Understanding the Role of Genetic Algorithms in Quantitative Finance
Understanding Genetic Algorithms in Quantitative Finance Quantitative finance is a field that combines mathematical models and statistical techniques …
Read Article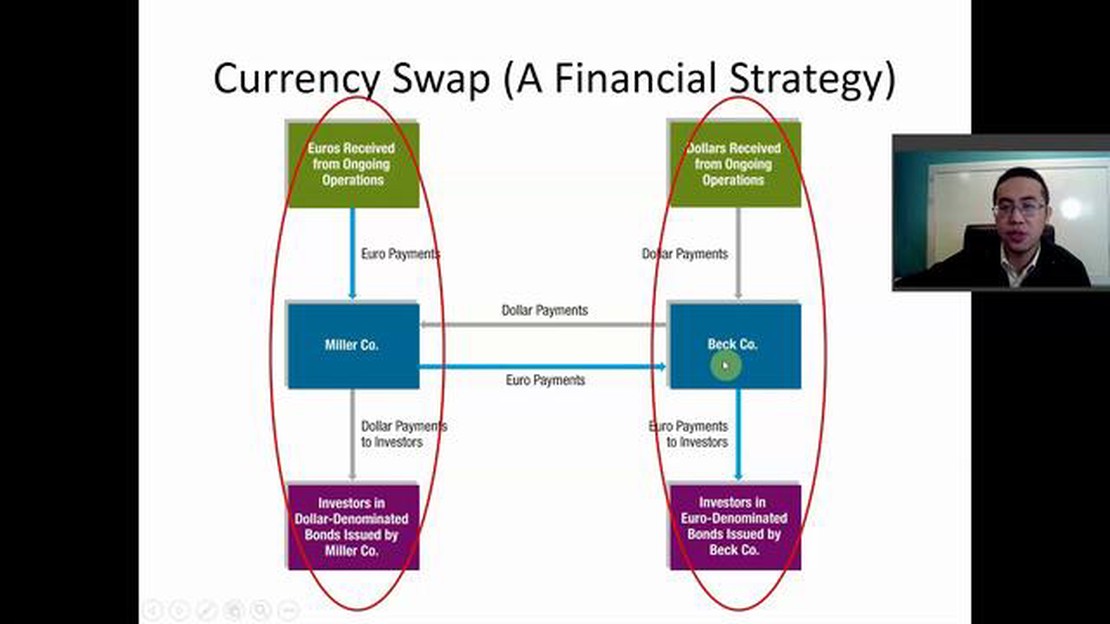
When it comes to managing financial risks, hedging strategies play a crucial role for investors and businesses alike. One popular tool in the hedging toolkit is a swap, which allows parties to exchange financial instruments or cash flows. In this article, we will dive into the details of hedging strategies using swaps, exploring how they work and the various ways they can be utilized.
A swap is essentially an agreement between two parties to exchange cash flows or other financial instruments based on a predetermined set of conditions. It can be viewed as a hedging strategy because it allows participants to protect themselves against adverse price movements, interest rate fluctuations, or other market risks.
One common type of swap is an interest rate swap, where two parties agree to exchange fixed and floating interest rate payments based on a notional principal amount. This type of swap can be used to hedge against interest rate fluctuations, protecting borrowers from rising rates and allowing savers to take advantage of potentially higher rates.
Another popular hedging strategy using swaps is currency swaps. This type of swap allows parties to exchange one currency for another at a specified exchange rate, often for a predetermined time period. Businesses that operate internationally can use currency swaps to hedge against exchange rate risks, ensuring that their profits are not eroded by currency fluctuations.
Overall, hedging strategies using swaps offer participants flexibility and protection against market risks. Whether it’s interest rate fluctuations, currency exchange rate risks, or other variables, swaps can be tailored to fit specific needs. By utilizing swaps effectively, investors and businesses can protect themselves from potential losses and position themselves for success in an ever-changing financial landscape.
Read Also: Is Forex Trading Worth It? Exploring the Pros and Cons of the Forex Market
Swaps are financial instruments that allow market participants to manage risks associated with fluctuations in interest rates, exchange rates, or other financial variables. In the context of hedging strategies, swaps can be used to offset and manage potential losses resulting from adverse price movements.
Swap contracts involve the exchange of cash flows between two parties over a specified time period. The parties involved are known as the “fixed rate receiver” and the “floating rate receiver.” The fixed rate receiver receives a fixed interest rate, while the floating rate receiver receives a rate that is linked to a reference rate, such as LIBOR.
For hedging purposes, a company may use an interest rate swap to protect itself from the risk of increased borrowing costs. For example, if a company has a variable rate loan and wants to hedge against the risk of rising interest rates, it can enter into an interest rate swap where it receives a fixed interest rate and pays a floating rate based on LIBOR.
By entering into the swap, the company effectively transforms its variable rate loan into a fixed rate loan, reducing its exposure to interest rate fluctuations. If interest rates increase, the company will receive higher payments from the swap counterparty to compensate for the increased borrowing costs on its loan. Conversely, if interest rates decrease, the company will make lower payments to the swap counterparty.
Swaps can also be used to hedge against foreign exchange risk. For example, a company that imports goods from another country and expects to pay in foreign currency can enter into a currency swap. In a currency swap, the company agrees to exchange principal amounts and periodic interest payments in different currencies with the counterparty. This allows the company to lock in a favorable exchange rate and protect itself from potential losses due to currency fluctuations.
In conclusion, swaps are powerful tools for hedging strategies as they enable market participants to manage risks associated with interest rates, exchange rates, and other financial variables. By entering into swap contracts, companies can mitigate potential losses and protect themselves from adverse price movements.
Swaps are financial agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows based on certain conditions. They are widely used in hedging strategies to manage risks and protect against adverse market movements. Here are some common hedging strategies that utilize swaps:
These are just a few examples of common hedging strategies using swaps. Swaps provide flexibility and customization, allowing market participants to design strategies tailored to their specific risk management needs. By using swaps, businesses and investors can effectively hedge against various risks and protect their portfolios from potential losses.
Read Also: Is Questrade only available in Canada?
A swap is a financial derivative contract in which two parties agree to exchange cash flows based on a specified underlying asset.
Swaps can be used for hedging by allowing one party to protect against or offset potential losses in another financial instrument or investment.
Some common hedging strategies using swaps include interest rate swaps, currency swaps, and commodity swaps.
An interest rate swap involves exchanging fixed and variable interest rate payments to protect against fluctuations in interest rates.
Understanding Genetic Algorithms in Quantitative Finance Quantitative finance is a field that combines mathematical models and statistical techniques …
Read ArticleWhat is the best way to exchange money when Travelling? When traveling abroad, it is essential to have a plan for exchanging money. Finding the best …
Read ArticleTrading Options in Pre and Post Market: Everything You Need to Know Options trading is a popular way for investors to take advantage of market …
Read ArticleCan you buy $500 worth of shares? Investing in stocks can be a great way to grow your wealth over time. However, many people are under the impression …
Read ArticleTaxation of Stocks Issued by Companies: Understanding the Process Investing in stocks can be a lucrative way to grow your wealth, but it’s essential …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the mechanics of the emission trading system The issue of climate change has become increasingly urgent in recent years. Governments, …
Read Article