Applications of ARMA Models: Understanding Their Use and Importance
Application of ARMA models ARMA models, which stands for Autoregressive Moving Average models, are widely used in various fields such as finance, …
Read Article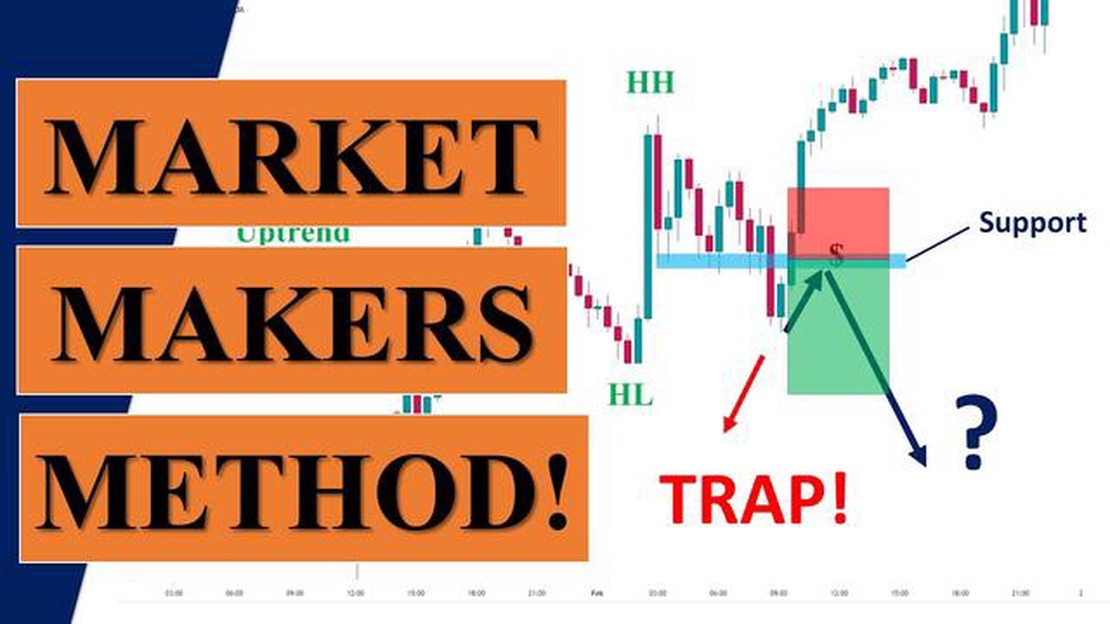
In the world of finance, the concept of the market maker strategy has gained significant attention and interest. This strategy plays a crucial role in maintaining liquidity and efficiency in financial markets, and has a profound impact on how trades are executed and prices are determined.
At its core, the market maker strategy involves a designated participant in the market who provides liquidity by quoting both buy and sell prices for a given security. These market makers essentially act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring that there is always a ready buyer or seller for a particular security.
One of the key features of the market maker strategy is the ability to create a two-sided market. This means that market makers are constantly providing both bid and ask prices, enabling market participants to trade at any given time. By doing so, they help to narrow the spread between bid and ask prices, which reduces transaction costs for investors.
The impact of the market maker strategy on the financial market cannot be overstated. By providing liquidity and maintaining a constant presence in the market, market makers help to ensure that trading can occur smoothly and without excessive price volatility. They also play a vital role in price discovery, as their quotes and trading activity help to determine the fair value of a security at any given time.
Overall, the market maker strategy is a fundamental aspect of the financial market ecosystem. It enables efficient trading, enhances liquidity, and contributes to the overall stability of financial markets. Understanding how this strategy works and its impact on the market is essential for any investor or market participant.
The market maker strategy is a trading approach used by financial institutions and brokers to provide liquidity and facilitate the smooth functioning of financial markets. Market makers play a crucial role by continuously quoting bid and ask prices for a particular financial instrument, such as stocks, bonds, or derivatives.
