distortion, and signal-to-interference ratio, also play a significant role in determining overall system quality. Therefore, it is crucial to consider multiple parameters when evaluating the performance of a system.
In summary, understanding the signal-to-noise ratio is essential for assessing the quality and performance of communication systems, audio equipment, and image processing systems. A higher SNR generally indicates better performance, but the desired SNR may vary depending on the specific application and environmental conditions.
SNR stands for Signal-to-Noise Ratio, and it represents the ratio of the power of a signal to the power of the background noise. In terms of performance, a higher SNR generally indicates a clearer and more reliable signal, leading to better performance.
The recommended SNR value for optimal performance can vary depending on the specific application. However, in general, an SNR of 20 dB or higher is considered good for most scenarios. Higher SNR values are always better, as they provide a stronger signal and minimize the impact of noise.
When the SNR is low, it means that the signal is weaker compared to the background noise. This can lead to degraded performance as the signal may become indistinguishable from the noise, causing errors or loss of information. A low SNR can result in decreased data transmission rates, poor audio or video quality, and overall decreased reliability.
While a high SNR generally indicates better performance, there can be situations where an excessively high SNR may not necessarily improve performance further. In some cases, a very high SNR can result in an overamplification of the signal, leading to distortion or other undesired effects. It is important to find the optimal balance for each specific application to achieve the best possible performance.
How to Purchase Novartis Shares If you are interested in investing in the pharmaceutical industry, Novartis could be a great option to consider. …
Read ArticleCurrency Code for Myanmar Kyat Myanmar kyat is the official currency of Myanmar, a country located in Southeast Asia. The currency code for the …
Read ArticleHow much can a trader earn? Trading has long been an enticing career path for those seeking potentially high earnings and financial independence. With …
Read ArticleFinding the moving average in Minitab: a step-by-step guide Calculating moving averages is a common statistical technique used to analyze time series …
Read ArticleWhat is the AVG expression in Access? When working with data in Microsoft Access, it is common to perform calculations and aggregate functions to …
Read ArticleHow long does it take to learn forex? Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the buying and selling of currencies on the foreign …
Read Article