Market makers benefit from the difference between the buy and sell price, known as the bid-ask spread. They simultaneously buy and sell an asset, profiting from this spread. By actively participating in the market, market makers ensure that there is a continuous flow of buy and sell orders, allowing investors to trade efficiently and at a relatively low cost.
One of the primary goals of market makers is to minimize the spread between the bid and ask price, as a tighter spread attracts more trading volume. This is achieved through the use of algorithms and sophisticated trading systems, enabling market makers to quickly and accurately adjust their prices based on market conditions and order flow.
Market makers also take on the role of risk management. They provide liquidity even when the market is volatile or when there is a lack of trading interest. This means that they are willing to buy or sell an asset at any given time, ensuring that there is always someone available to facilitate trading.
Read Also: ASC 718 10 25 15: Everything You Need to Know
Furthermore, market makers often maintain an inventory of the assets they trade. This inventory allows them to meet the demand of buyers and sellers when there are imbalances in the market. By adjusting their own positions, market makers can stabilize the market and maintain liquidity.
The market maker strategy can have a significant impact on the financial market. It promotes price stability, reduces bid-ask spreads, and prevents abrupt price swings. Market makers also enhance market efficiency by providing liquidity and enabling faster execution of trades.
However, it is important to note that market makers are profit-driven entities, and their actions may not always align with the best interests of individual investors. They may prioritize their bottom line and utilize various strategies to maximize their profits.
Overall, understanding the market maker strategy is essential for investors to navigate the financial markets effectively. By being aware of the role and impact of market makers, investors can make more informed trading decisions and take advantage of the liquidity and stability provided by these market participants.
Read Also: Learn how to trade news stocks and make profitable investments
The market maker strategy is a trading approach used by financial institutions to provide liquidity to the market and facilitate the smooth functioning of the financial markets. Market makers play a crucial role in ensuring that there is a constant supply and demand for securities, which helps to establish a fair and efficient marketplace.
Here are the key elements of how the market maker strategy works:
The market maker strategy is essential for maintaining liquidity in the financial markets and ensuring a fair and efficient trading environment. By providing continuous quotes, managing inventory, and mitigating risks, market makers contribute to the stability and functioning of the financial ecosystem.
The market maker strategy is a trading technique used by financial institutions to provide liquidity to the markets. Market makers play the role of intermediaries, buying and selling securities to ensure that there is always a buyer or seller available.
The market maker strategy works by constantly adjusting bid and ask prices to buy and sell securities. When there is a difference between the bid and ask price, market makers profit from the spread. This helps to keep the market liquid and ensures that there is always a supply of securities available.
The market maker strategy has a significant impact on the financial market. Market makers provide liquidity to the markets, ensuring that there is always a buyer or seller available. This helps to reduce volatility and allows for efficient price discovery. Without market makers, the financial market would be much less liquid and more prone to large price swings.
The market maker strategy offers several benefits. It helps to increase market liquidity, which makes it easier for investors to buy and sell securities. Market makers also help to reduce bid-ask spreads, which lowers transaction costs for investors. Additionally, the presence of market makers can help to stabilize prices and reduce market volatility.
Application of ARMA models ARMA models, which stands for Autoregressive Moving Average models, are widely used in various fields such as finance, …
Read ArticleUnderstanding Forex Position Size Calculator As a forex trader, one of your top priorities should be managing your risk effectively. One tool that can …
Read ArticleConnecting to an IRC Channel: Step-by-Step Guide Internet Relay Chat (IRC) is a popular form of real-time communication that has been around since the …
Read ArticleUrban forex ownership: Find out who owns Urban forex Urban forex, a leading provider of forex education and trading services, is owned by a team of …
Read ArticleHow much is 1 VGX worth in dollars? Are you interested in knowing the current value of 1 VGX in dollars? Look no further! In this article, we will …
Read ArticleUnderstanding the Strength of the Dollar in Sweden In recent years, the strength of the dollar in Sweden has become a topic of great interest and …
Read Article